This document discusses the classification and components of highways. It covers:
1) Static characteristics like lane widths and vertical clearances that affect highway design.
2) Kinematic characteristics like acceleration and passing maneuvers that influence design elements.
3) Functional classification of highways as arterial, collector, or local roads based on their balance of mobility versus accessibility.
4) Distinctions between freeways and expressways based on access control.
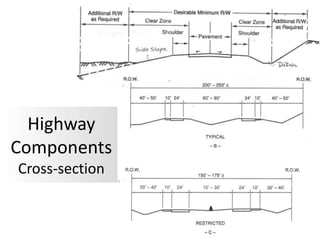
5) Components of highway cross-sections including lanes, medians, shoulders, ditches, and slopes.










![11
Freeway versus expressway
• The distinction between freeways and expressway is
based on the accessibility control
– Freeways have a full control of access [access or exit are
permitted only at controlled locations (exit ramp)]
– Expressways have a partial access control. (access or exit
are maybe permitted directly from or adjacent land or via
a limited number of at grade intersections)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/geometricdesign2-230508125143-eae46a49/85/Geometric-Design-2-ppt-11-320.jpg)