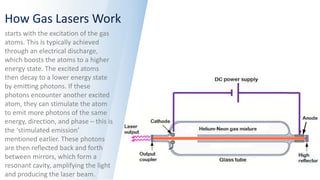
Gas lasers utilize a gas medium for light amplification, initiated by exciting gas atoms through electrical discharge, leading to stimulated emission of photons. They have applications in industries, medicine, scientific research, and telecommunications, with notable types being carbon dioxide, helium-neon, and argon-ion lasers. Advantages include high efficiency and spatial coherence, while drawbacks consist of high voltage requirements and potential hazards from certain gases.