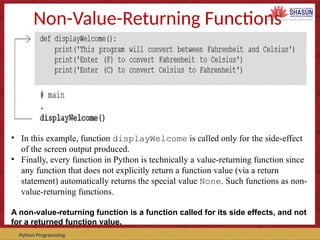
The document provides an overview of functions in Python programming, detailing how to define, call, and utilize both value-returning and non-value-returning functions. It covers key concepts such as parameters, default values, and the return statement, while providing multiple examples to illustrate function usage. The document emphasizes the importance of function definitions and highlights the distinction between returning values and side effects in function calls.












![Course Code – Course Name Prepared by:
Python Programming
Example 4 - Passing a List as an Argument
def my_function(food):
for x in food:
print(x)
fruits = ["apple", "banana", "cherry"]
my_function(fruits)
Output
apple
banana
cherry
We can send any data types of argument to a
function (string, number, list, dictionary etc.),
and it will be treated as the same data type
inside the function.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/functions-240910161324-6a65c4f2/85/Functions-in-python-programming-and-its-calling-statement-15-320.jpg)
![Course Code – Course Name Prepared by:
Python Programming
Example 5 – Return Values
def my_function(x):
return 5 * x
print(my_function(3))
print(my_function(5))
print(my_function(9))
Output
15
25
45
The statement return [expression] exits a function,
optionally passing back an expression to the caller.
A return statement with no arguments is the same as
return None.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/functions-240910161324-6a65c4f2/85/Functions-in-python-programming-and-its-calling-statement-16-320.jpg)