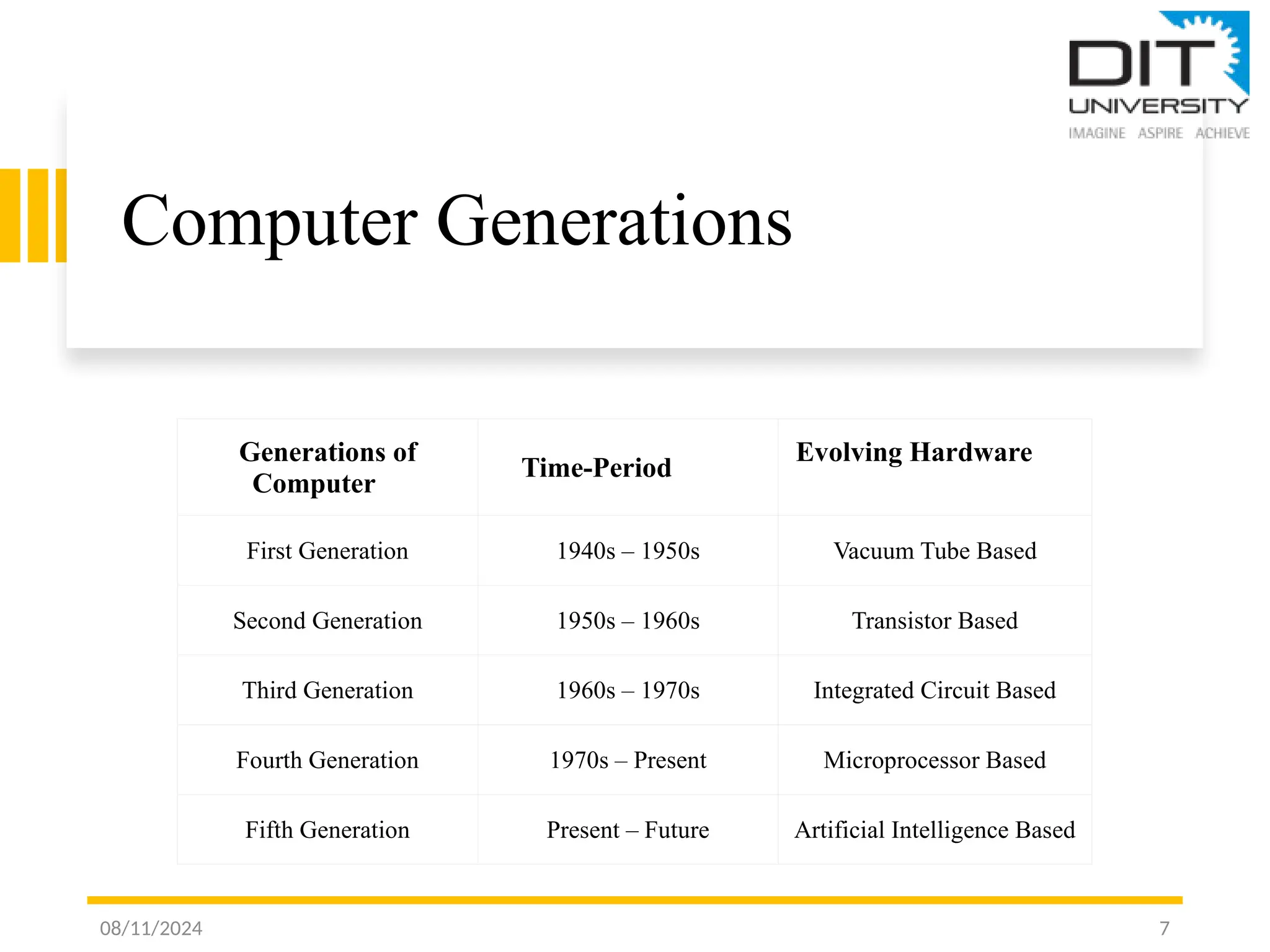
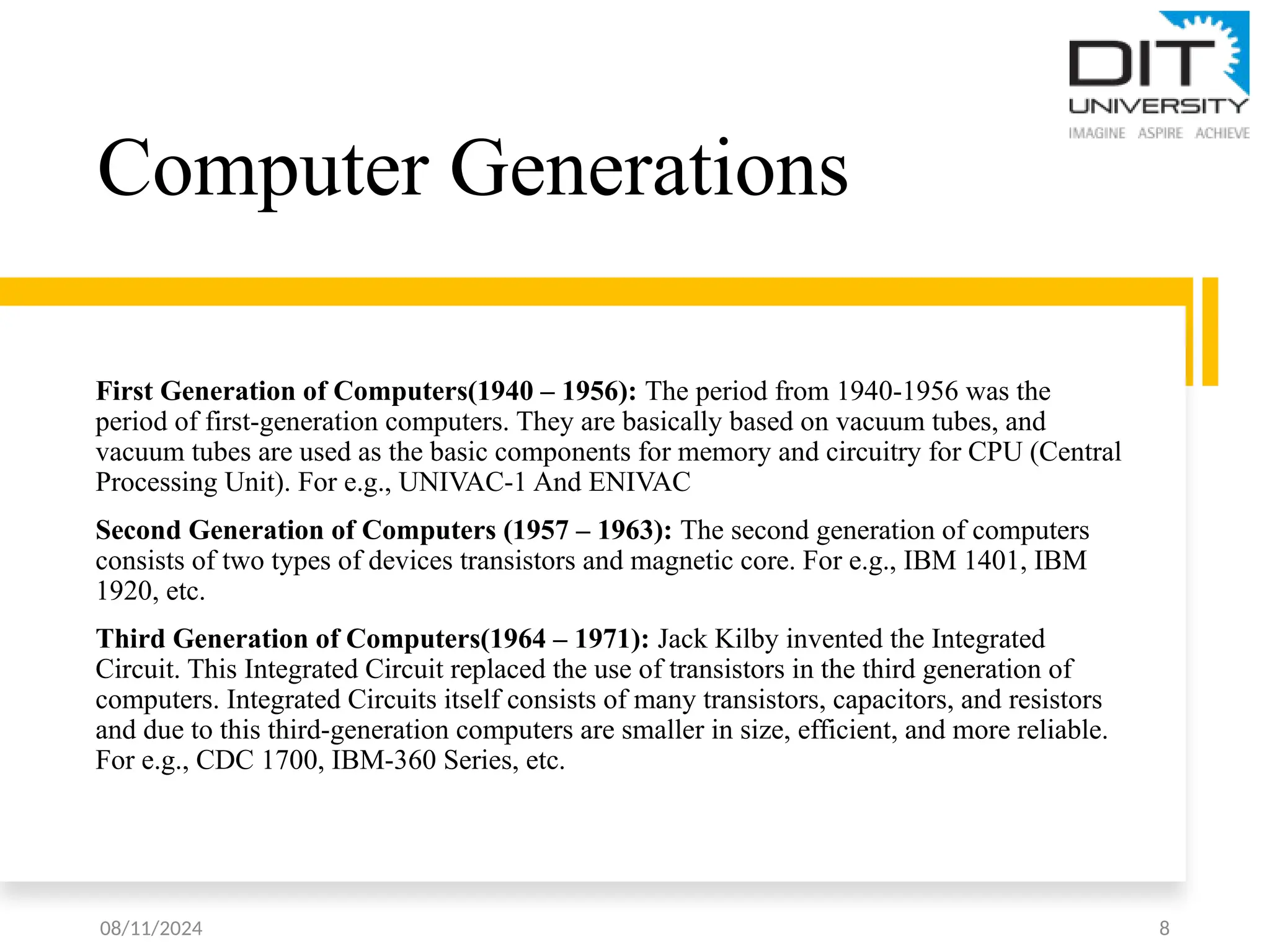
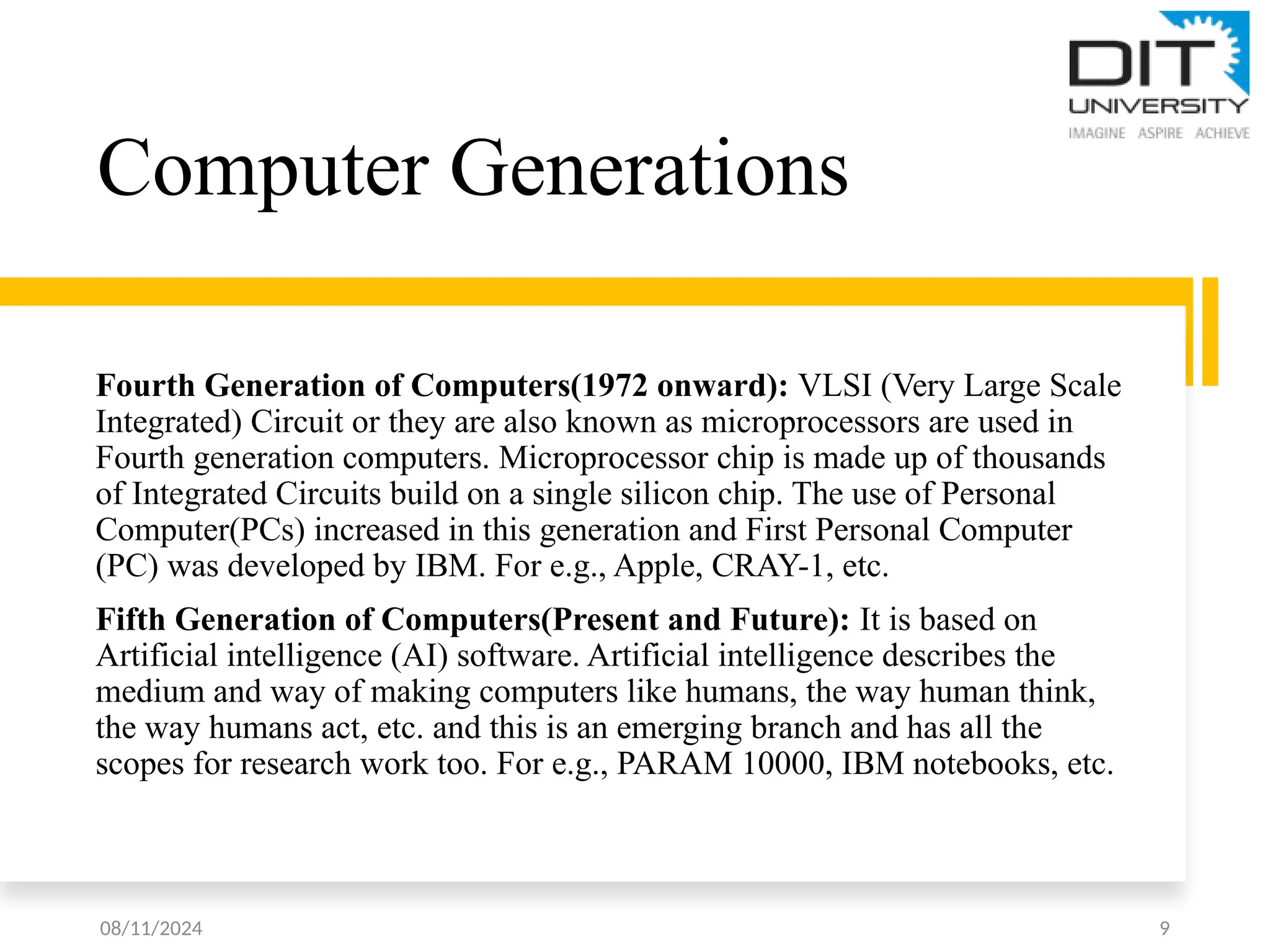
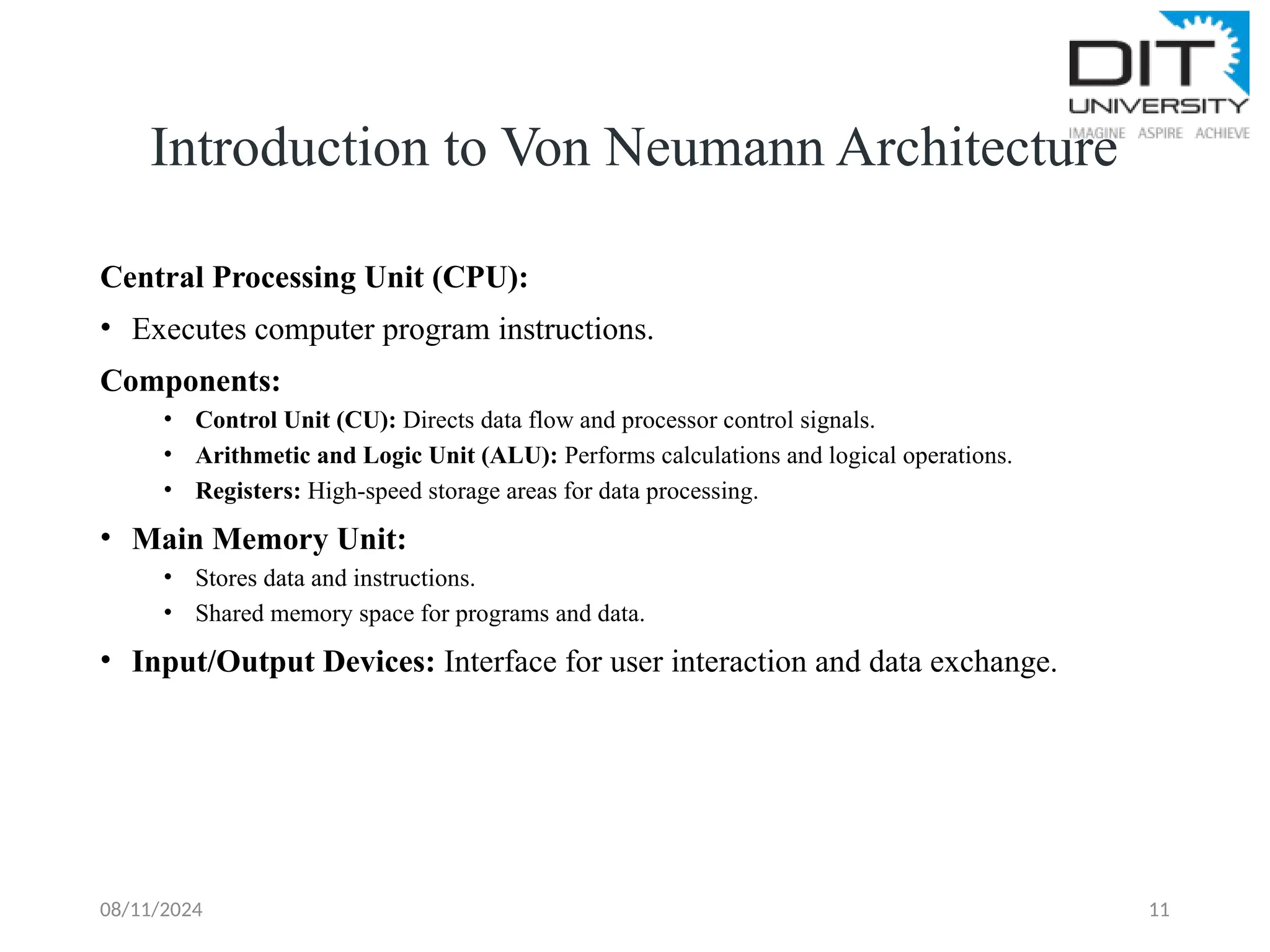
The document provides an overview of computer fundamentals, including definitions, components of the central processing unit (CPU), and characteristics of computer systems such as speed, reliability, and accuracy. It also discusses the five generations of computers, from vacuum tube-based systems to present and future AI-based systems, and introduces the von Neumann architecture, emphasizing the shared memory space for programs and data. Key terms related to computer technology, such as transistors, microprocessors, and machine language, are also defined.