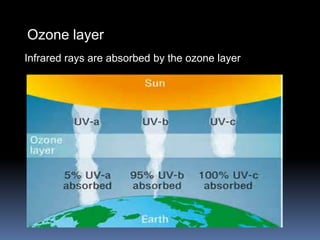
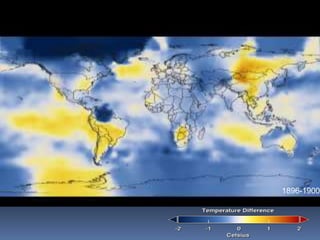
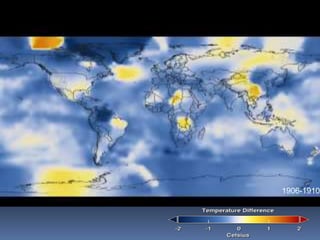
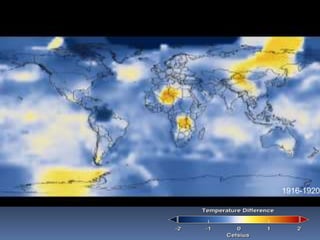
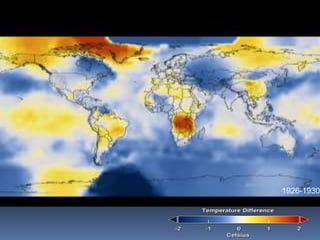
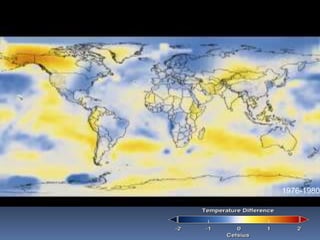
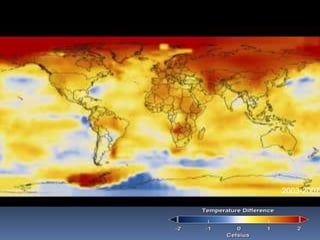
Global warming is caused by greenhouse gases like carbon dioxide trapping heat in the atmosphere. This is due to factors like the burning of fossil fuels and deforestation. The greenhouse effect allows life on Earth by keeping temperatures warm, but too much global warming threatens the environment through rising sea levels, more fires, and damage to ecosystems. Solutions include reducing electricity usage, driving and flying less, improving efficiency, and increasing renewable energy and reforestation efforts to remove carbon from the atmosphere.