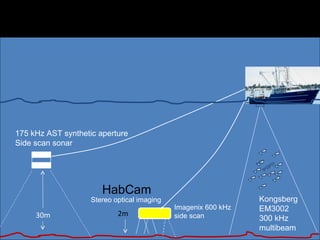
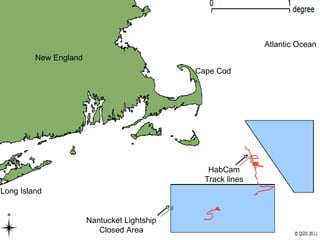
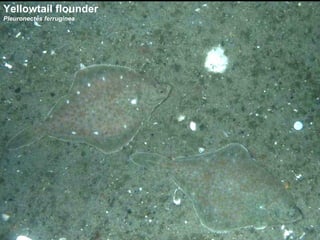
The document describes a habitat mapping camera system called HabCam that is used to study sea scallops and other organisms on the seafloor. HabCam is towed above the seafloor and takes high resolution images to identify species and behaviors. Scientists and fishermen work together on the project. HabCam images are analyzed to estimate biomass of species like sea scallops and identify different seafloor substrates like sand and gravel.