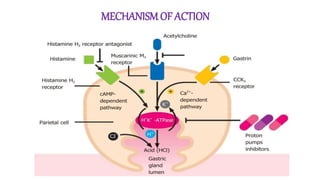
This document discusses gastric proton pump inhibitors (PPIs), which are a class of medications that powerfully reduce stomach acid production by irreversibly inhibiting the proton pump in the stomach. It describes the mechanism of action of PPIs, including how they are activated in acidic environments to covalently bind to and deactivate the proton pump. Four common PPI medications - omeprazole, lansoprazole, rabeprazole, and pantoprazole - are profiled, outlining their chemical properties, bioavailability, uses in treating acid-related gastrointestinal conditions, and potential side effects.





![Medical Uses
These medications are used in the treatment of many conditions, such as:
• Dyspepsia
• Peptic ulcer disease including after endoscopic treatment for bleeding
• As part of Helicobacter pylori eradication therapy
• Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD or GORD) including symptomatic endoscopy-
negative reflux disease[10] and associated laryngopharyngeal
reflux causing laryngitis[11] and chronic cough[12]
• Barrett's esophagus
• Eosinophilic esophagitis
• Stress gastritis and ulcer prevention in critical care
• Gastrinomas and other conditions that cause hypersecretion of acid
including Zollinger–Ellison syndrome (often 2–3x the regular dose is required)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/protonpumpinhibitor-221111095545-b7ca6980-221128200037-7d03f7c3/85/protonpumpinhibitor-221111095545-b7ca6980-pdf-7-320.jpg)







