This document discusses GraphQL and DGraph with GO. It begins by introducing GraphQL and some popular GraphQL implementations in GO like graphql-go. It then discusses DGraph, describing it as a distributed, high performance graph database written in GO. It provides examples of using the DGraph GO client to perform CRUD operations, querying for single and multiple objects, committing transactions, and more.



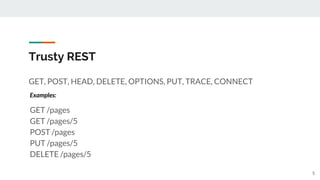



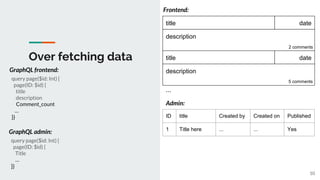
![Over fetching data
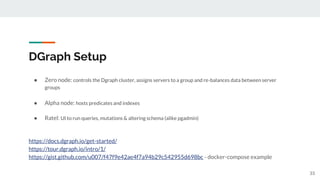
9
● Frontend: fetch /pages
● Admin: fetch /pages
Frontend:
Admin:
title date
description
title date
description
...
ID title Created by Created on Published
1 Title here ... ... Yes
2 comments
5 comments
[
{ id: 1, title: “title”,
description: “...”,
created_at: “...”,
created_by: { name: “...” },
Comments_count: 2
}, …
]
REST Frontend & admin:](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/discussiongraphqldgraphwithgo-181127152425/85/GraphQL-DGraph-with-Go-9-320.jpg)








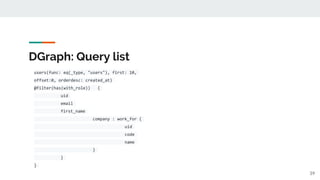
![DGraph: Query Single object
q := `query all($a: string) {
all(func: eq(name, $a)) {
name
}
}`
resp, err := txn.QueryWithVars(ctx, q,
map[string]string{"$a": "Alice"})
fmt.Println(string(resp.Json))
{
user(func: uid(0xc351)) {
First_name
Last_name
Email
roles: with_role {
Uid
Name
}
}
}
38](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/discussiongraphqldgraphwithgo-181127152425/85/GraphQL-DGraph-with-Go-38-320.jpg)