Embed presentation
Downloaded 85 times








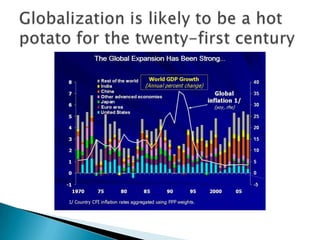





Globalization is defined as the expansion of economic and social ties between countries through the spread of corporate institutions and capitalist philosophy, shrinking the world economically. It has been made possible by technology, communication networks, internet access, growth of economic cooperation through trading blocs, the collapse of communism, and movement to free trade. Globalization results in increasing reliance between economies, and opportunities to buy and sell and locate labor and capital anywhere in the world, growing global financial markets. While it increases choice, growth, and employment opportunities through trade, it can also increase gaps between rich and poor and allow dominance and exploitation in global trade.













