1. The document describes the development of the male and female genital systems from early embryonic stages through formation of the internal and external genitalia.
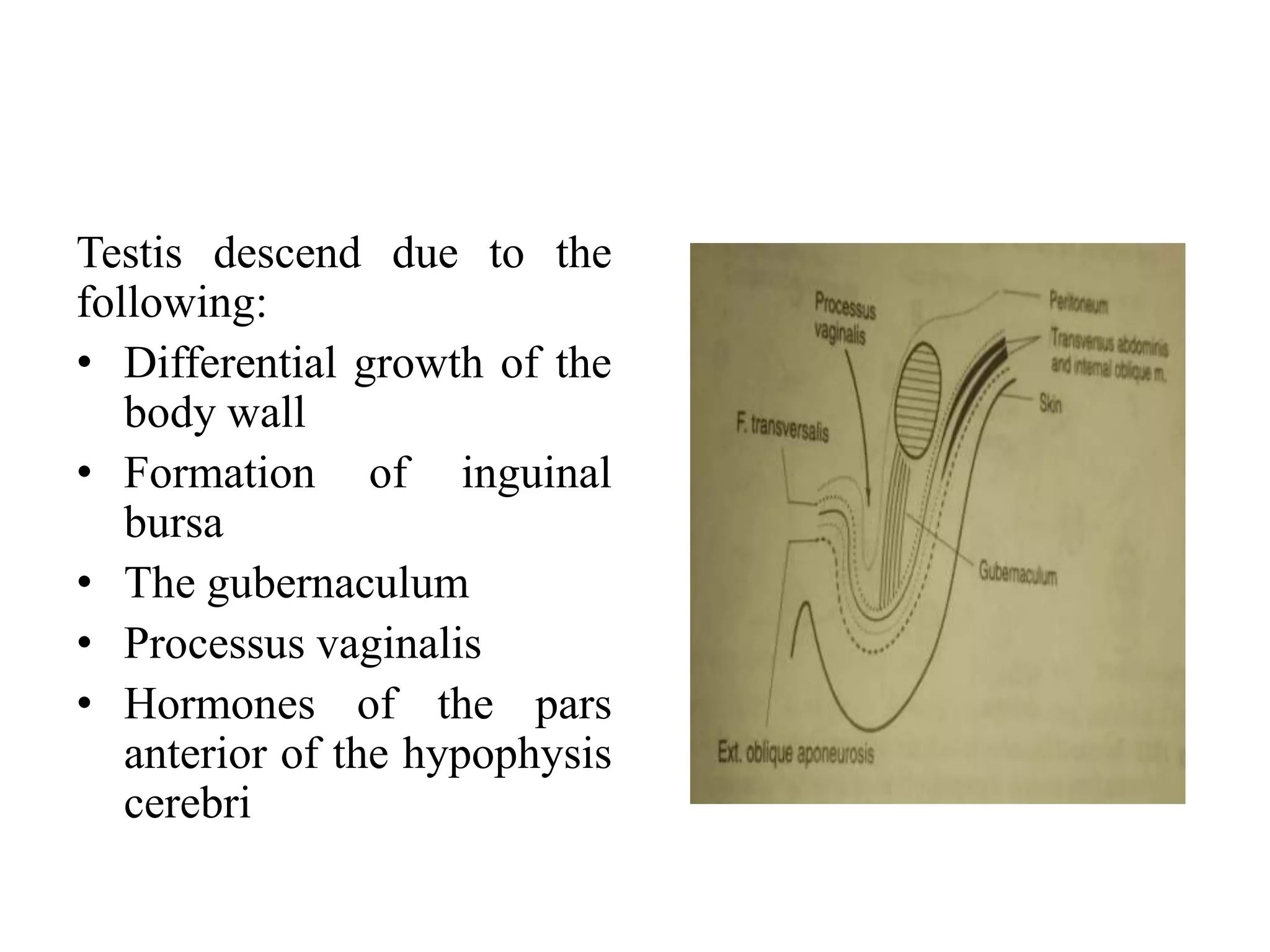
2. Key events include formation of the genital ridges which develop into testes in males and ovaries in females, descent of the testes into the scrotum, development of the duct systems including the vas deferens and epididymis in males and Mullerian duct regression leading to formation of the uterus and vagina in females.
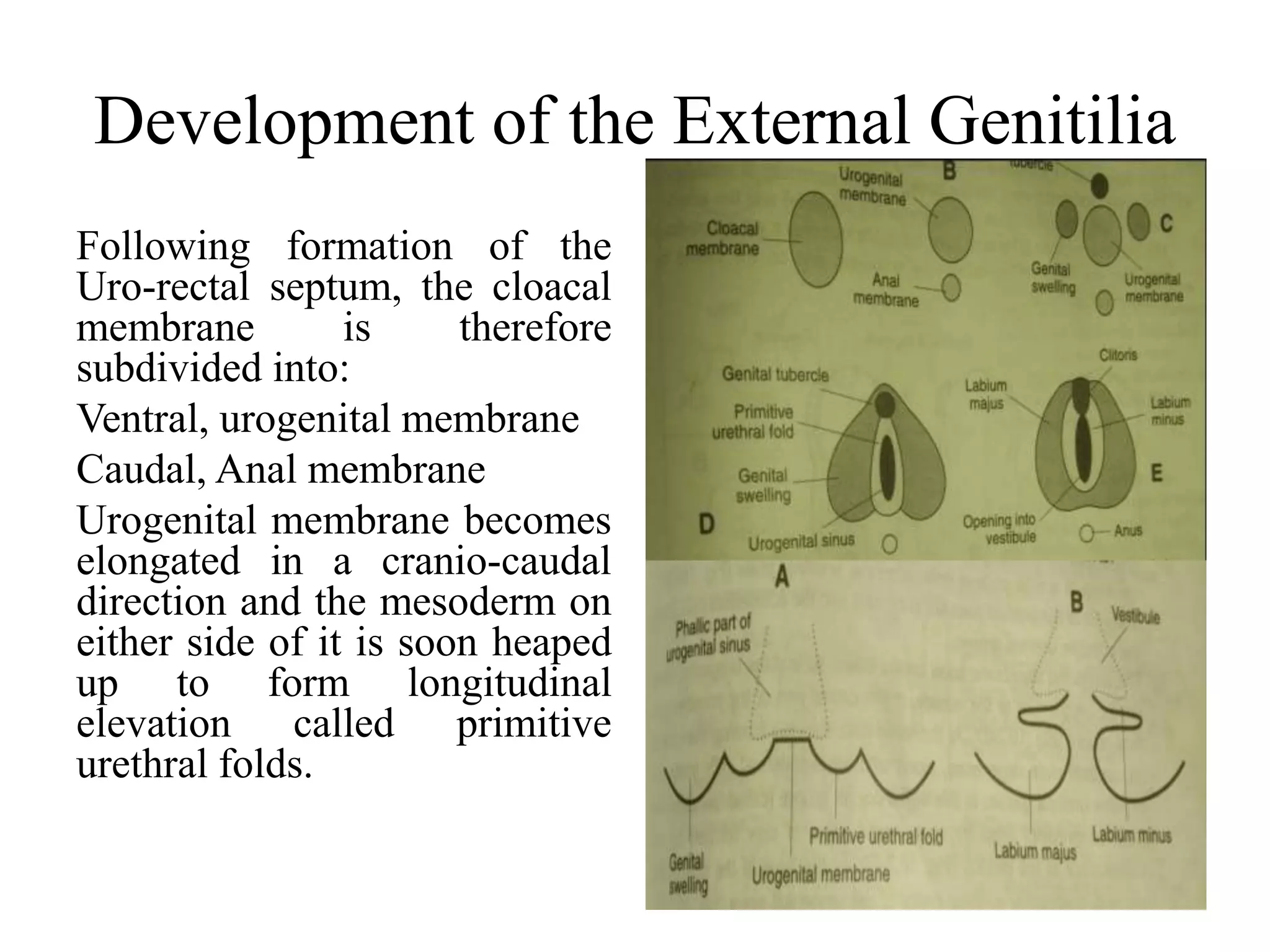
3. External genitalia develop from the genital tubercle and swellings, with the penis and scrotum forming in males and clitoris, labia, and vagina developing in females.