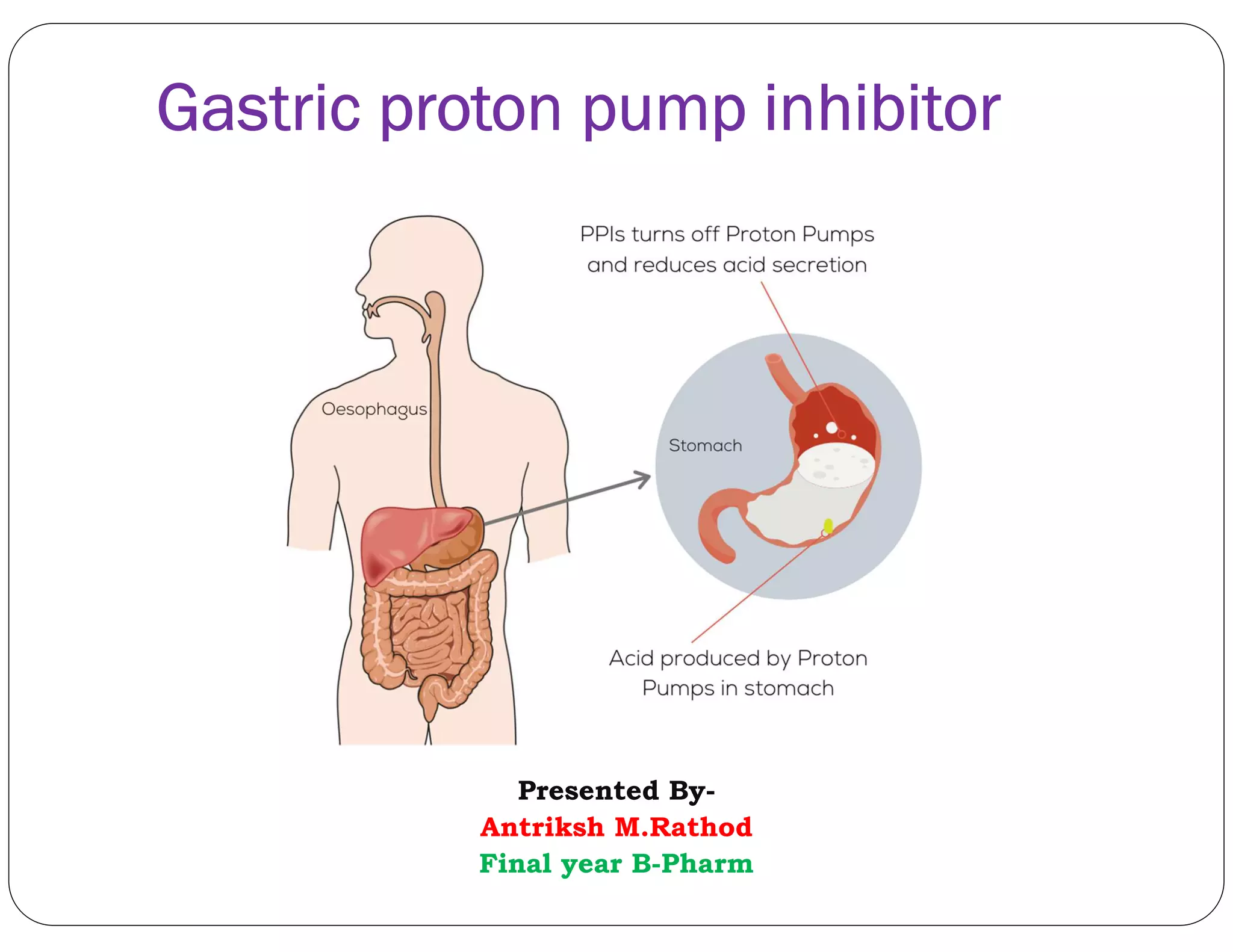
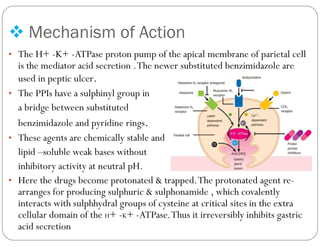
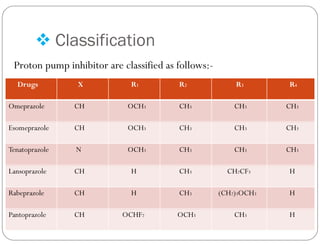
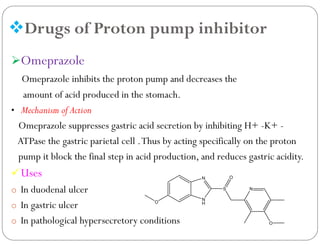
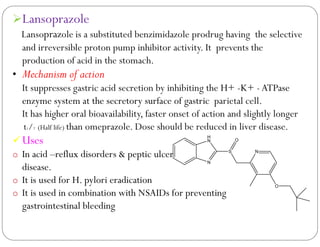
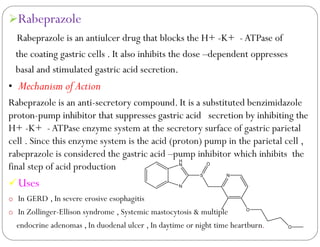
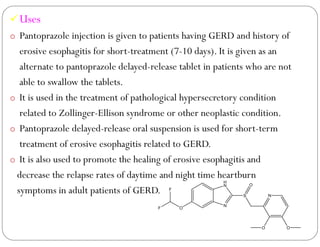
This document discusses gastric proton pump inhibitors (PPIs). It describes their mechanism of action as selectively inhibiting the proton pump in parietal cells through accumulation in cell membranes. Four specific PPI drugs are discussed - omeprazole, lansoprazole, rabeprazole, and pantoprazole - along with their mechanisms, classifications, and uses in treating conditions like ulcers and acid reflux.