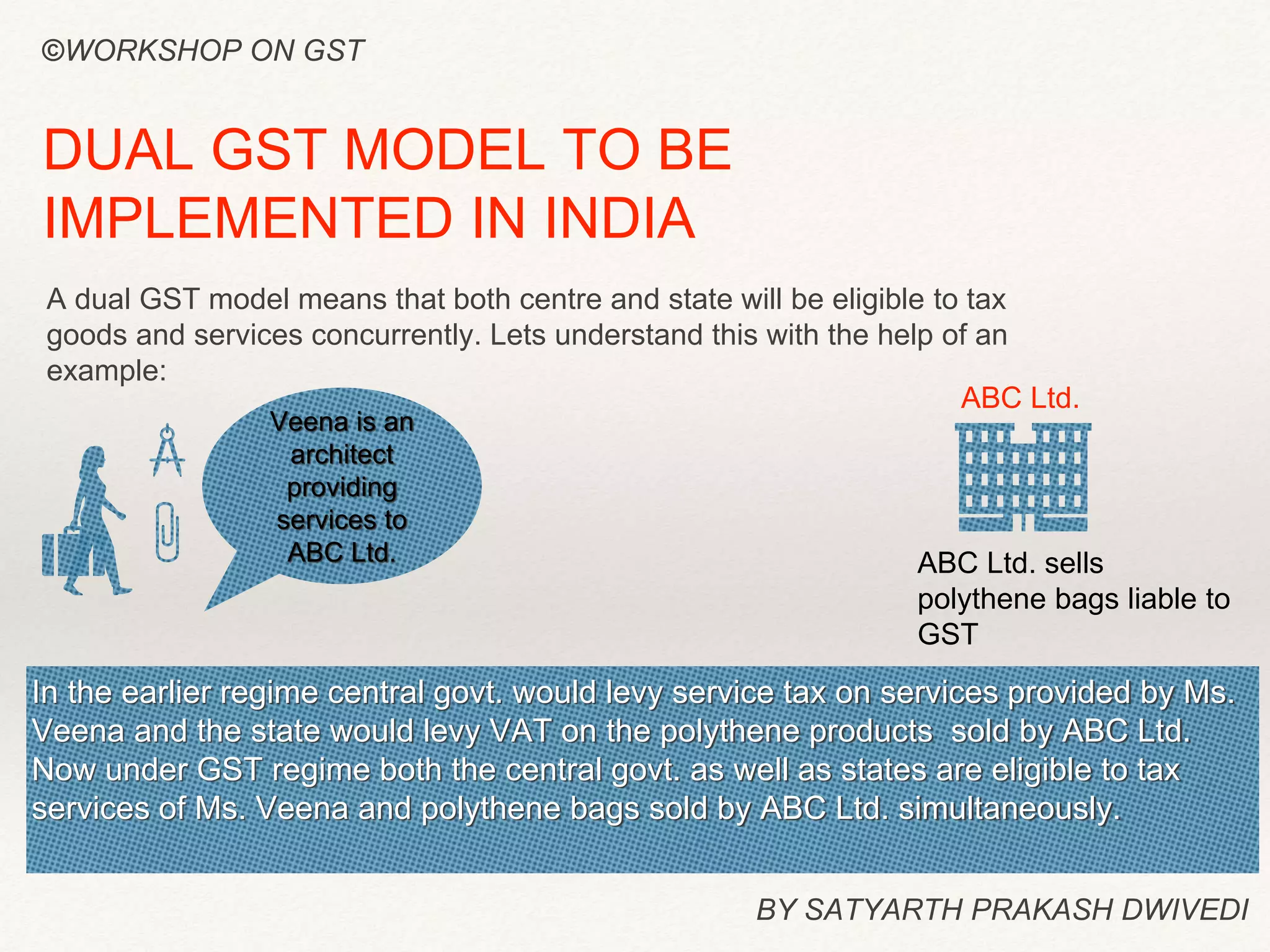
Goods and Services Tax (GST) is a value-added tax levied on the manufacture, sale, and consumption of goods and services. It provides continuous tax credits at each stage of production and distribution, ensuring that the entire supply chain is taxed only on the value added at each stage. The document discusses key aspects of GST including what it replaces, how input tax credits work, rates to be charged by central and state governments, and returns to be filed. It also provides an example to illustrate intra-state and inter-state transactions under GST.