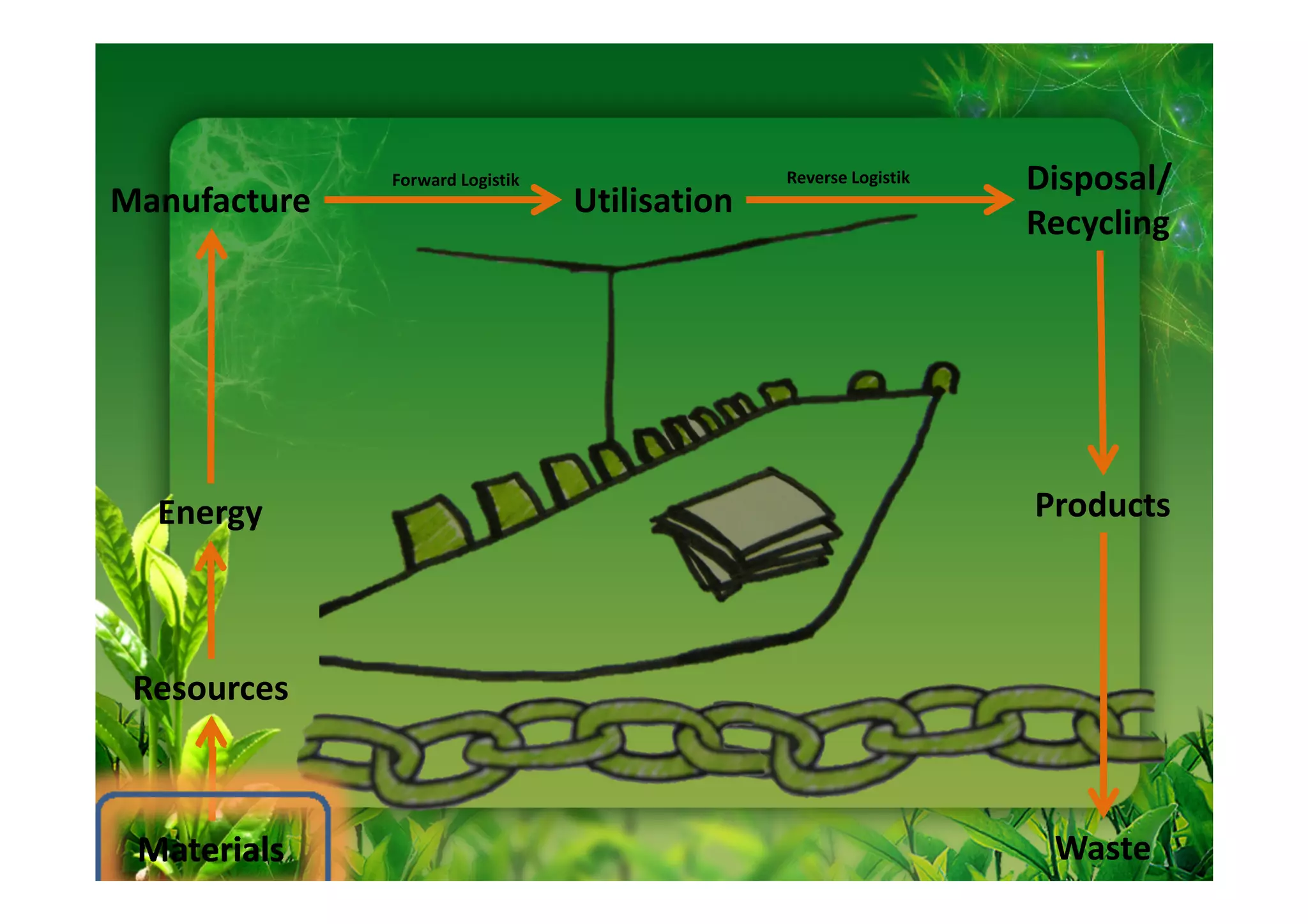
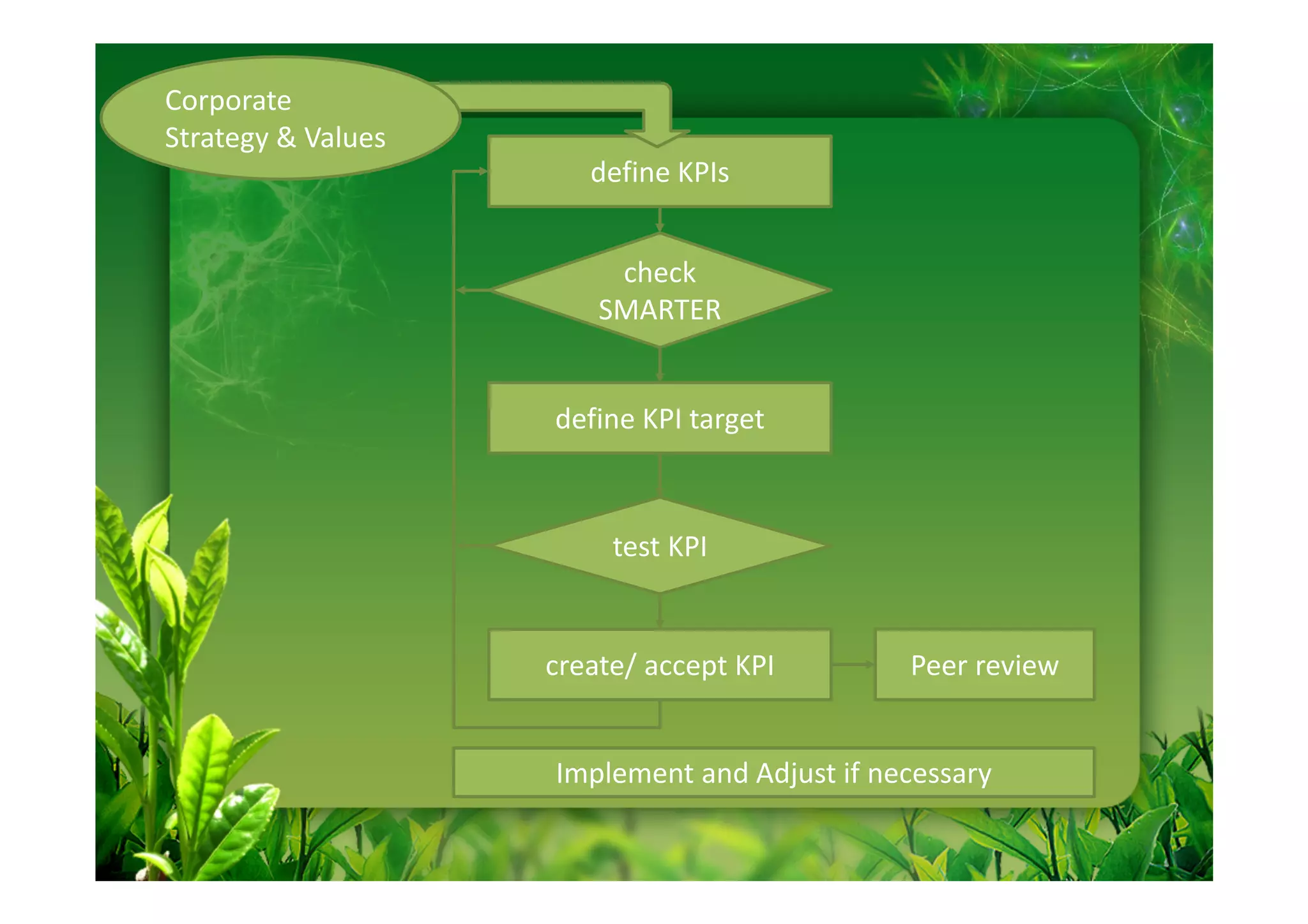
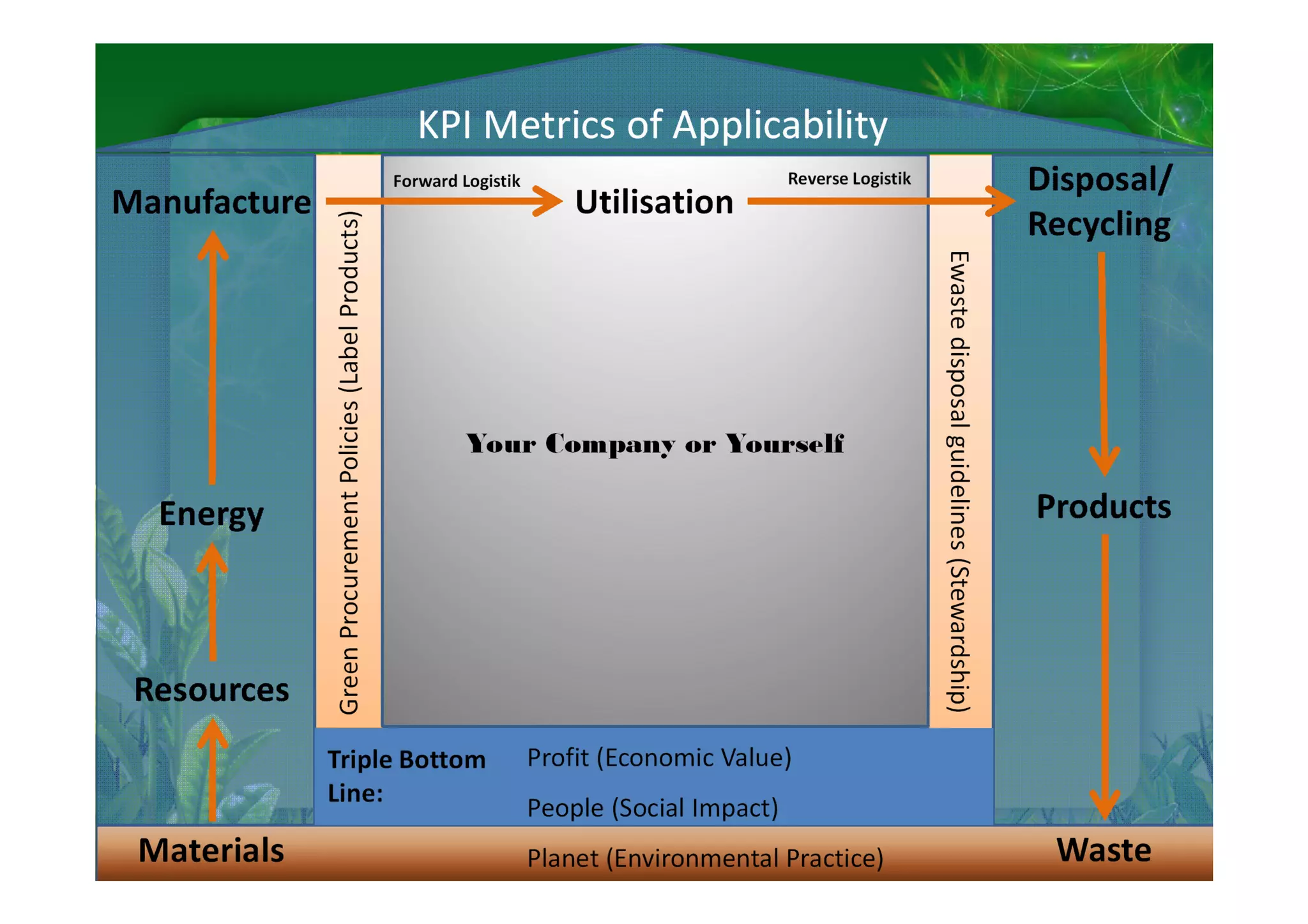
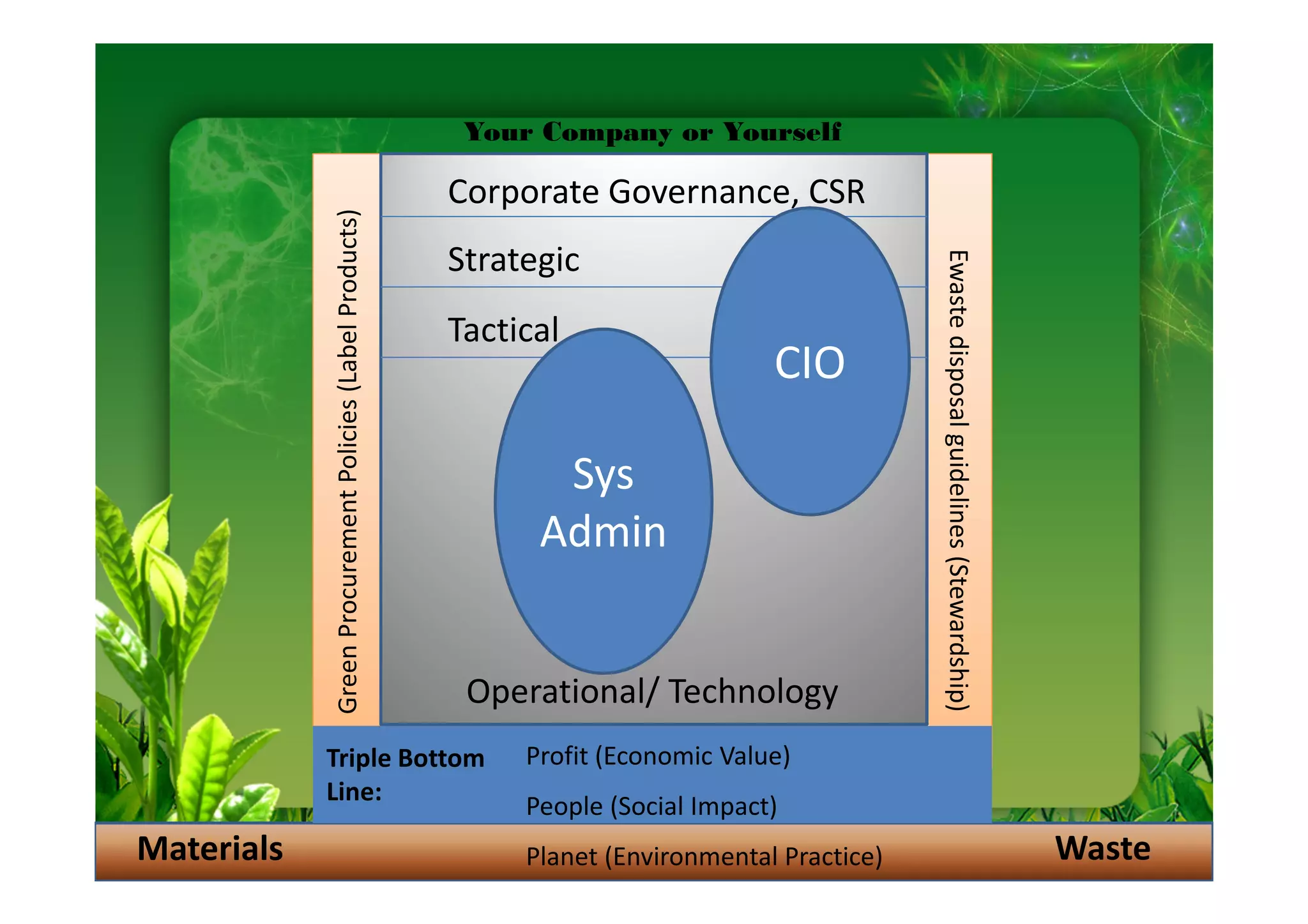
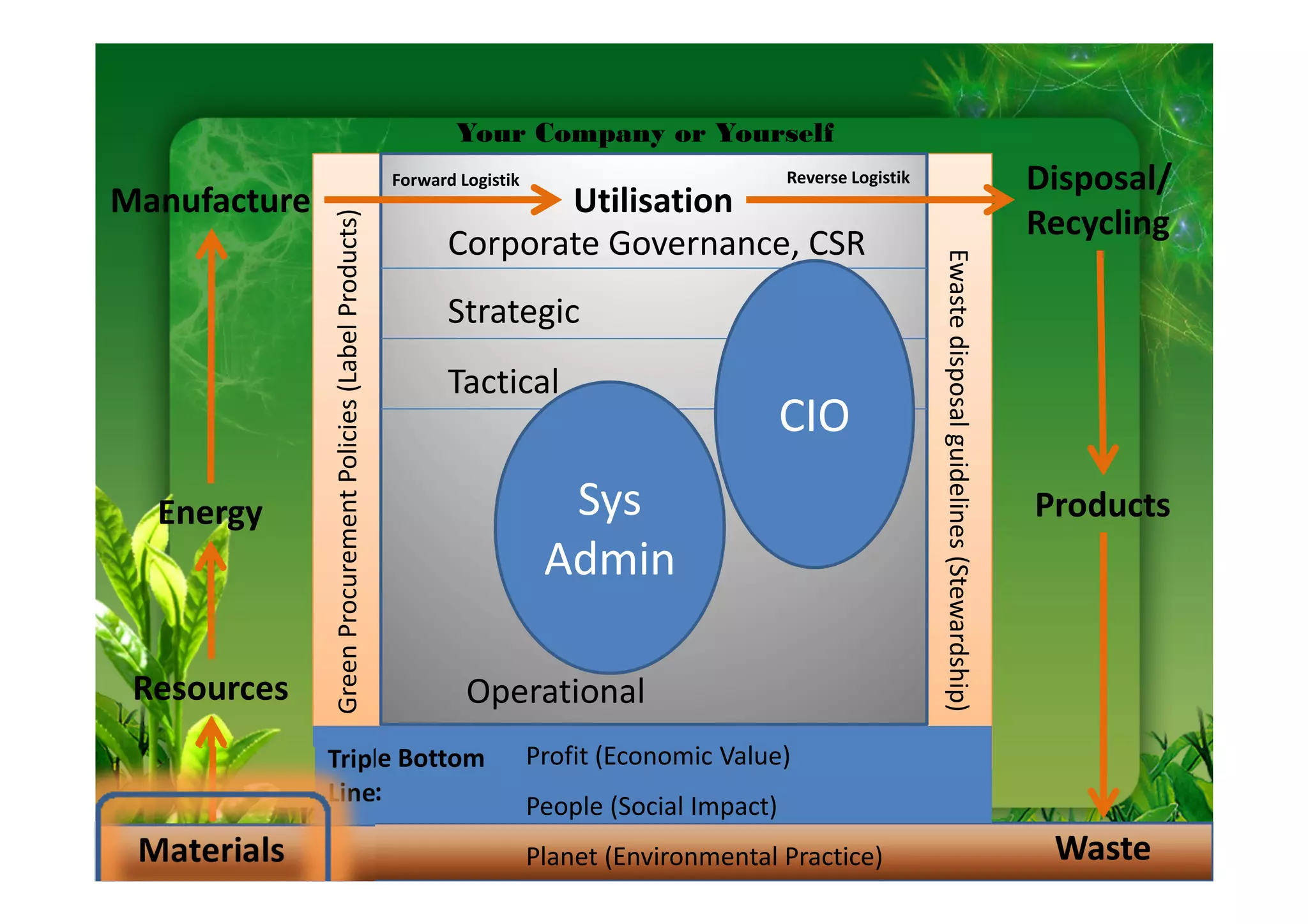
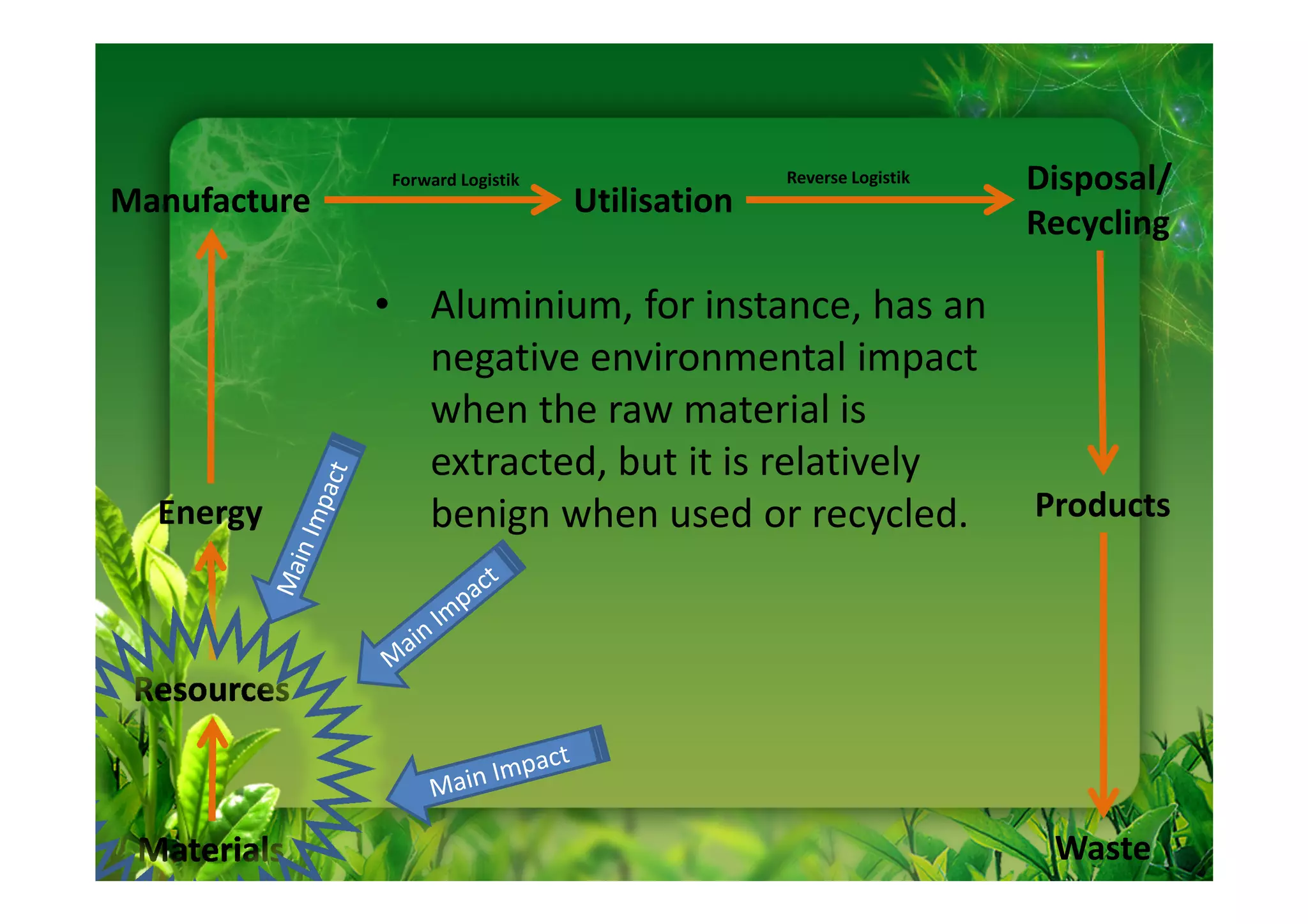
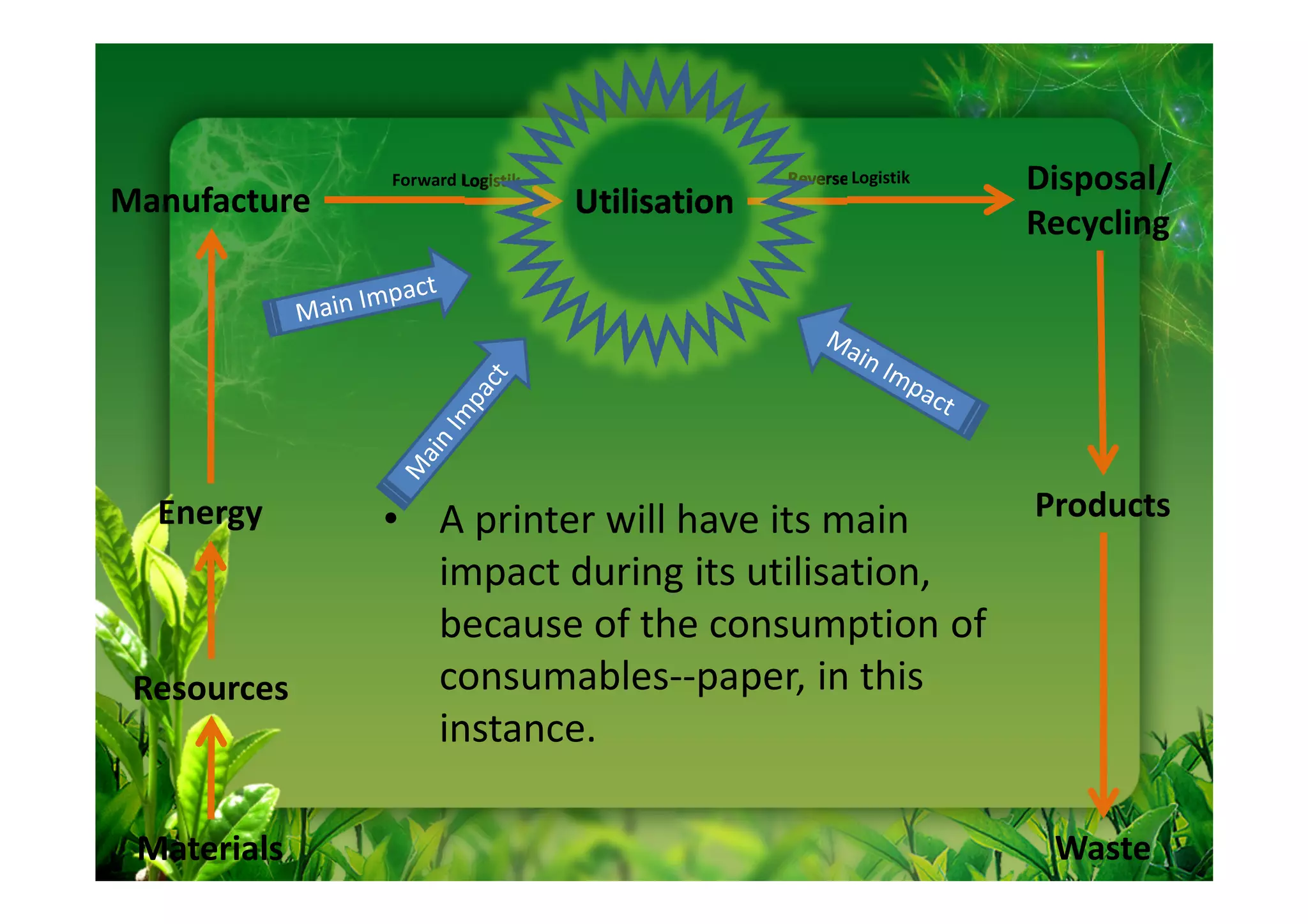
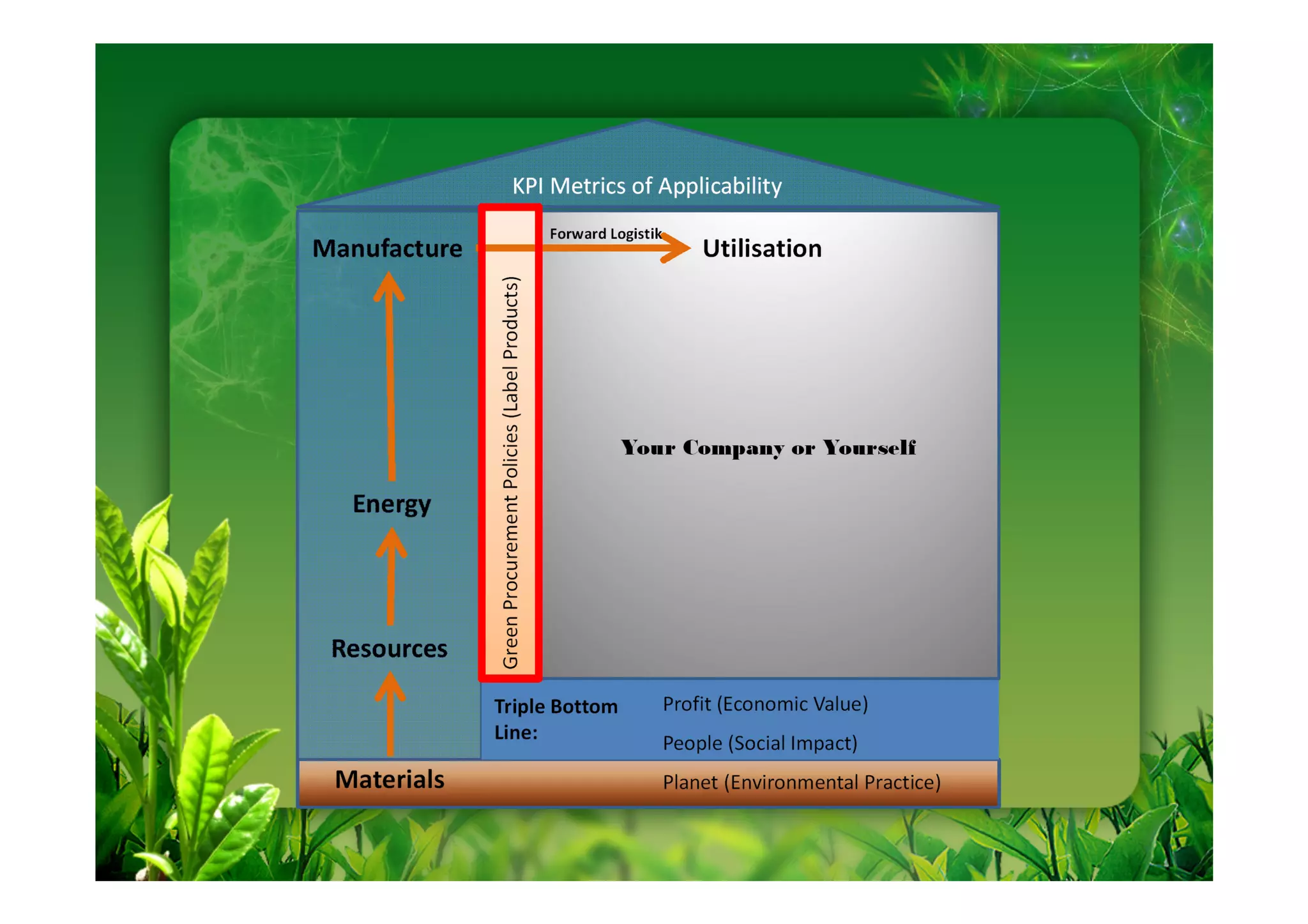
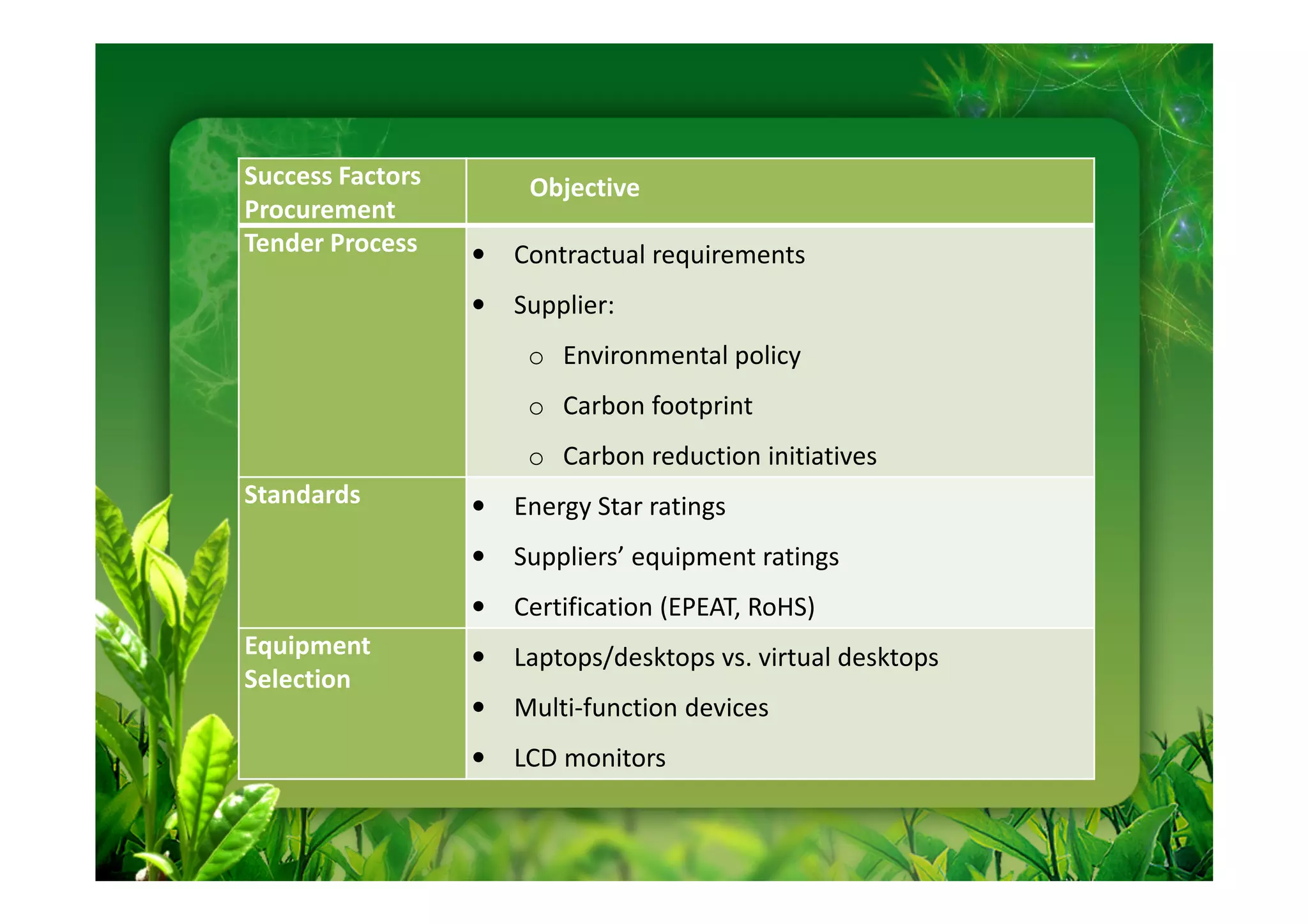
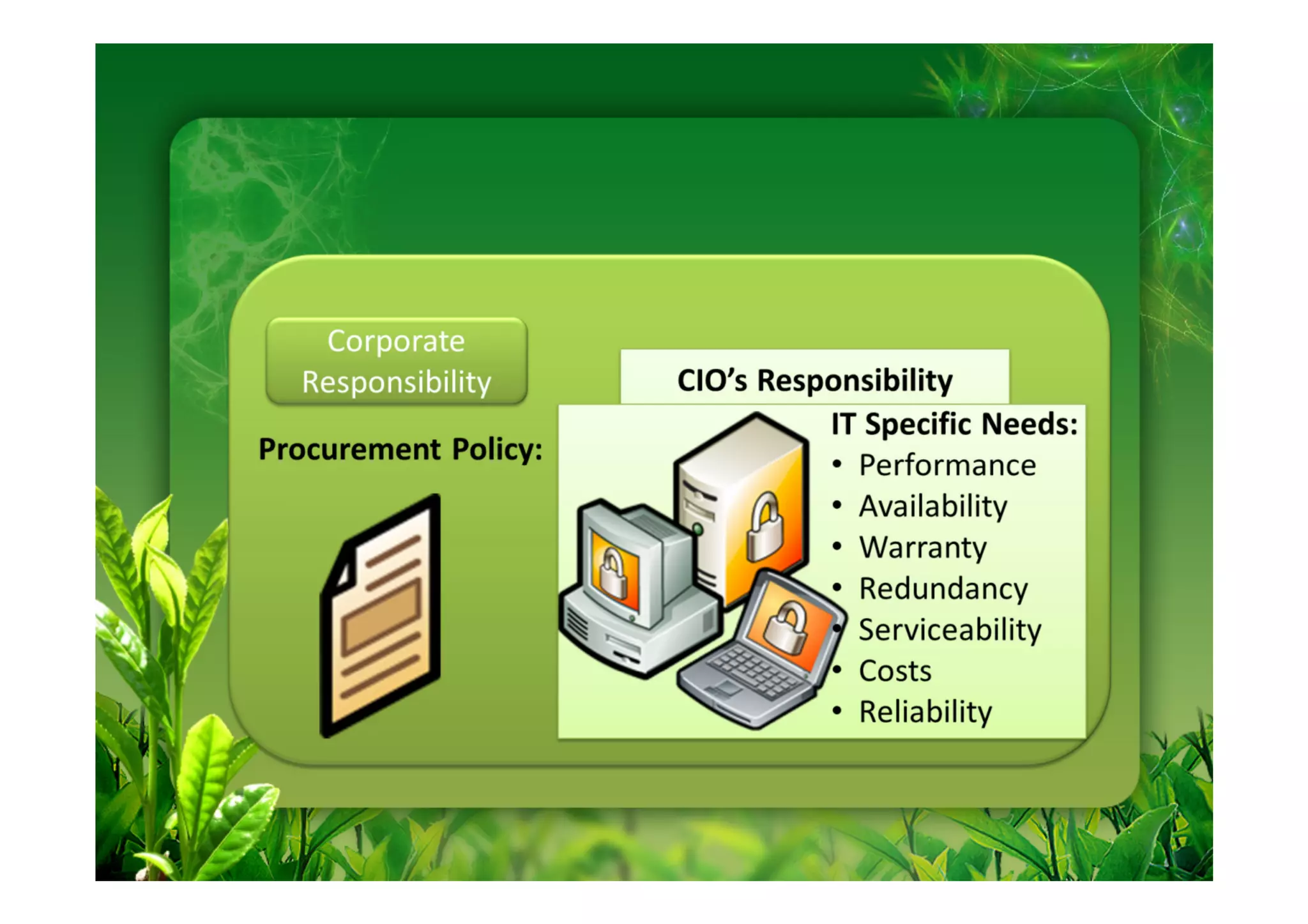
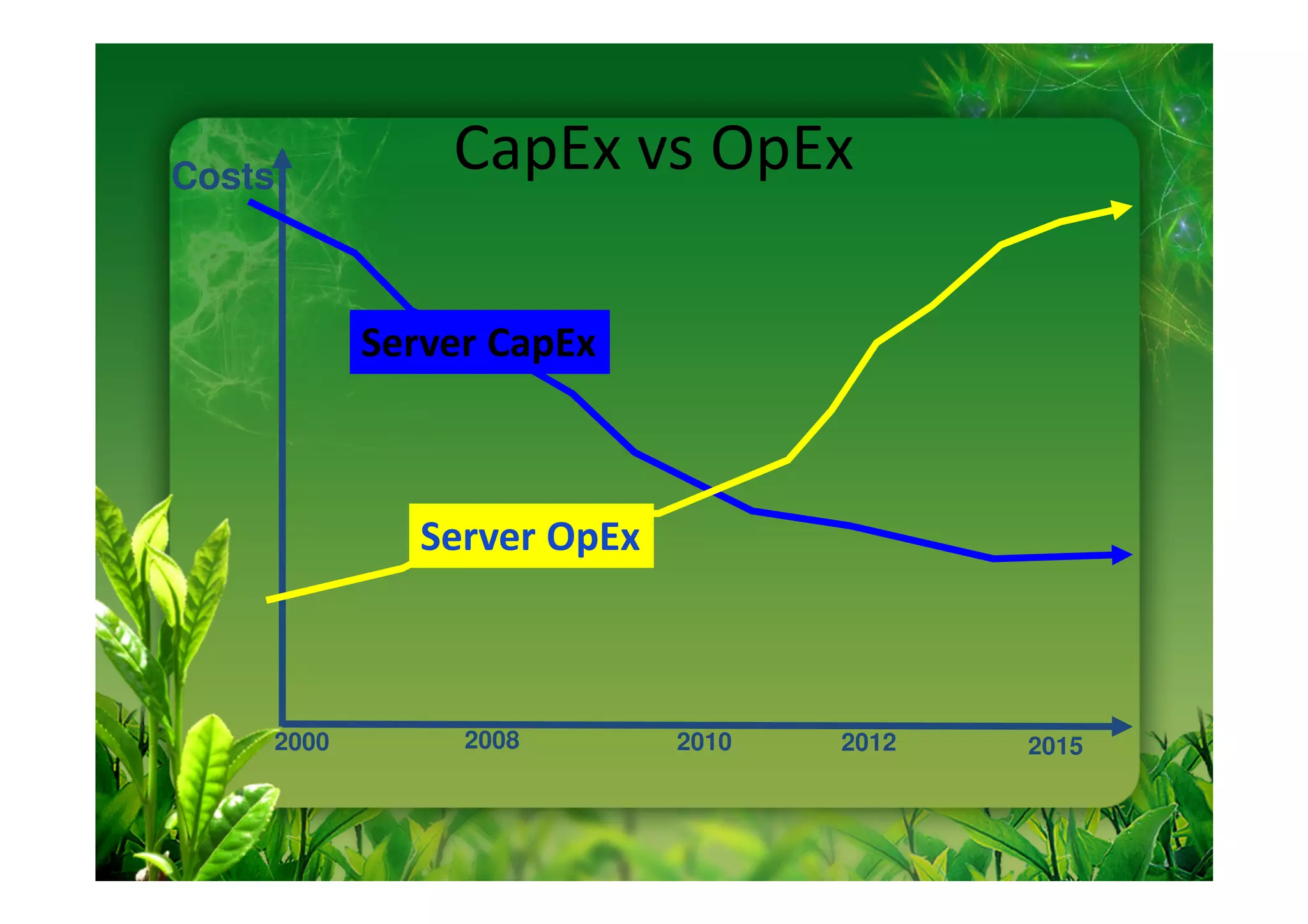
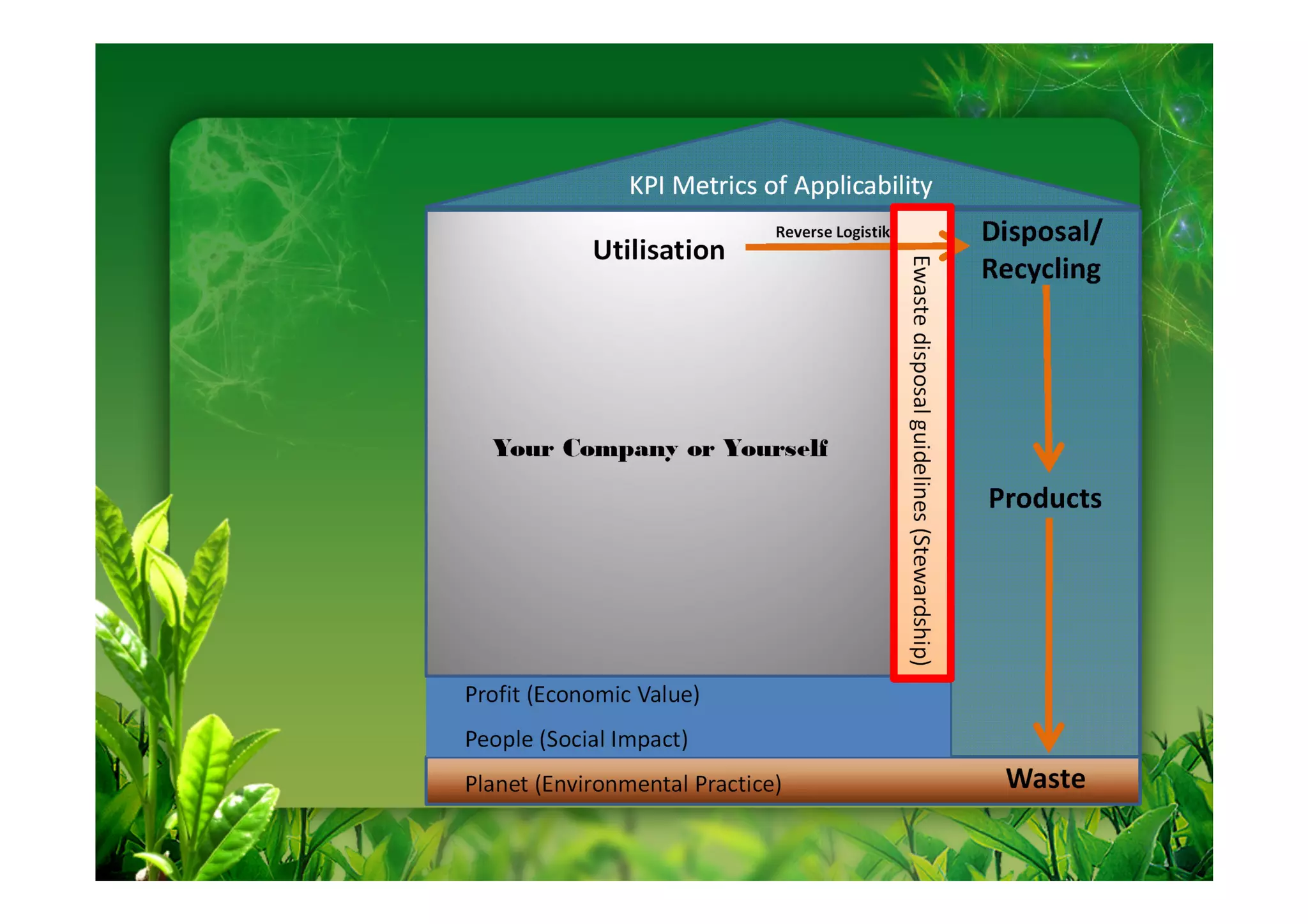
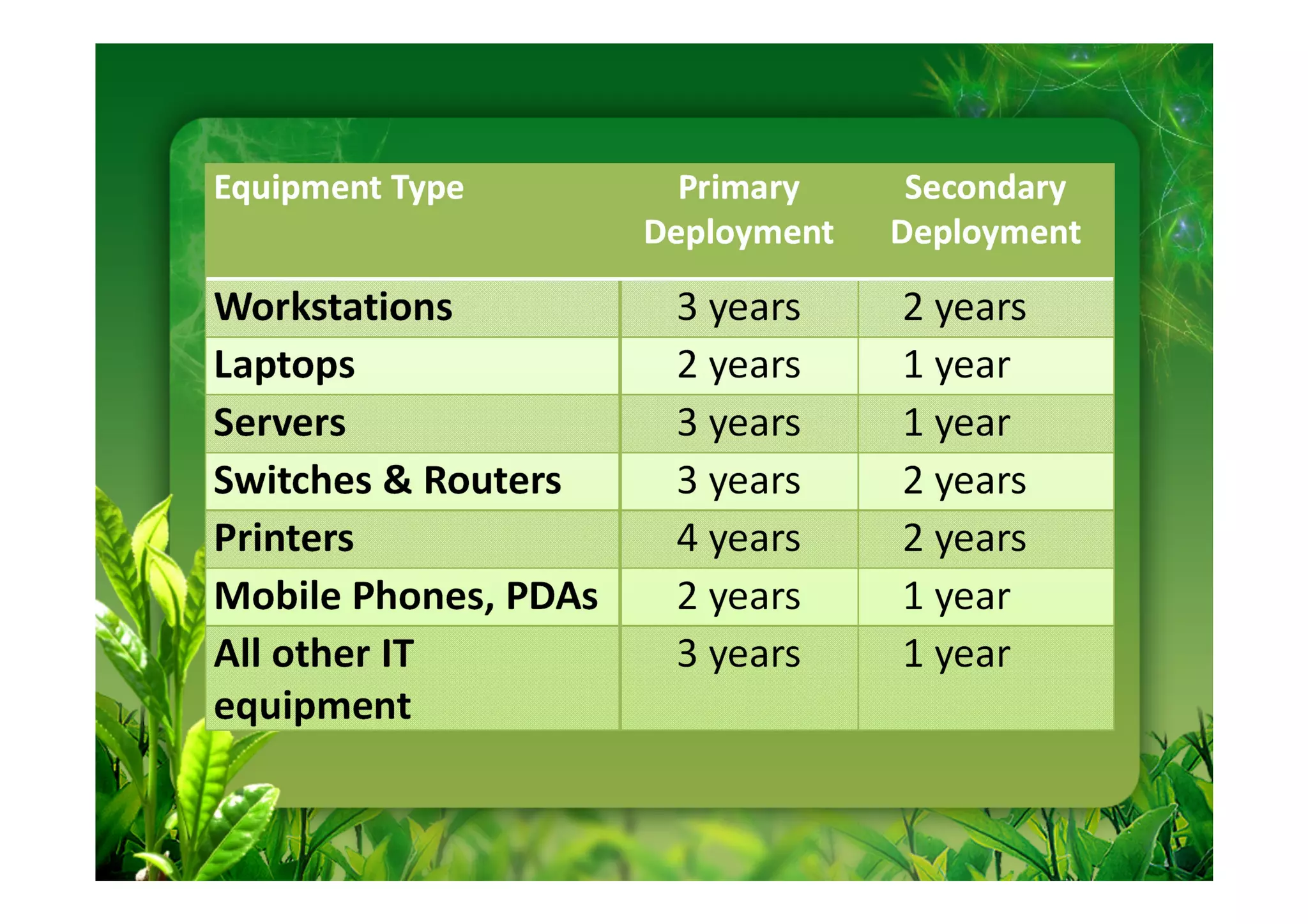
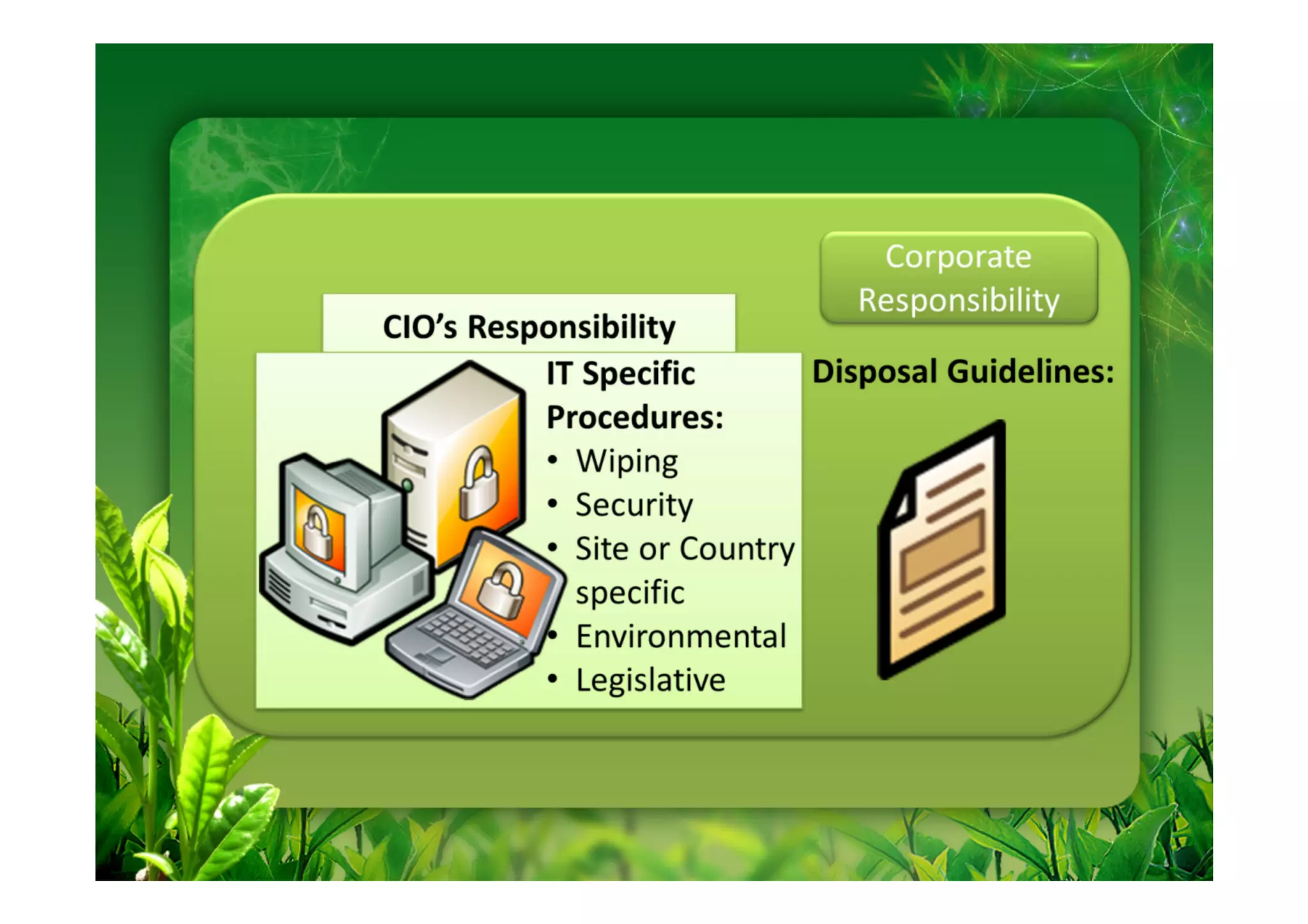
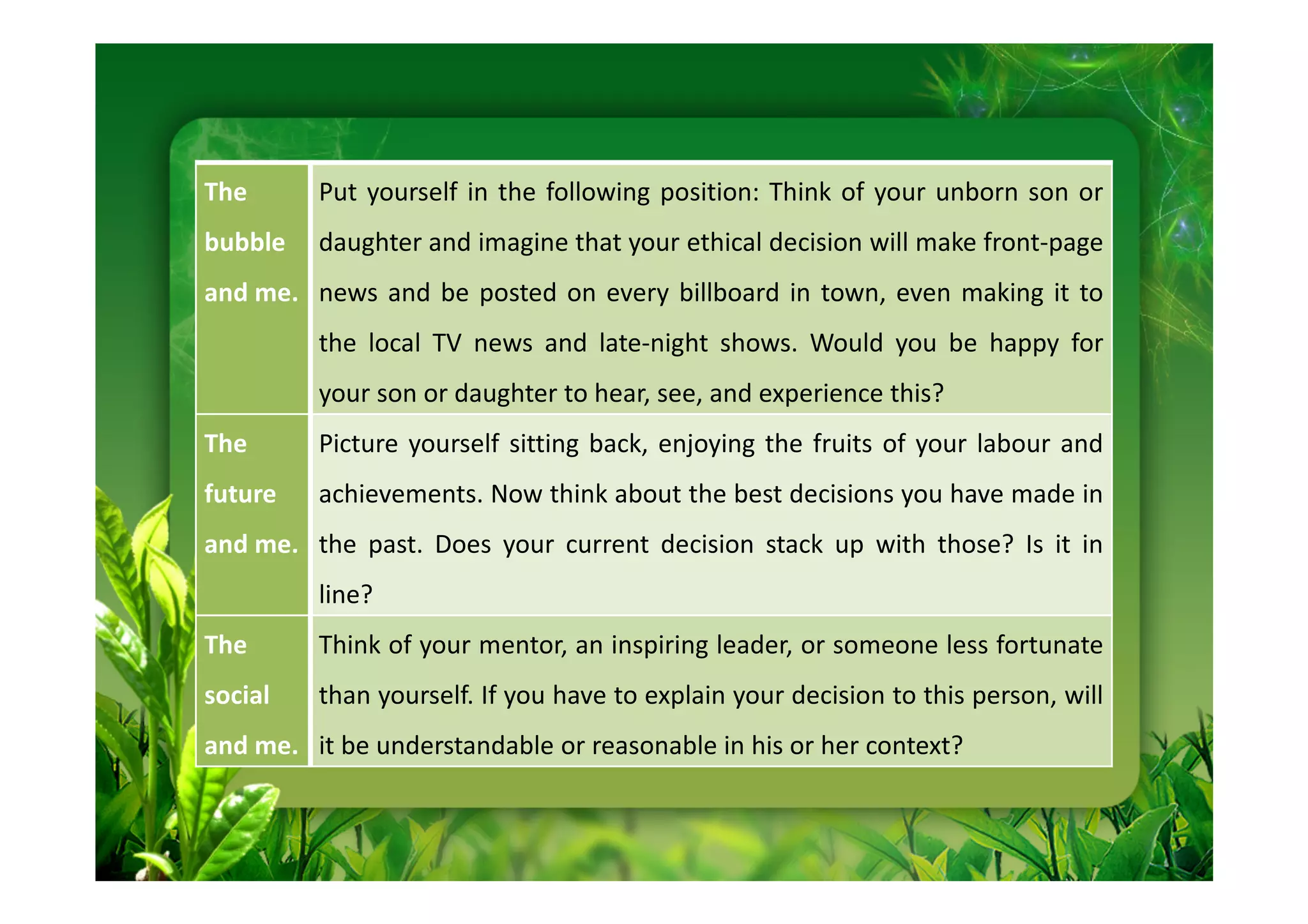
This document discusses key performance indicators (KPIs) for measuring the environmental impact and return on investment of green IT initiatives. It provides examples of good and bad KPIs, emphasizing metrics that are specific, measurable, aligned with organizational goals, realistic, timely, ethical, and recorded. The document outlines how to develop KPIs that apply to different levels of an organization, from corporate governance to operations. It also discusses developing a business case for green procurement policies and guidelines for end-of-life disposal of electronics waste.