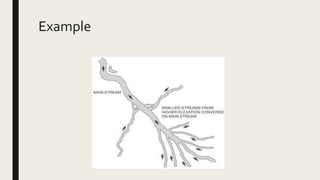
Mr. X will teach a geography lesson on fluvial processes and drainage patterns to a class of 32 Grade 12 students in South Africa. The lesson will introduce terminology like interfluve and aquifer, explain how rock types influence drainage patterns, and have students identify landforms and drainage patterns on a map. Through activities like pictionary and a lecture, students will learn to differentiate drainage patterns, appreciate how landforms impact water distribution, and apply their map skills. The lesson aims to help students connect landform geomorphology to fluvial processes and recognize the real-world effects of landforms on water supply.