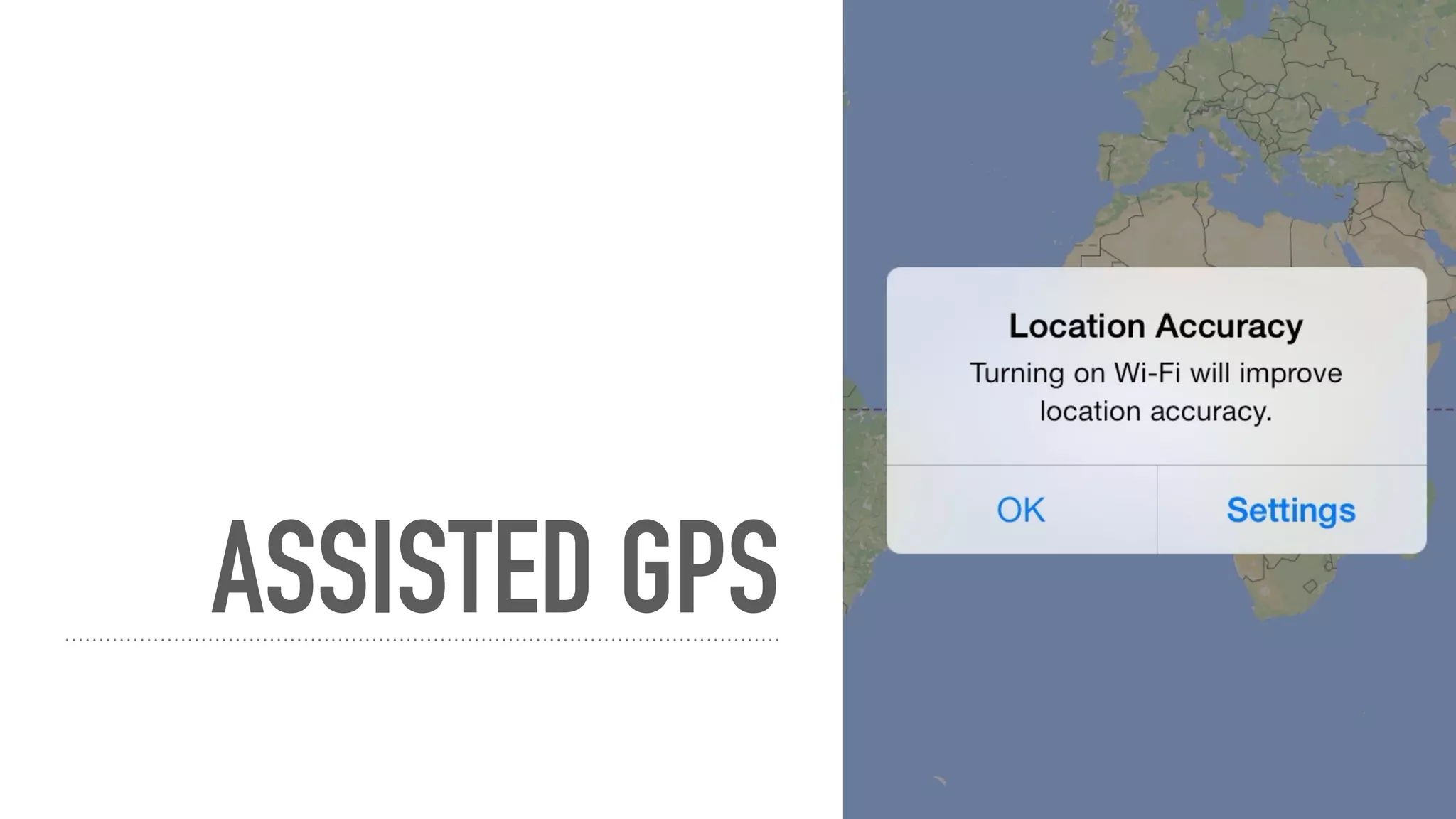
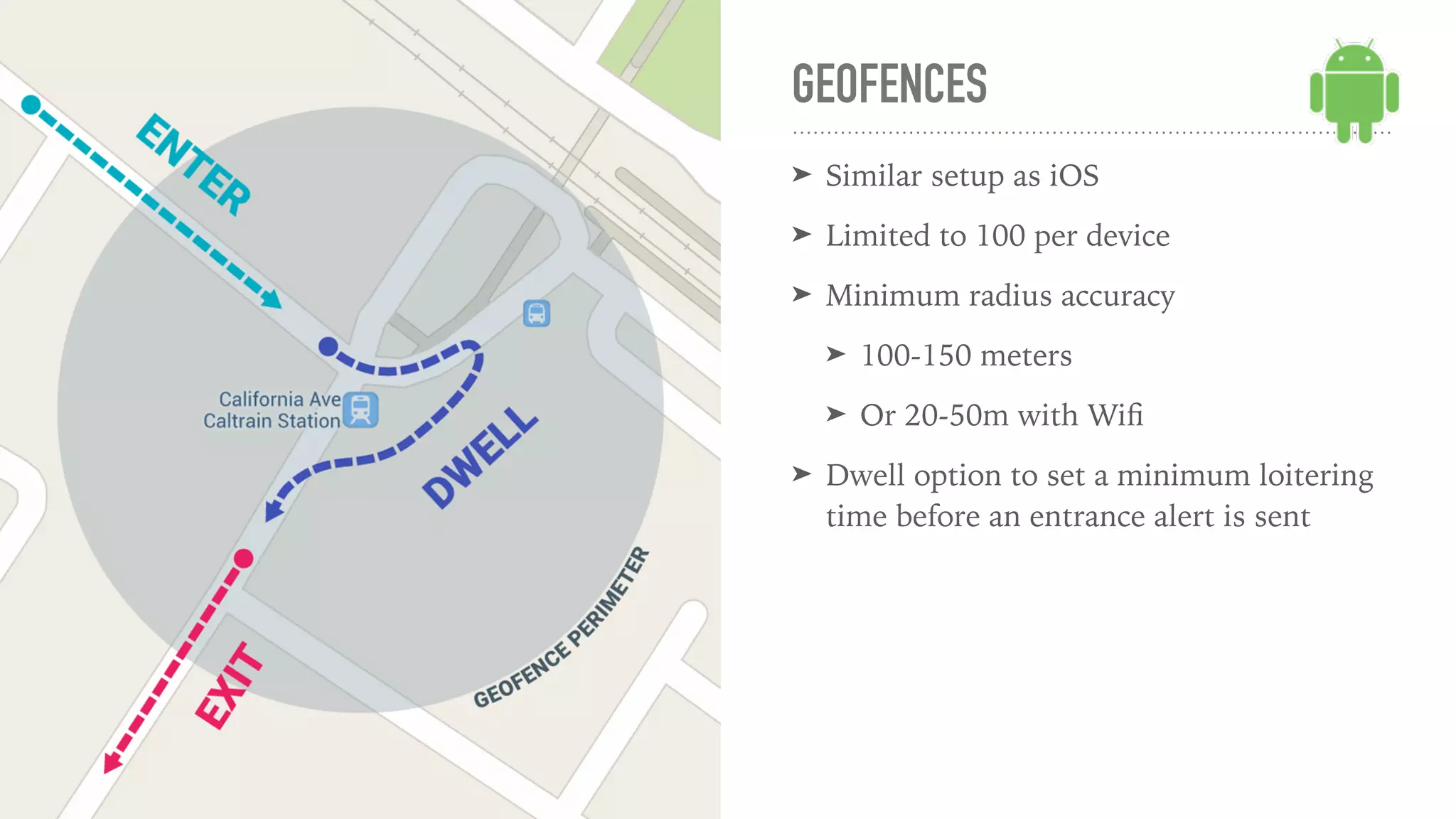
The presentation discusses geolocation capabilities in mobile apps, focusing on GPS, assisted GPS, and the responsibilities of developers regarding user privacy and battery conservation. It contrasts location services on iOS and Android, detailing their specific functionalities, advantages, and challenges, including issues like permission management and background location services. Overall, the talk emphasizes careful implementation and cross-platform considerations to enhance user experience while safeguarding privacy.