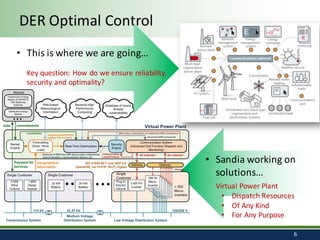
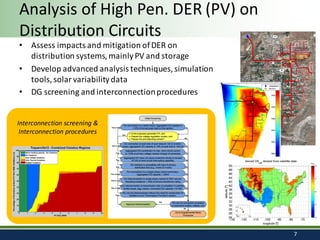
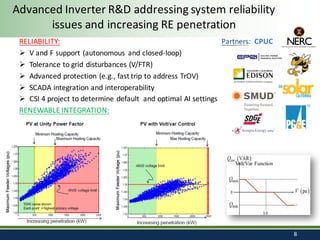
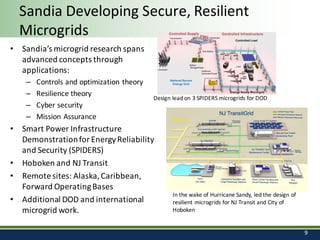
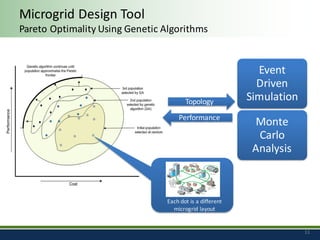
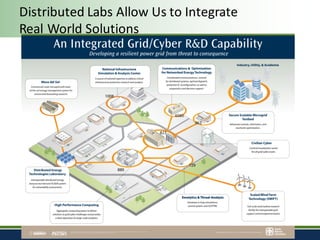
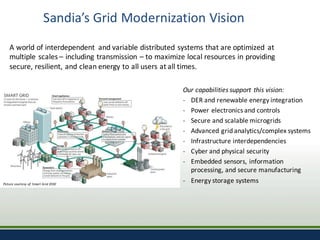
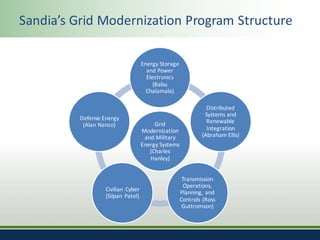
Sandia National Laboratories, operated by Sandia Corporation for the U.S. Department of Energy, focuses on a vision of grid modernization that optimizes distributed energy resources for secure, resilient, and clean energy. The document outlines various research and development areas, including energy storage, microgrids, cybersecurity, and renewable integration. It highlights Sandia's efforts to enhance grid resilience and operational optimization through innovative technologies and partnerships.


![Improving Grid Resilience
in Planning and Operations
• Sandia developed a framework for
rigorous quantification of energy
system resilience
• This framework enables decision
making to obtain demonstrable
resilience improvements
• PJM Partnership: Applied to
GMD as a threat we consider
– Multiple scenarios for worst case
GMD intensity and uncertainty in
the orientation of the GMD
– Formulate an optimization
problem where minimizing
consequences of one or multiple
types is the objective
– This results in a non-linear
program (operations) or a mixed-
integer non-linear program
(planning)
5
ProbabilityofConsequences
[$]GivenThreatX
Consequences [$]
Reduced Expected Financial
Consequence
Reduced Risk
Baseline System
Resilience
Resilience of System
after Improvements
Improvements
must cost
significantly less
than E-E’
E’(C) E(C)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/hanleysandiagridmodforciesesepuertorico-161222211657/85/Grid-Modernization-Program-Area-5-320.jpg)