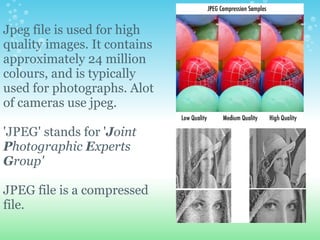
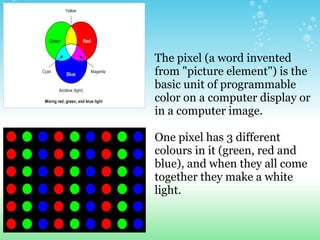
An animated GIF is a graphic file that contains a series of images displayed sequentially to create the illusion of movement. It contains up to 256 colors and the file is compressed. A JPEG file contains approximately 24 million colors and is used for photographs. It is also a compressed file. A pixel is the basic unit of programmable color that, when combined with other pixels, makes up an image on a computer display. A BMP file stores digital images but is a large file because it is not compressed.