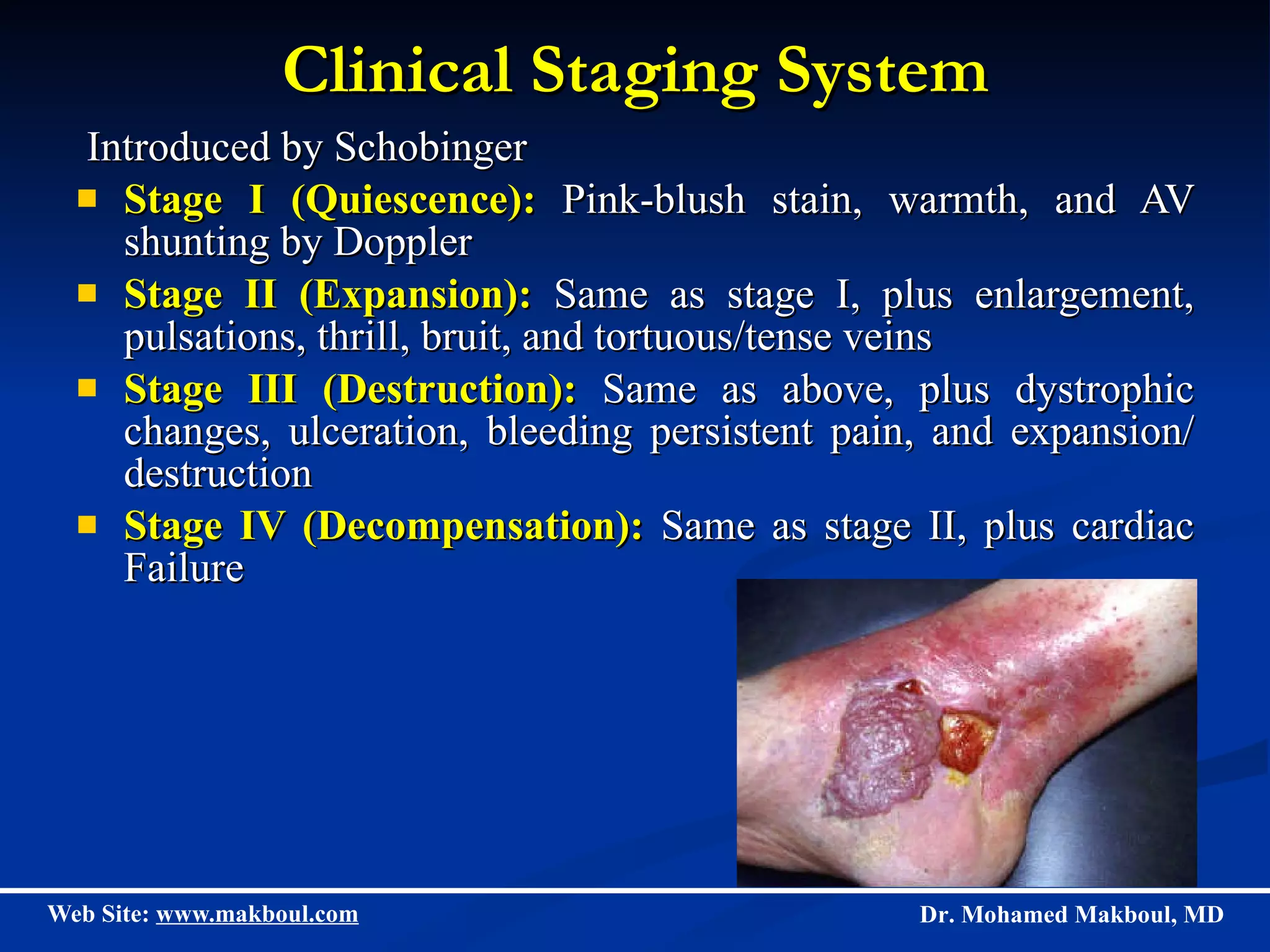
Vascular anomalies can be classified as hemangiomas or vascular malformations, with hemangiomas exhibiting rapid growth and slow regression in infants while malformations are present at birth and do not regress. Hemangiomas are the most common tumor in infants and progress through proliferating, involuting, and involuted phases, while various types of vascular malformations including venous, lymphatic, and arteriovenous anomalies can cause complications and are typically treated with sclerotherapy, laser therapy, or surgery. Accurate diagnosis and differentiation of these conditions is important to guide appropriate clinical management and treatment.