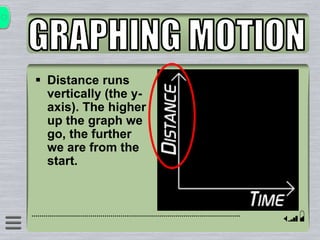
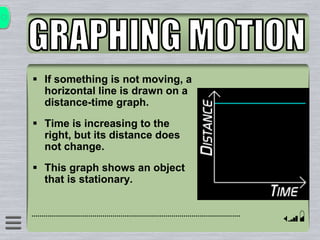
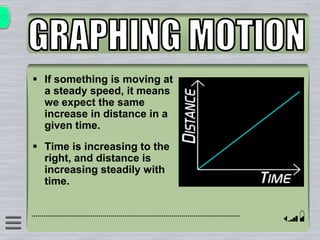
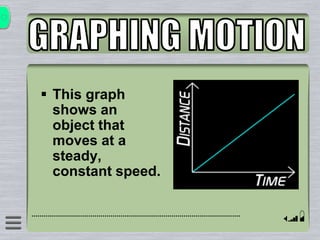
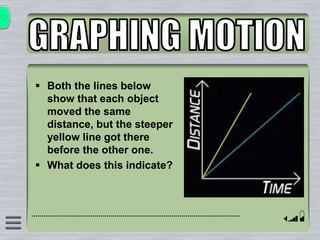
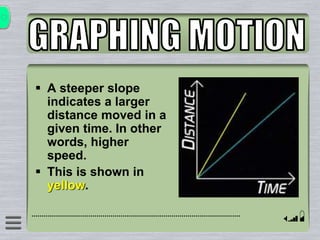
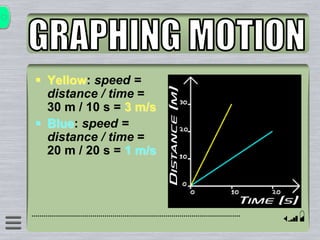
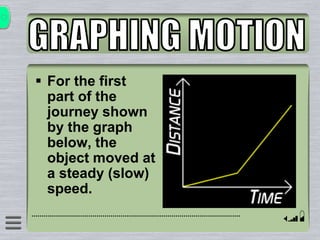
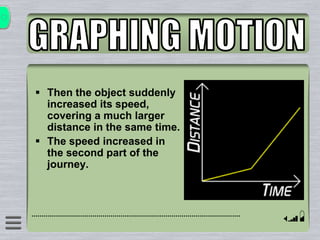
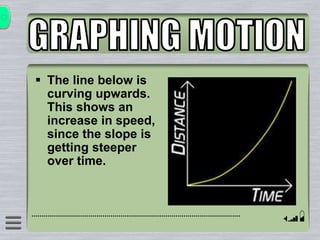
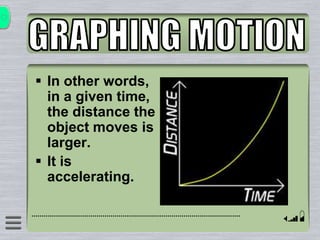
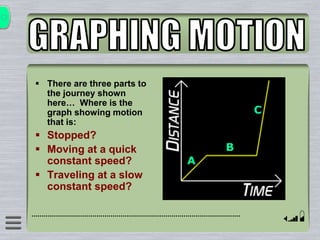
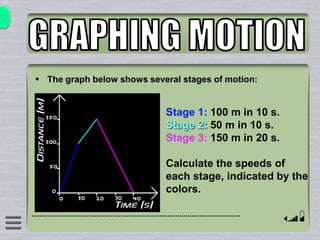
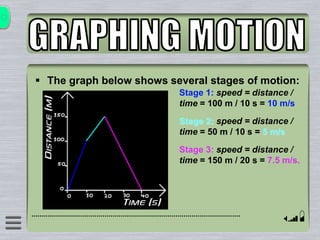
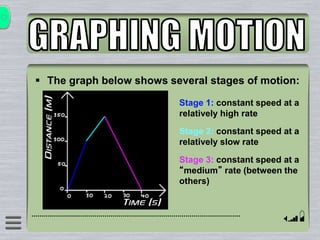
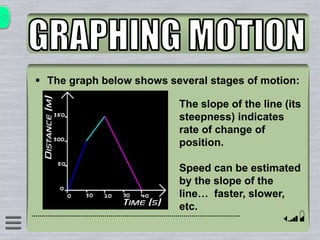
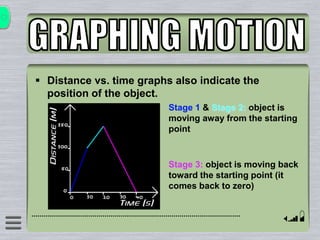
This document explains how to interpret distance-time graphs. It discusses that distance is plotted on the y-axis and time on the x-axis. A horizontal line indicates no movement, a straight upward sloping line indicates constant speed, and a curved line shows changing speed. Steeper lines correspond to higher speeds as they represent greater distance covered in the same time. The direction of the line also shows if an object is moving away from or toward the starting point. Examples are provided to illustrate constant, changing, and stopping speeds.