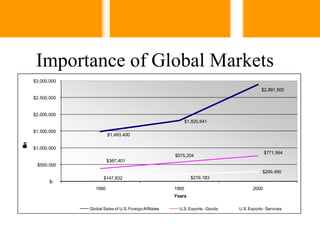
This document discusses factors driving globalization and the implications for businesses. It notes that technology has reduced distances, and factors like IT, transportation, and trade policies have accelerated globalization. This creates intensifying competition for companies from around the world. The document also notes that most of the world's population and GDP now lies outside the US, and educational and income factors are shaping global consumption. It outlines six imperatives for global business success and emphasizes the importance of designing global supply chain networks that consider compatibility, configuration, coordination, and control across culturally diverse markets.