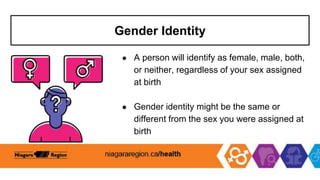
This document outlines a Grade 6 land acknowledgment presentation focused on stereotypes and assumptions related to diversity, gender roles, and identity. It includes interactive activities, discussions, and curriculum objectives aimed at helping students understand the impacts of stereotypes, promote inclusivity, and challenge harmful assumptions. The presentation emphasizes the importance of creating a safe environment and encourages dialogue about diversity and discrimination.