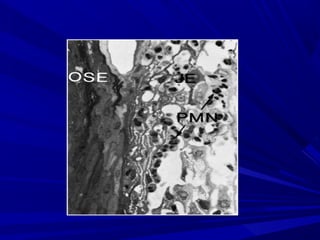
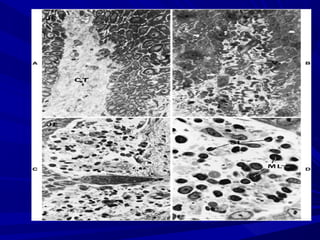
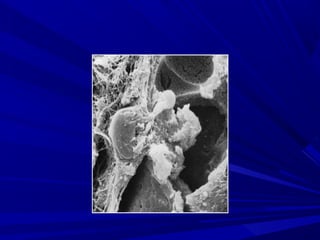
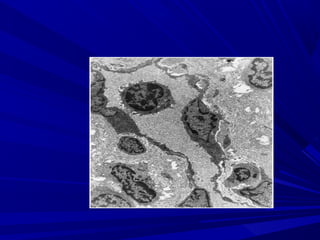
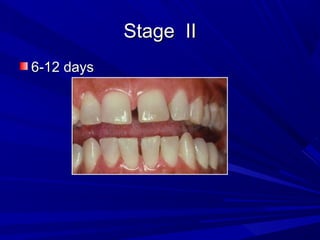
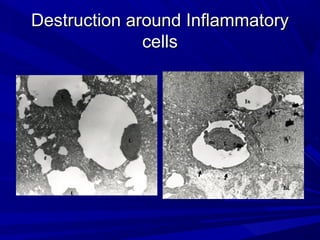
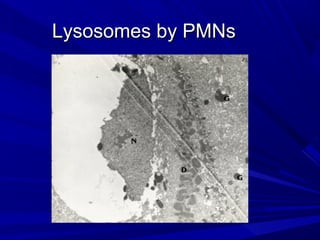
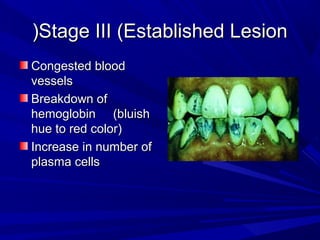
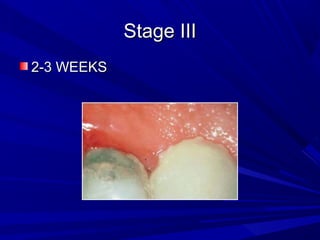
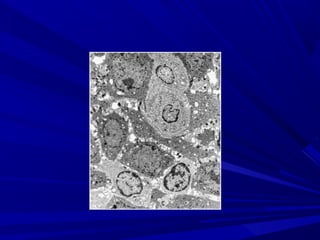
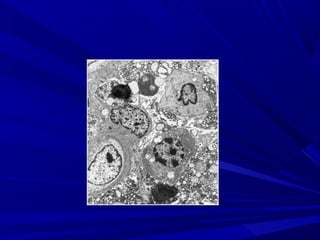
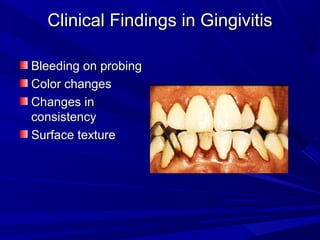
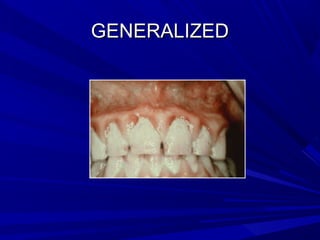
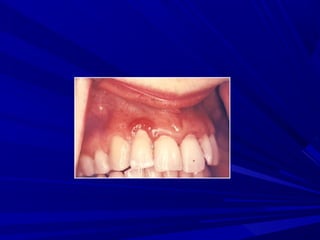
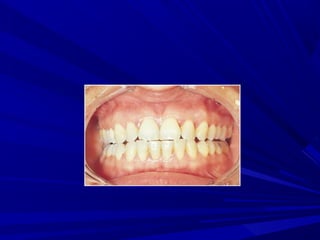
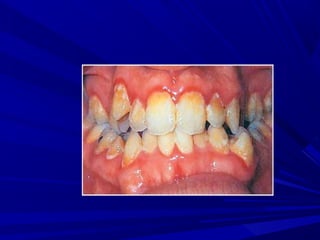
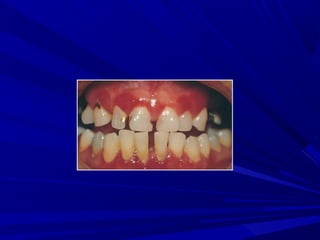
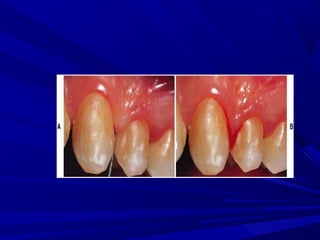
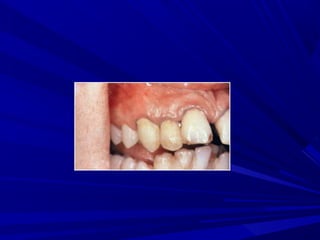
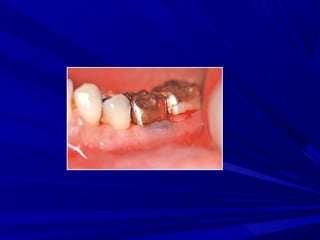
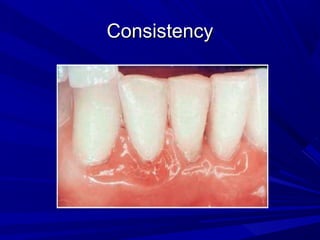
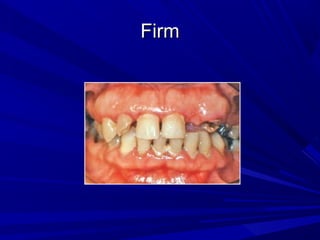
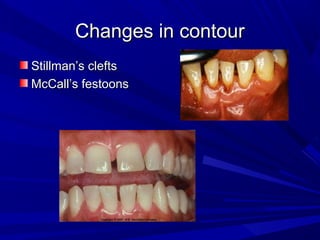
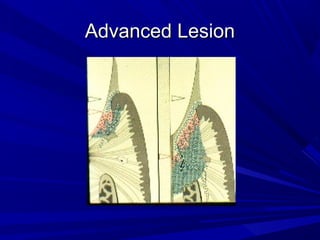
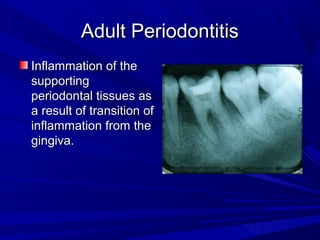
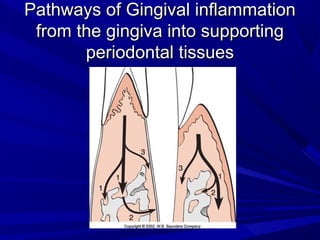
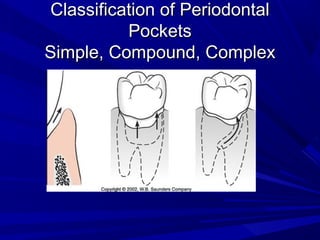
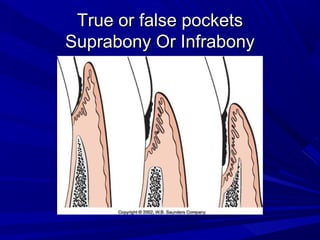
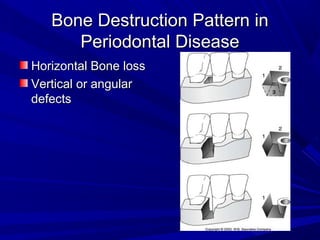
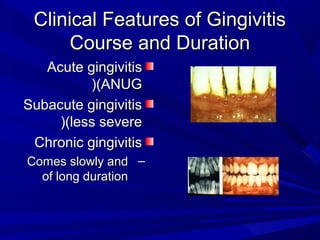
This document describes the histopathological stages of gingivitis from initial to established lesions. Stage I occurs within 1 week and shows vascular changes and PMN predominance. Stage II occurs within 6-12 days and shows erythema, bleeding, and lymphocyte predominance with collagen destruction around inflammatory cells. Stage III occurs within 2-3 weeks and shows congested blood vessels, increased plasma cells, and breakdown of hemoglobin. The clinical findings of gingivitis include bleeding, color changes, texture changes, and localized or generalized distribution. Advanced gingivitis can lead to periodontitis through pathways of inflammation from the gingiva into the supporting periodontal tissues.