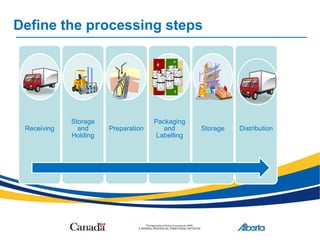
This document provides an introduction to Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Points (HACCP), a systematic preventative approach to food safety. It discusses that HACCP identifies potential food safety hazards, establishes control measures for those hazards, and monitors the controls to help ensure food safety. The document outlines the key components of HACCP including conducting a hazard analysis to identify potential hazards at different process steps, establishing critical control points to monitor for and control hazards, and implementing prerequisite programs to establish good practices. Finally, it discusses how to develop and implement a HACCP plan to control hazards for a specific food process or product.