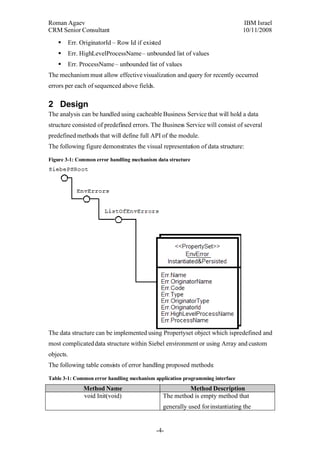
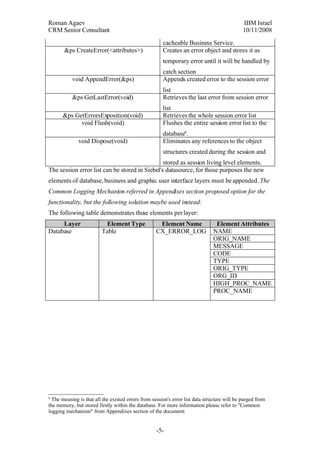
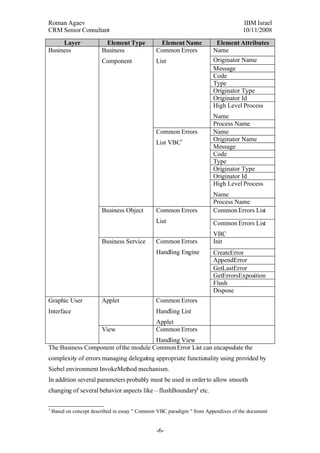
The document proposes a general error handling approach for Siebel applications. It involves designing a common error object model and cacheable Business Service that can generate, store, and retrieve error objects. The error objects would contain standardized fields to provide visibility into errors across different Siebel components. The Business Service would have methods for creating errors, appending them to a session list, and retrieving the last or full list of errors for an application session. The errors would also be logged to a database table for long-term storage and analysis.