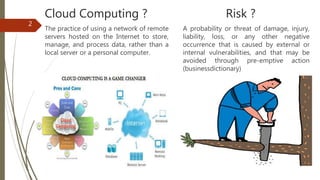
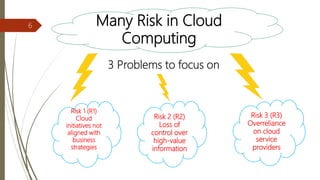
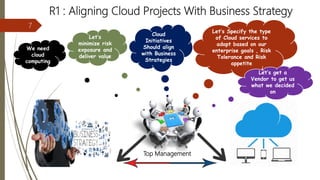
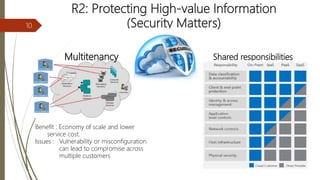
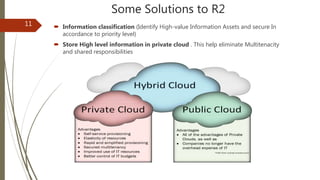
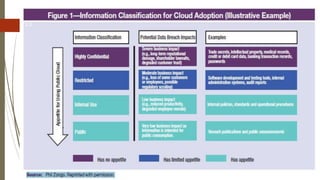
The document discusses key considerations for business leaders regarding cloud computing and associated risks. It emphasizes the importance of aligning cloud initiatives with business strategies, managing high-value information security, and minimizing overreliance on cloud service providers. Additionally, it outlines solutions for risk management, ensuring maximum value from cloud computing while also implementing necessary security measures.