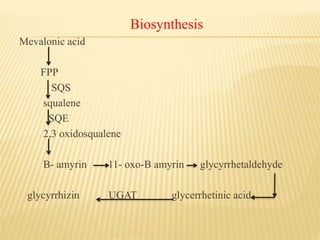
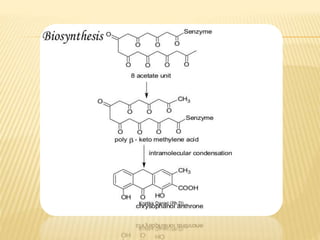
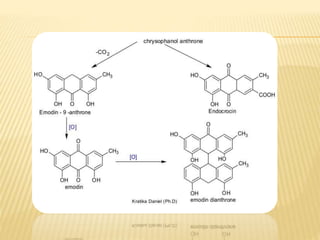
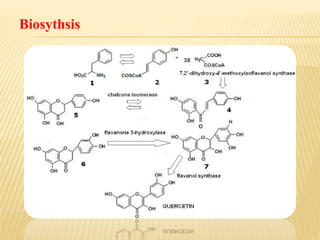
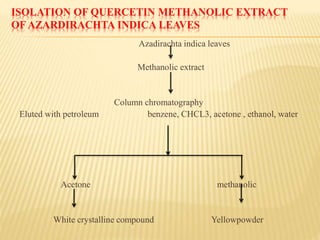
This document provides information about glycosides. It discusses various types of glycosides including glycyrrhizin from liquorice root, sennosides from senna leaves, bacosides from Bacopa monnieri leaves, and quercetin found in oak bark. Glycosides are composed of a sugar and aglycone. They play various roles in plants such as detoxification and storing compounds. The document describes the extraction and isolation methods for these specific glycosides and provides references for further information.