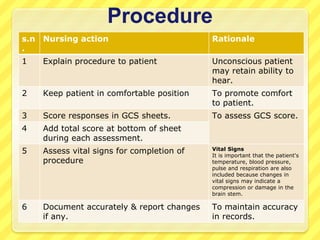
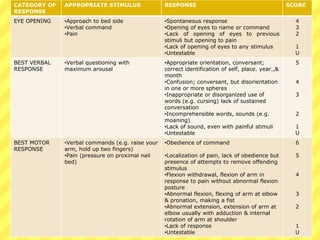
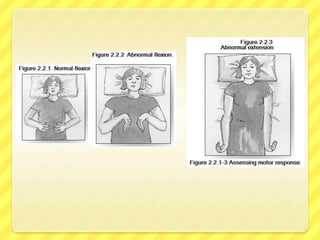
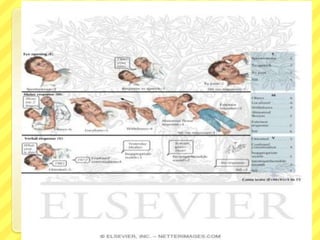
The Glasgow Coma Scale (GCS) is a standardized system used to assess consciousness by evaluating eye opening, verbal response, and motor response. Each category is scored from 1 to 4 or 6 and the total score ranges from 3 to 15, with lower scores indicating worse neurological function or coma. The GCS is used to assess patients with impaired consciousness due to head injuries, seizures, overdoses, or other neurological impairments. It provides important information about a patient's brain functioning that can help determine if their condition is stable, improving, or deteriorating over time.