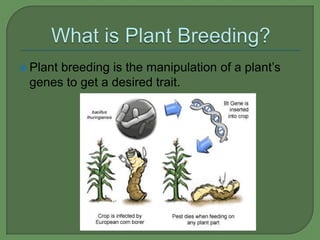
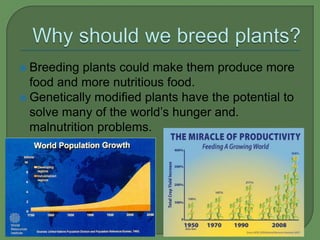
Plant breeding involves manipulating a plant's genes to produce desired traits. The process involves identifying a beneficial trait, extracting the genes responsible, inserting them into other plants, growing the plants, and allowing the genes to express themselves, resulting in crops with increased yields that benefit farmers. Genetically modifying plants has potential to solve world hunger and malnutrition problems by engineering crops that produce more food and nutrients and are resistant to pests and disease.