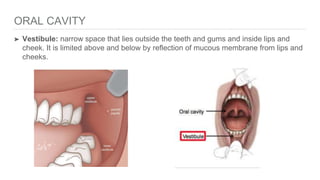
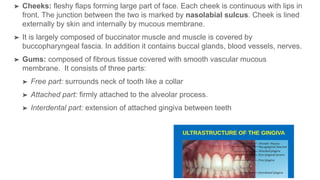
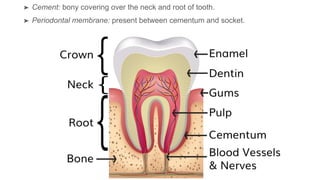
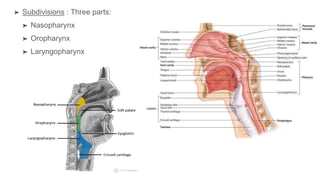
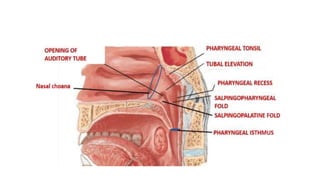
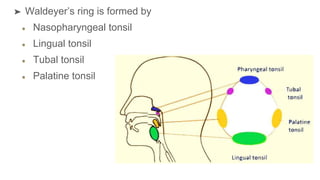
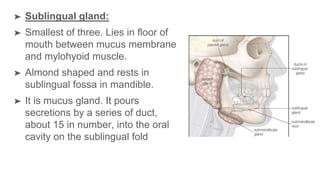
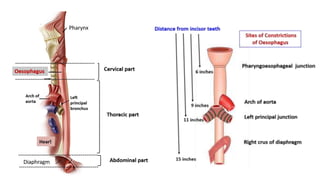
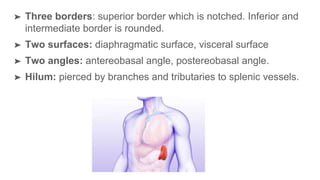
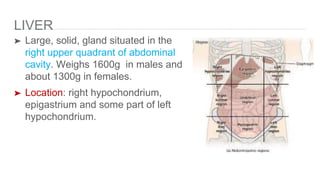
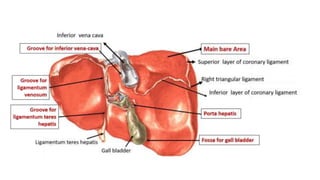
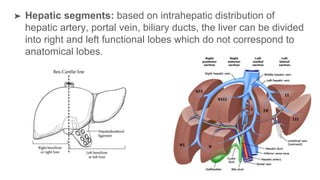
The oral cavity contains the lips, cheeks, gums, teeth, tongue, and floor and roof of the mouth. It leads posteriorly into the oropharynx. The tongue has papillae and muscles that aid in functions like taste, speech, and swallowing. The pharynx is a muscular tube divided into nasopharynx, oropharynx, and laryngopharynx that functions as a common passage for food and air and connects the oral and nasal cavities to the esophagus and larynx.