This document discusses key concepts related to management including administration, management definitions, concepts of management, functions of management, planning, controlling, coordination. Some main points:
- Administration involves collective effort towards goals while management is creative problem solving.
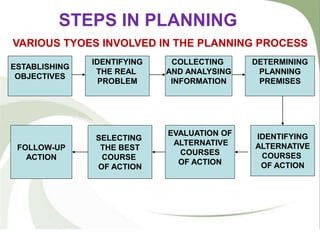
- Management functions include planning, organizing, staffing, directing, and controlling. Planning involves determining objectives and courses of action. Controlling checks performance against standards.
- Coordination synchronizes activities to accomplish common goals and ensures harmony between departments. Clear communication and defining roles are important for effective coordination.
- Planning helps minimize uncertainty and promotes coordination. Good plans have clear objectives and are flexible. Planning involves identifying problems, collecting data, evaluating alternatives, and selecting actions.