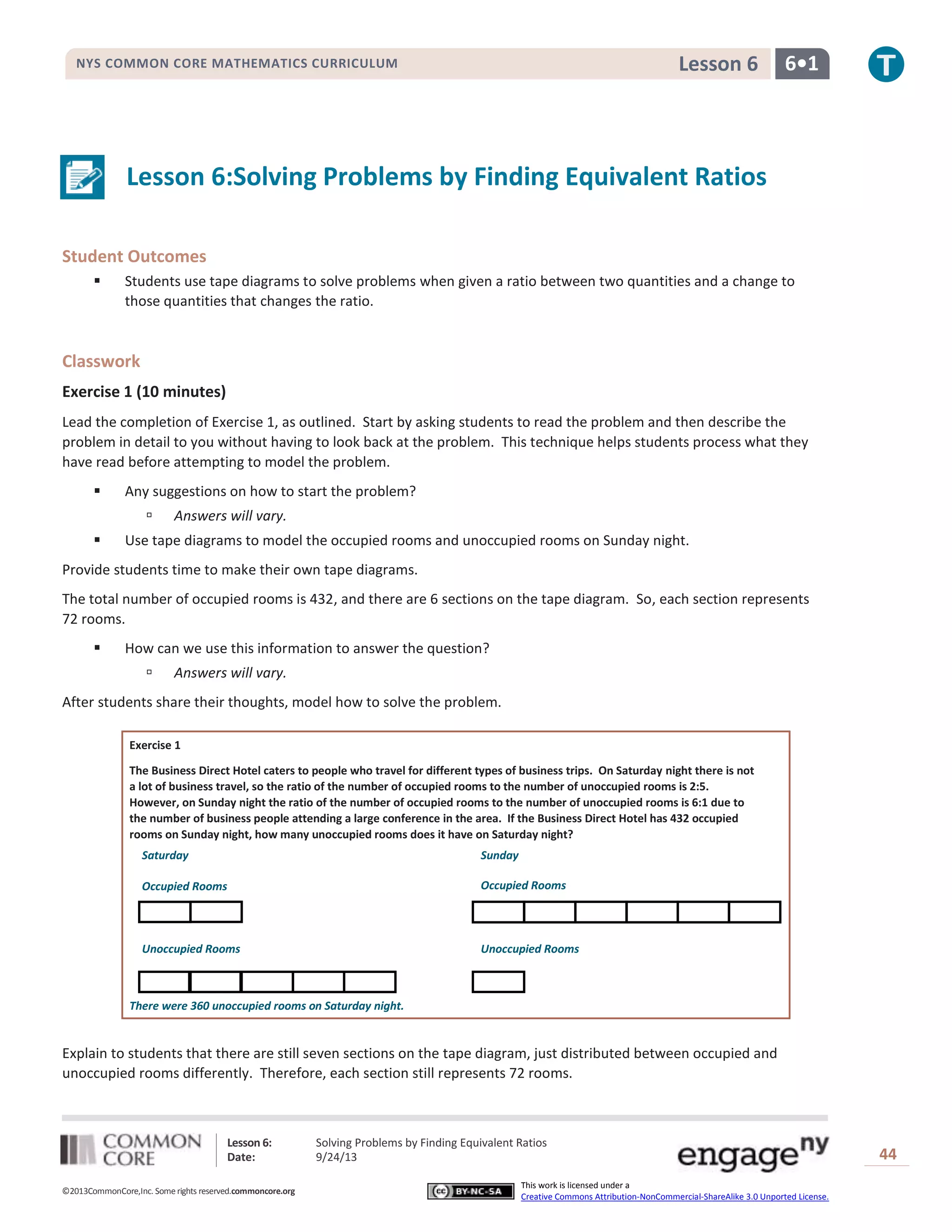
This document provides a lesson on solving ratio problems by finding equivalent ratios. It includes an example problem using tape diagrams to model ratios before and after a change. Students then work in groups on multiple practice problems involving ratios that change between situations. The lesson emphasizes drawing separate tape diagrams to visualize the ratios and quantities before and after a change occurs.