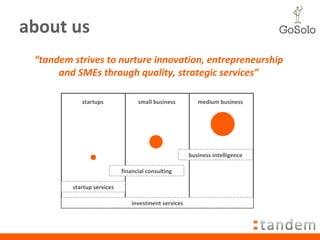
The document outlines the importance of business planning and provides a comprehensive guide on how to create a business plan, including its structure and key components such as the executive summary, market overview, and financial forecasts. It emphasizes the role of a business plan in solidifying ideas, identifying critical success factors, and serving as a roadmap for achieving business goals. Additionally, the document mentions upcoming workshops focused on entrepreneurship and business development.





















![upcoming GoSolo workshops wednesday september 8 th 2010 fundraising wednesday october 13 th 2010 incorporation wednesday november 10 th 2010 marketing on a budget register at [email_address]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/gosoloworkshop3-101002230526-phpapp01/85/GoSolo-Workshop-3-Business-Planning-24-320.jpg)