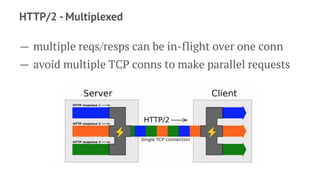
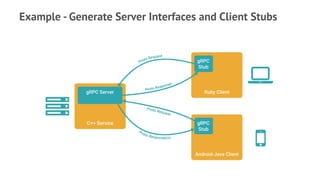
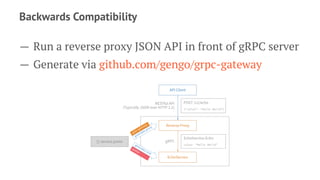
gRPC is an open source framework that allows for communication between services using HTTP/2 and Protocol Buffers. It provides features like low latency and high scalability. Key benefits include focusing on service design, language interoperability, and growing community support. gRPC uses Protocol Buffers for serialization, HTTP/2 for transport, and an IDL for service definitions. It supports various request-response and streaming call types and provides libraries in many languages.