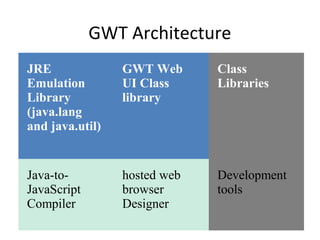
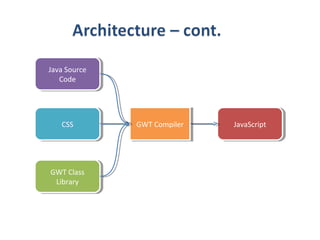
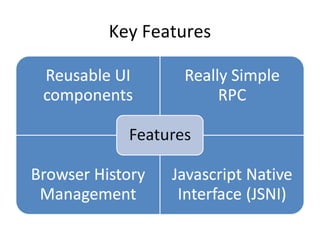
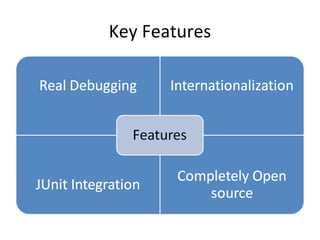
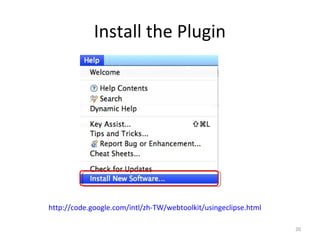
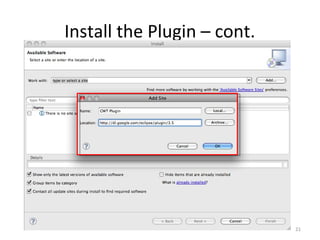
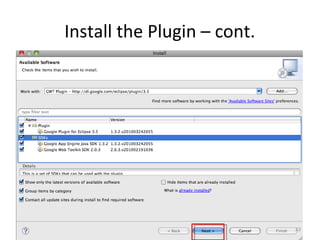
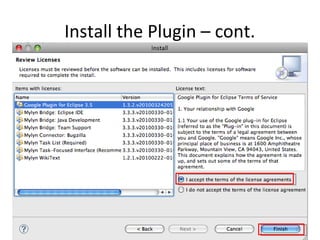
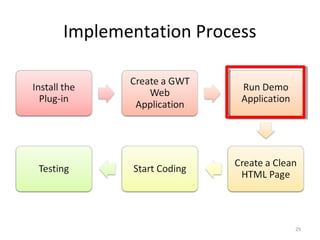
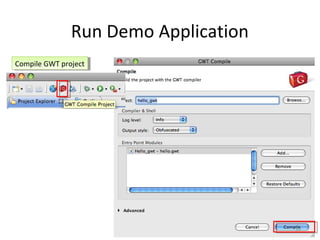
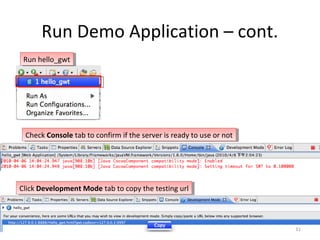
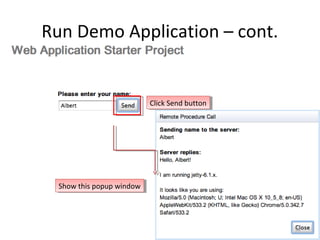
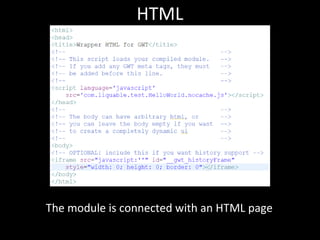
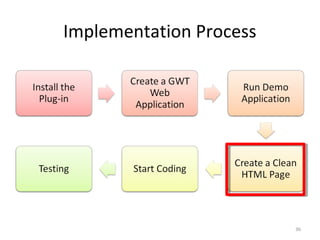
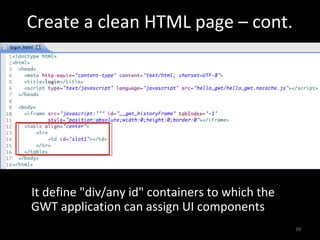
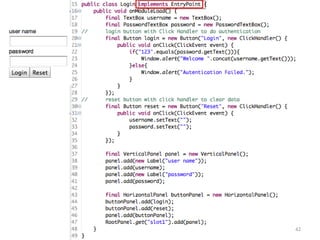
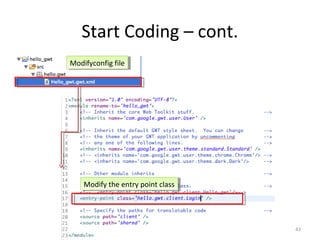
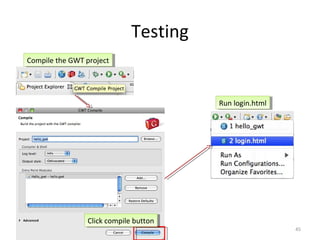
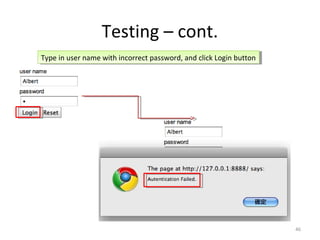
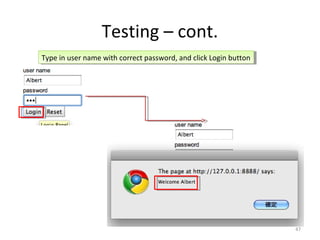
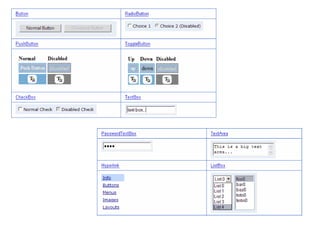
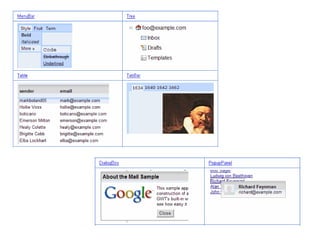
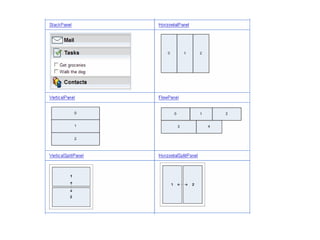
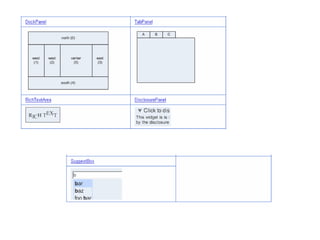
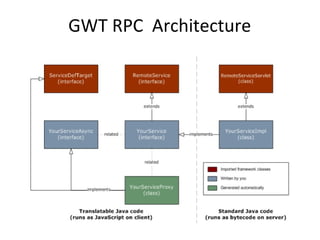
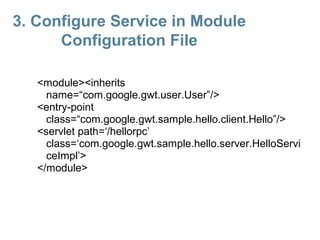
This document provides an overview of the Google Web Toolkit (GWT). It begins with a short introduction and history of GWT, including that it was announced in 2006 and is an open-source Java framework for building complex JavaScript front-end applications. It then covers GWT's architectural overview, key features, when and why it would be used, and includes a simple code example. The document also discusses GWT's components, the development process, and introduces various web frameworks.