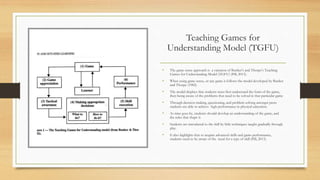
Game sense is an approach to physical education (PE) that focuses on using modified games as the main part of lessons rather than isolated skill drills. It is student-centered and aims to develop fundamental movement skills through inquiry-based learning within game play. Some key strengths of this approach are that it promotes participation and enjoyment for all ability levels, builds students' confidence through experience of success, and allows skills to develop organically through game play rather than direct instruction. The game sense approach aligns well with the goals of developing positive attitudes towards physical activity and interpersonal skills in the NSW PDHPE curriculum.