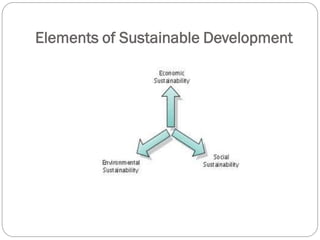
Geography consists of four academic traditions: spatial studies, area studies, human-land interaction, and an earth science perspective. It has a long history dating back to Greek geographers like Herodotus. There are six elements studied in geography: spatial terms, places and regions, physical and human systems, environment/society interactions, and applications. Geography branches into human geography (including cultural, political, urban, economic, and social studies), physical geography (landforms, soils, climate, oceans, etc.), environmental geography, and regional geography. Environmental planning considers sustainable resource use and management to balance human and natural systems.