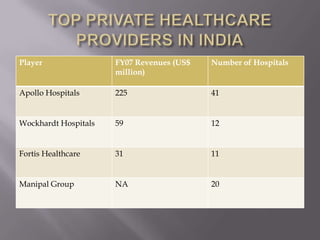
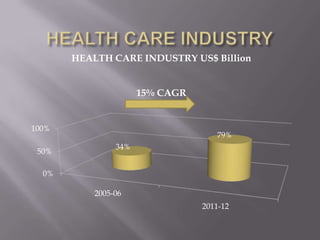
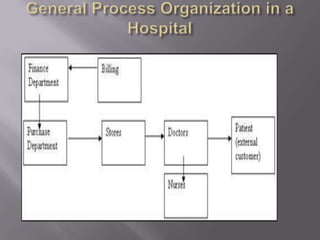
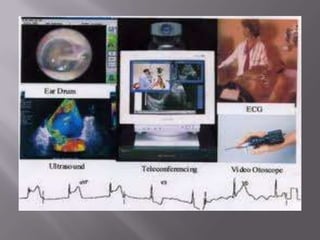
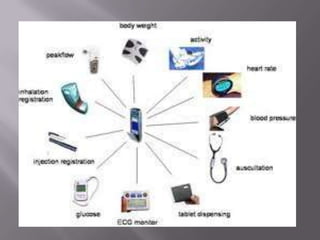
The document discusses healthcare in India and the use of telemedicine. It provides an overview of the size and structure of the healthcare industry in India. It then discusses hospital service marketing and the key elements of the marketing mix for hospitals. The document introduces Apollo Hospitals and its telemedicine network, which uses technologies like video conferencing to provide remote access to medical experts and services.