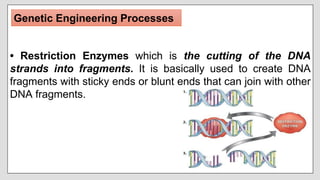
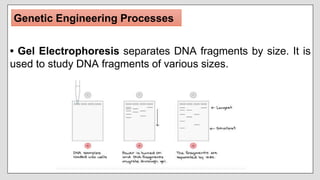
Genetic engineering involves directly manipulating an organism's genes using biotechnology. Key genetic engineering processes include using restriction enzymes to cut DNA, gel electrophoresis to separate DNA fragments by size, recombinant DNA technology to combine DNA from different sources, gene cloning to produce large amounts of recombinant DNA, polymerase chain reaction to copy specific DNA regions, and DNA sequencing to identify DNA sequences. Genetic engineering can be used to modify plants, animals, and microbes for various purposes like increasing crop yields, enhancing livestock, and improving microbe-dependent food production. Potential advantages include reducing pesticide use and developing disease resistance, while disadvantages include limited diversity and potential for technological abuse.