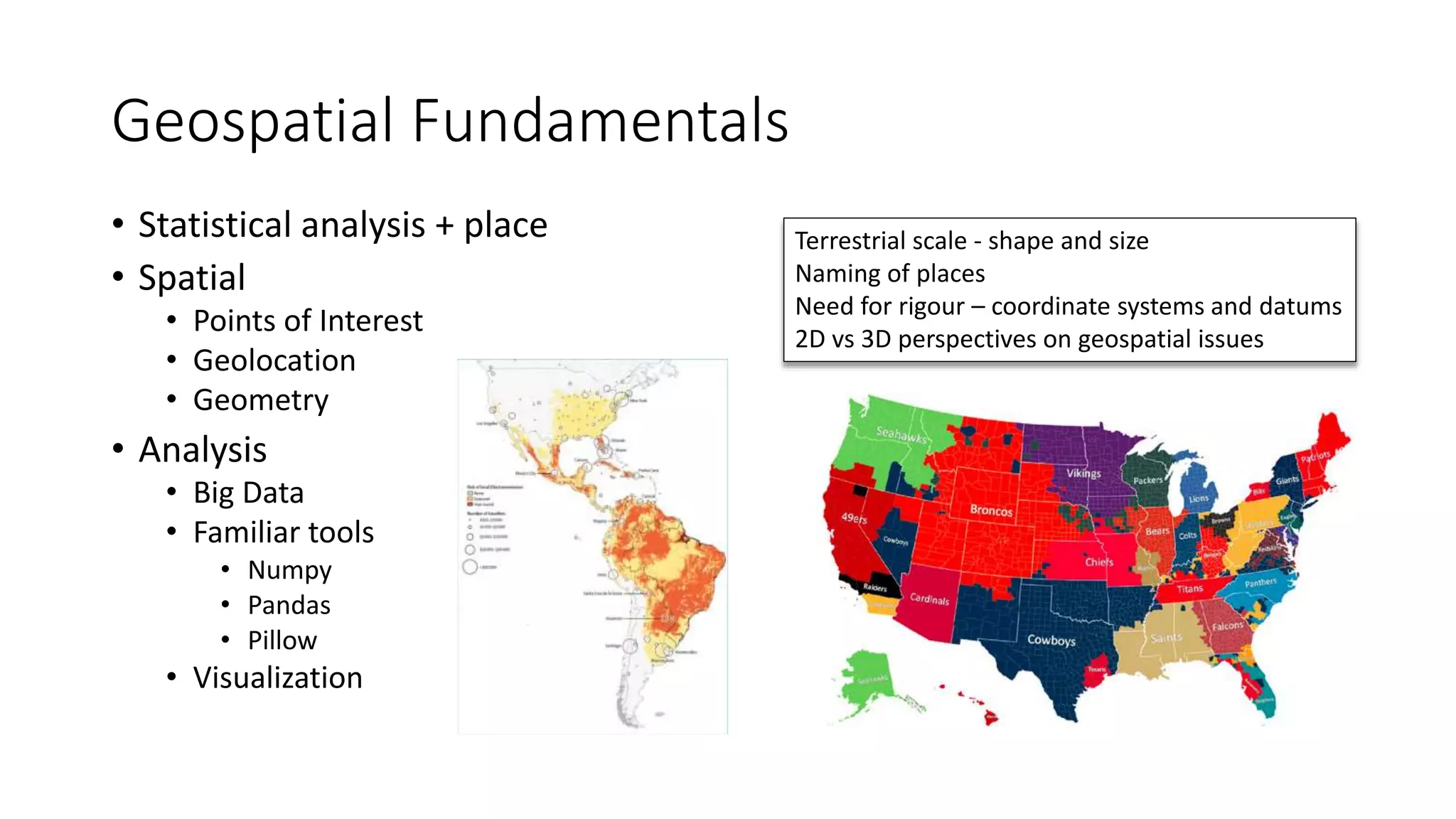
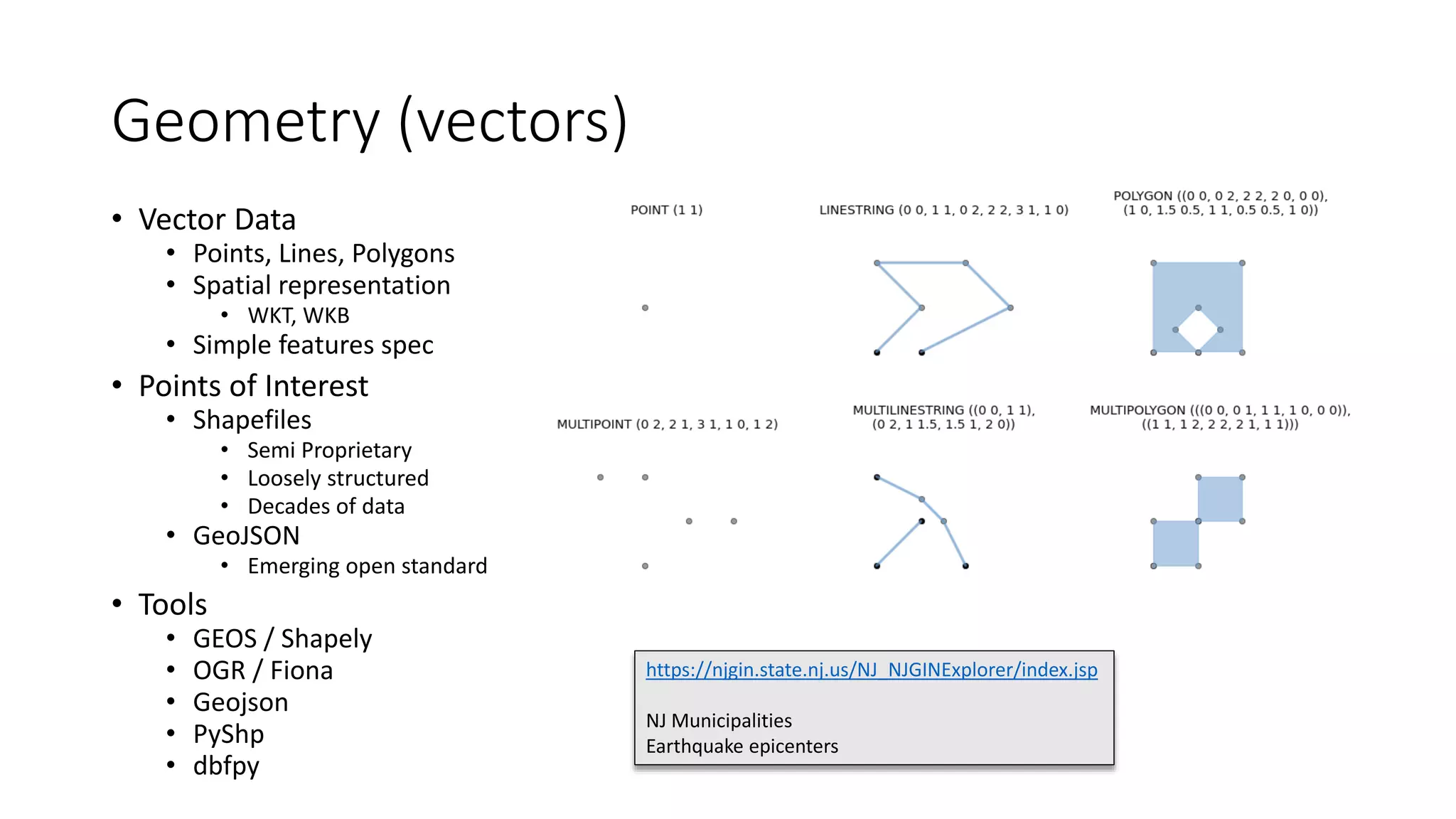
The document provides an overview of geospatial analysis using Python, covering fundamental concepts such as coordinate systems, projections, and geometry. It highlights various tools and libraries for data handling and visualization, including GDAL, GeoPandas, and Matplotlib. Additionally, it discusses remote sensing imagery and functions utilized in geospatial analysis.