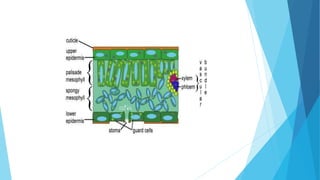
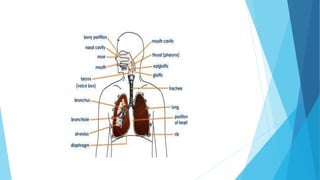
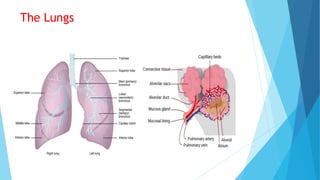
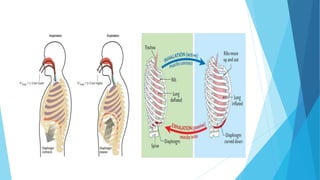
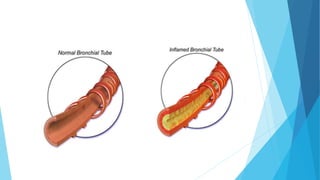
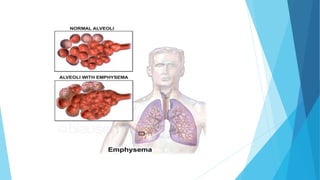
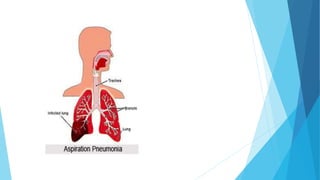
The document discusses gaseous exchange and respiration in plants and humans. In plants, gaseous exchange occurs through stomata in leaves and lenticels in stems. Photosynthesis and respiration regulate gas exchange. In humans, respiration involves the respiratory system including the nose, pharynx, larynx, trachea, bronchi, bronchioles and alveoli where gas exchange occurs. The lungs and associated muscles and diaphragm facilitate inhalation and exhalation. Common respiratory diseases like bronchitis, emphysema and pneumonia are also summarized.