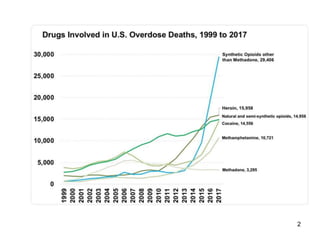
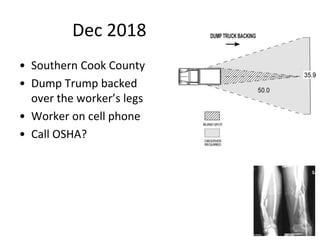
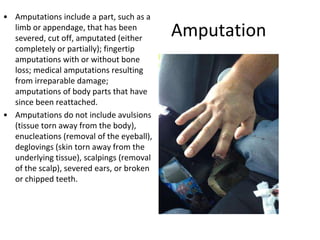
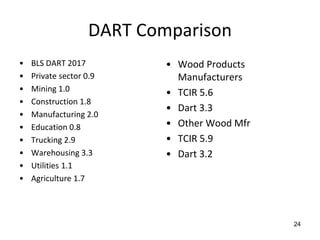
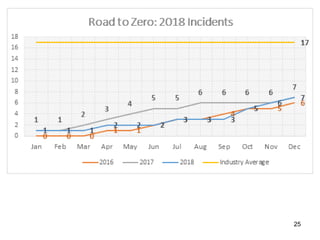
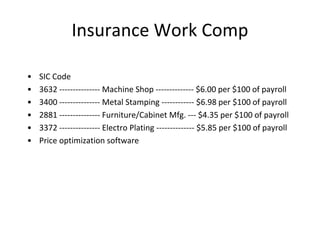
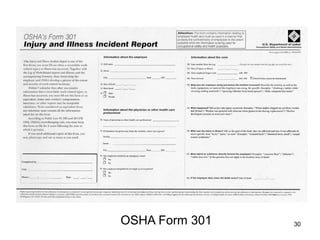
This document provides guidance on OSHA's recordkeeping and reporting requirements for workplace injuries and illnesses. It discusses what types of injuries and illnesses must be recorded, including those that result in death, days away from work, job transfer or restriction, medical treatment beyond first aid, loss of consciousness, or diagnosed significant injury/illness. It also outlines requirements for reporting fatalities, hospitalizations, amputations, and losses of an eye to OSHA and maintaining records like OSHA forms 300, 301, and 300A. Employers must consistently apply drug testing policies and keep detailed records to comply with OSHA regulations.