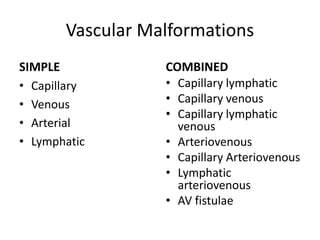
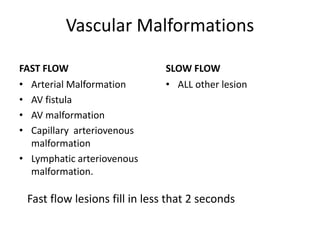
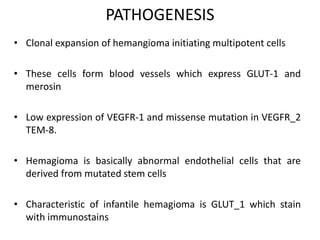
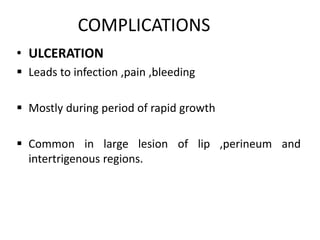
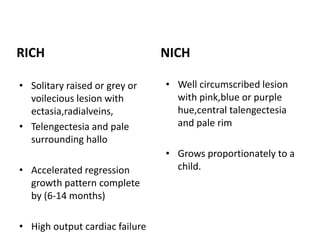
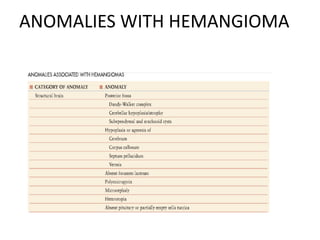
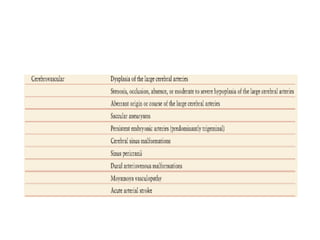
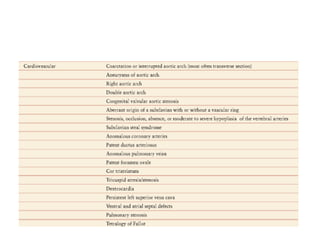
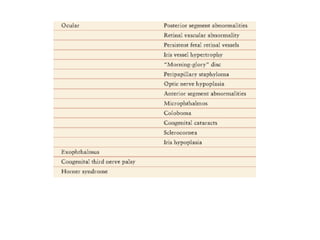
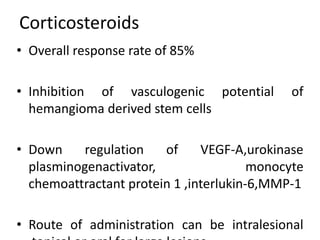
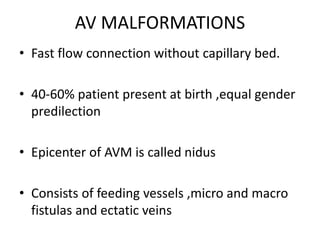
Vascular anomalies are classified as hemangiomas or vascular malformations based on their clinical course, biological behavior, and histological features. Hemangiomas are vascular tumors that grow rapidly during infancy through endothelial proliferation and then slowly regress. Vascular malformations are present at birth and grow proportionately with the patient. They never regress and consist of abnormal vascular channels. Diagnosis involves clinical history, examination, imaging like ultrasound or MRI, and biopsy if needed. Management depends on type, location, growth phase and involves observation, medical therapies like corticosteroids or propranolol, procedures like sclerotherapy or laser, or surgery.