genetics notes.docx
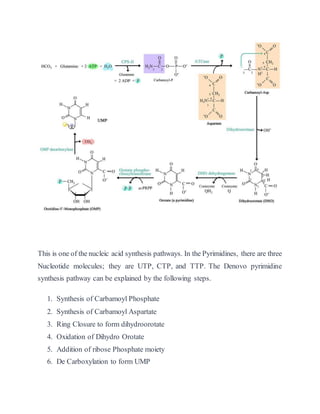
- 1. This is one of the nucleic acid synthesis pathways. In the Pyrimidines, there are three Nucleotide molecules; they are UTP, CTP, and TTP. The Denovo pyrimidine synthesis pathway can be explained by the following steps. 1. Synthesis of Carbamoyl Phosphate 2. Synthesis of Carbamoyl Aspartate 3. Ring Closure to form dihydroorotate 4. Oxidation of Dihydro Orotate 5. Addition of ribose Phosphate moiety 6. De Carboxylation to form UMP
- 2. Step 1: Synthesis of Carbamoyl Phosphate The first reaction of Pyrimidine synthesis is the synthesis of Carbamoyl phosphate by utilizing the amide form of Glutamine (Glutamate) and HCO3 – (Carbonic acid). This reaction is catalyzed by Carbamoyl phosphatesynthetase-II, the enzyme is cytosolic enzyme is a- cytosolic enzyme. In this reaction, 2 ATP molecules are consumed. HCO3 – (Carbonic acid) + Glutamine (Gln) → CarbamoylPhosphate + 2 AMP Step 2: Synthesis Carbamoyl Aspartate Carbamoyl phosphate is condensing with Aspartic acid it forms carbamoyl aspartate is catalyzed by Aspartate Transcarbamoylase (ATCase). Carbamoyl Phosphate + Aspartate → Carbamoyl Aspartate + H3PO4 Step 3: Ring Closure to form dihydroorotate: Carbamoyl Aspartate is converted into Dihydro Orotate by ring closure mechanism. This reaction is catalyzed by Dihydro Orotase. Carbamoyl Aspartate → Dihydro Orotate + H20
- 3. Step 4: Oxidation of dihydroorotate The hydro Orotate irreversibly oxidized to Orotate the enzyme Dihydro Orotate Dehydrogenase. The Eukaryotic enzyme, which contains FMN and Non-heme iron, is located on the outer surface of the inner mitochondrial membrane where quinines supply its oxidizing power. Oxidized Dihydro Orotate + Quinone → Orotate + Reduced Quinone (quinone gains a hydrogen q---qh2) Step 5: Addition of Ribose-Phosphate Moiety Orotate reacts with PRPP to yield Orotidine-5-MonoPhosphate (OMP). This reaction is catalyzed by Orotate Phosphoribosyltransferase. In this reaction, a pyrophosphate is released from the PRPP molecules. Orotate + PRPP → OMP + PPi Step 6: Decarboxylation to form UMP The final reaction of the pathway is the decarboxylation of OMP by the OMP decarboxylase to form UMP this is an unusual reaction in that it requires no cofactors. OMP → UMP + CO2
- 4. Synthesis of UTP and CTP The synthesis of UTP forms UMP, done by phosphate exchange mechanism. This reaction is catalyzed by nucleoside monophosphate kinase and Nucleoside diphosphate Kinase. UMP + ATP ↔ UDP + ADP UDP + ATP ↔ UTP + ADP
- 5. CTP is formed by the amination of UTP by CTP synthetase. In animals, the amino group is donated by Glutamine whereas in bacteria it is supplied directly in Ammonia. UTP + Gln +ATP + H2O → CTP + Glu + ADP + Pi The Synthesis of pyrimidine derivatives is TTP, CTP, and UTP.
- 6. 1. How are pyrimidines synthesized? Pyrimidines are synthesized from amines using a series ofreactions called the synthesis of purines. These reactions are turned on by the enzyme polynucleotide phosphorylaseholoenzyme. This is an important molecule, as it allows RNA to be converted into nucleic acids that can then serve as a template for synthesizing DNA until later in development when they become functional chromosomes. It makes genes necessary for cell division and maintenance ofclosed organelles suchas mitochondria in eukaryotic cells that produce energy via ATP synthase. 2. How many steps are there in pyrimidine synthesis? There are six steps in pyrimidine synthesis. The growth and division of living organisms require a constantsupply of energy. In eukaryotes, it takes place in the form of ATP from adenosine triphosphate (ATP). Phosphorylation is required for mitochondrial function, where glucose can be used to produce ATP via oxidative phosphorylation. A free-radical oxidation pathway involves glycolysis—which releases pyruvate to run three different metabolic pathways: the citric acid cycle, pyruvate dehydrogenase (PDH), and Krebs— which allows mitochondria to get energy from glucose by converting it into acetyl-CoA. The acyl group is used to make fatty acids in a process called ketogenesis, powered by oxidizing glucose via oxidative phosphorylation using FAD instead of NAD, which can happen during photosynthesis. 3. What is the product of pyrimidine synthesis? Pyrimidine synthesis produces uracil, which is a component of RNA. 4. What was the first pyrimidine synthesized? The first pyrimidine synthesized was acetic acid cyanamide. 5. What is required for pyrimidine ring synthesis?
- 7. It is required to have a nitrogen atom in the correct position on the molecule to allow carbon-nitrogen double bonds to form. 6. How is pyrimidine metabolized? Pyrimidine is metabolized by the liver. Pyrimidine is converted into uracil, which is eliminated in the urine. 7. What is the end product of pyrimidine metabolism? The end productofpyrimidine metabolism is uracil (U), which is a by-product of the breakdown of cytosine. 8. Why is pyrimidine metabolism important? Pyrimidine metabolism is essential becausepyrimidines are essential forDNA synthesis. 9. Which enzyme of pyrimidine synthesis is inhibited by CTP and activated by ATP? The enzyme that catalyzes the conversion of UTP to TTP is inhibited by CTP and activated by ATP.
- 8. DNA REPLICATION DNA replication is the process by which DNA makes a copy of itself during cell division. 1. The first step in DNA replication is to ‘unzip’ the double helix structure of the DNA? molecule. 2. This is carried out by an enzyme? called helicase which breaks the hydrogen bonds? holding the complementary? bases? of DNA together (A with T, C with G). 3. The separation of the two single strands of DNA creates a ‘Y’ shape called a replication ‘fork’. The two separated strands will act as templates for making the new strands of DNA. 4. One of the strands is oriented in the 3’ to 5’ direction (towards the replication fork), this is the leading strand?. The other strand is oriented in the 5’ to 3’ direction (away from the replication fork), this is the lagging strand?. As a result of their different orientations, the two strands are replicated differently:
- 9. An illustration to show replication of the leading and lagging strands of DNA. Image credit: Genome Research Limited 1. Leading Strand: 2. A short piece of RNA? called a primer? (produced by an enzyme called primase) comes along and binds to the end of the leading strand. The primer acts as the starting point for DNA synthesis. 3. DNA polymerase? binds to the leading strand and then ‘walks’ along with it, adding new complementary? nucleotide? bases (A, C, G, and T) to the strand of DNA in the 5’ to 3’ direction. 4. This sort of replication is called continuous. 1. Lagging strand: 2. Numerous RNA primers are made by the primase enzyme and bind at various points along the lagging strand.
- 10. 3. Chunks of DNA, called Okazaki fragments, are then added to the lagging strand also in the 5’ to 3’ direction. 4. This type of replication is called discontinuous as the Okazaki fragments will need to be joined up later. 1. Once all of the bases are matched up (A with T, C with G), an enzyme called exonuclease strips away the primer(s). The gaps where the primer(s) are then filled by yet more complementary nucleotides. 2. The new strand is proofread to make sure there are no mistakes in the new DNA sequence. 3. Finally, an enzyme called DNA ligase? seals up the sequence of DNA into two continuous double strands. 4. The result of DNA replication is two DNA molecules consisting of one new and one old chain of nucleotides. This is why DNA replication is described as semi-conservative, half of the chain is part of the original DNA molecule, and half is brand new. 5. Following replication, the new DNA automatically winds up into a double helix.