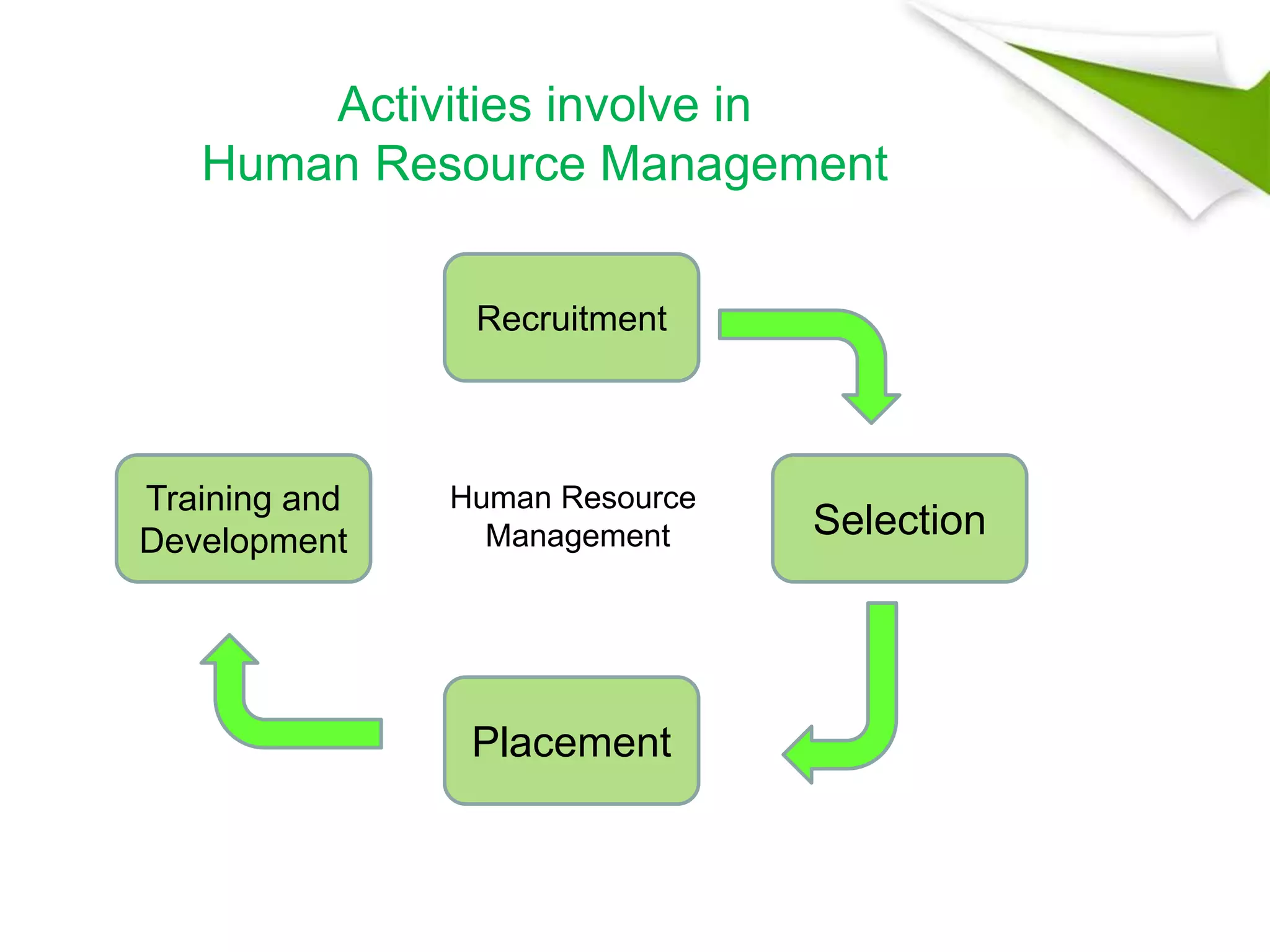
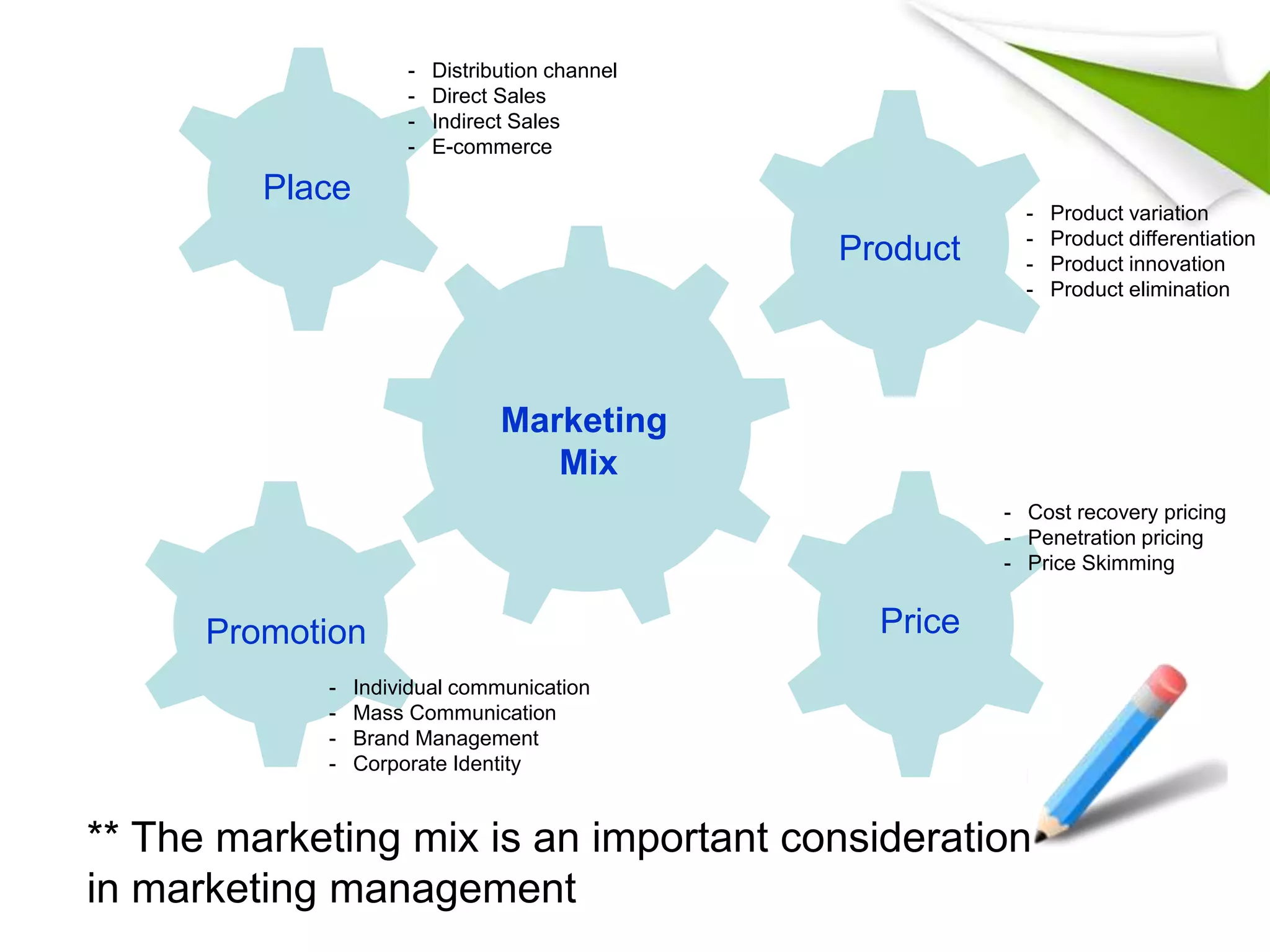
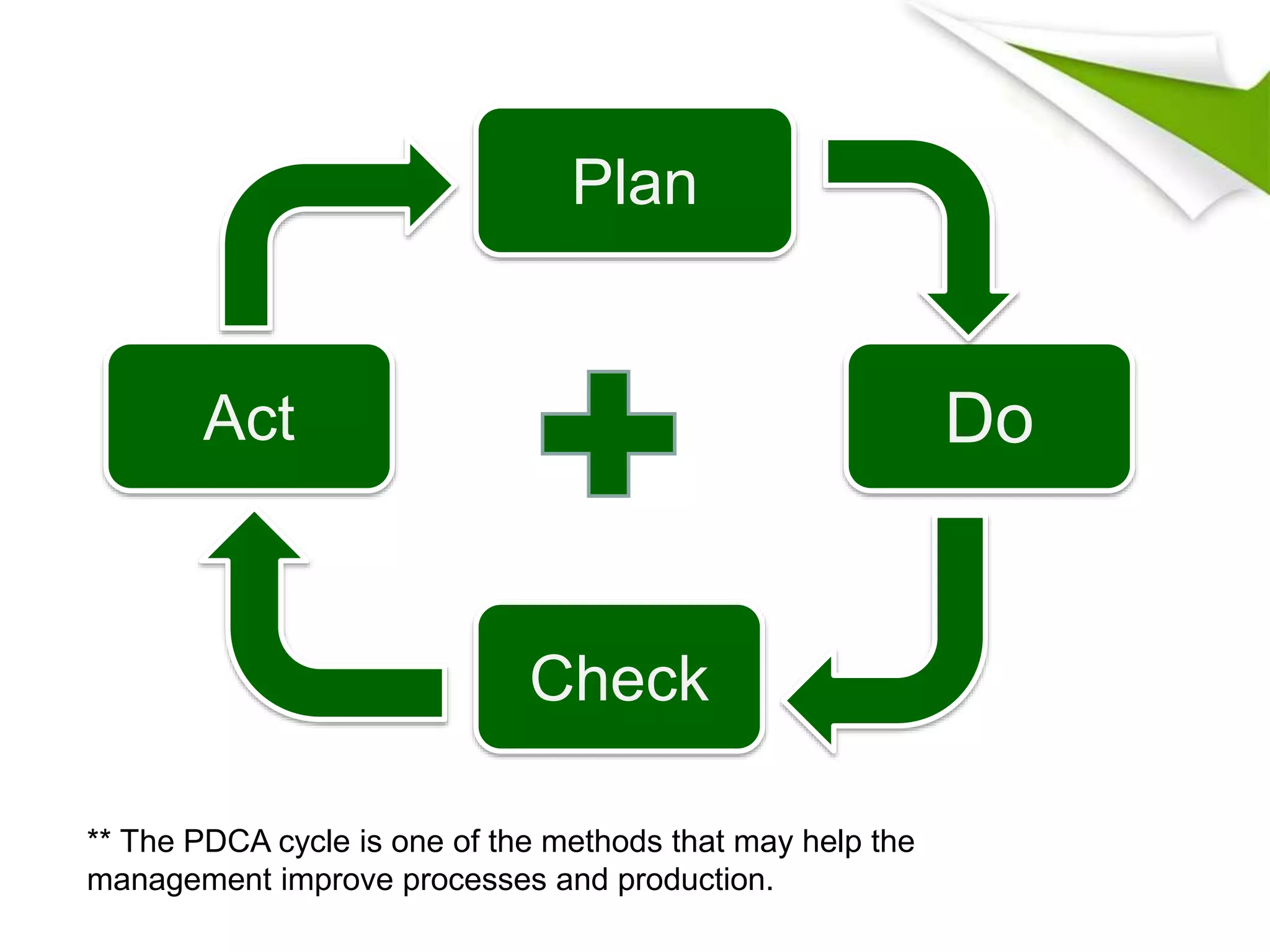
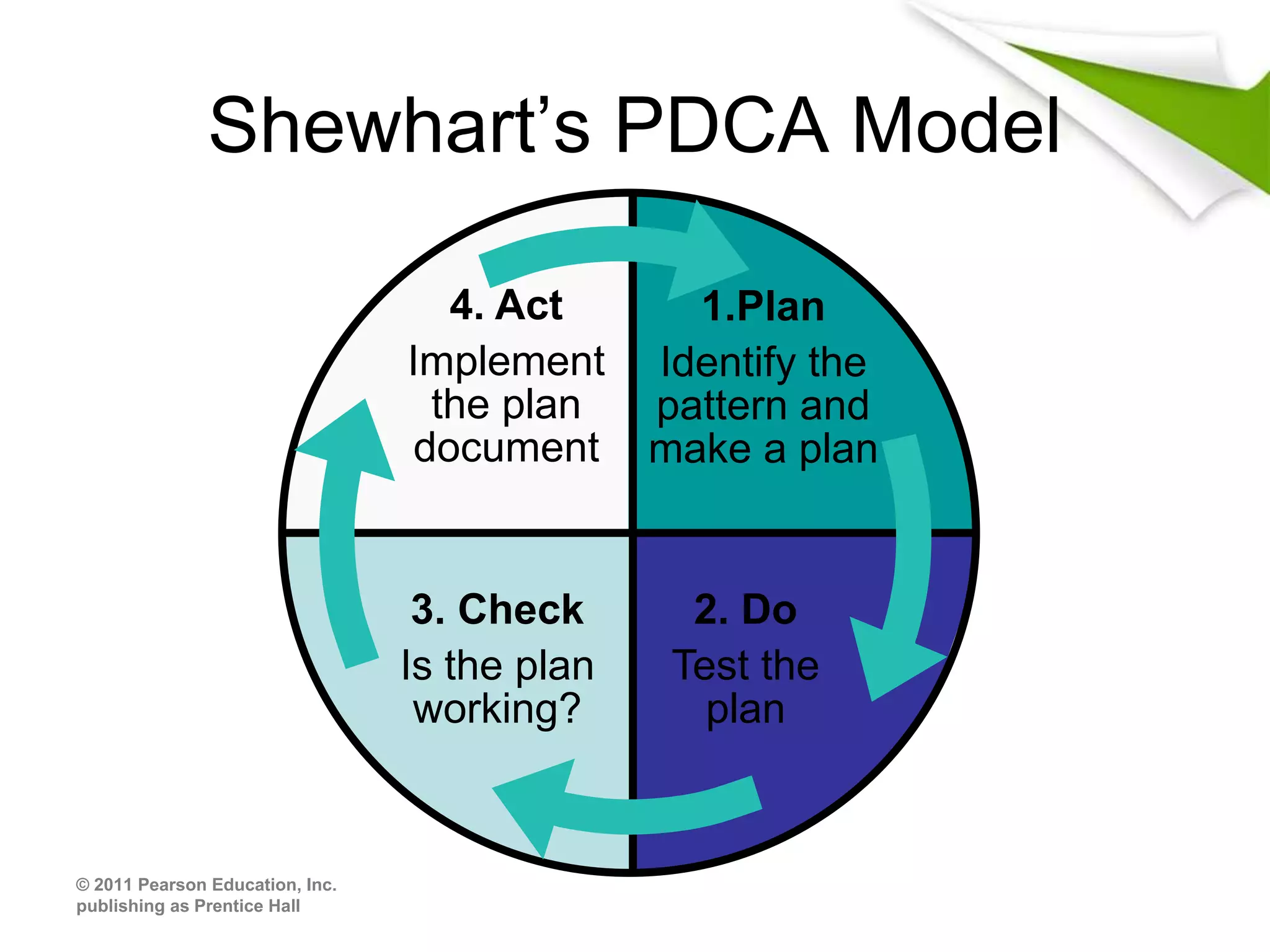
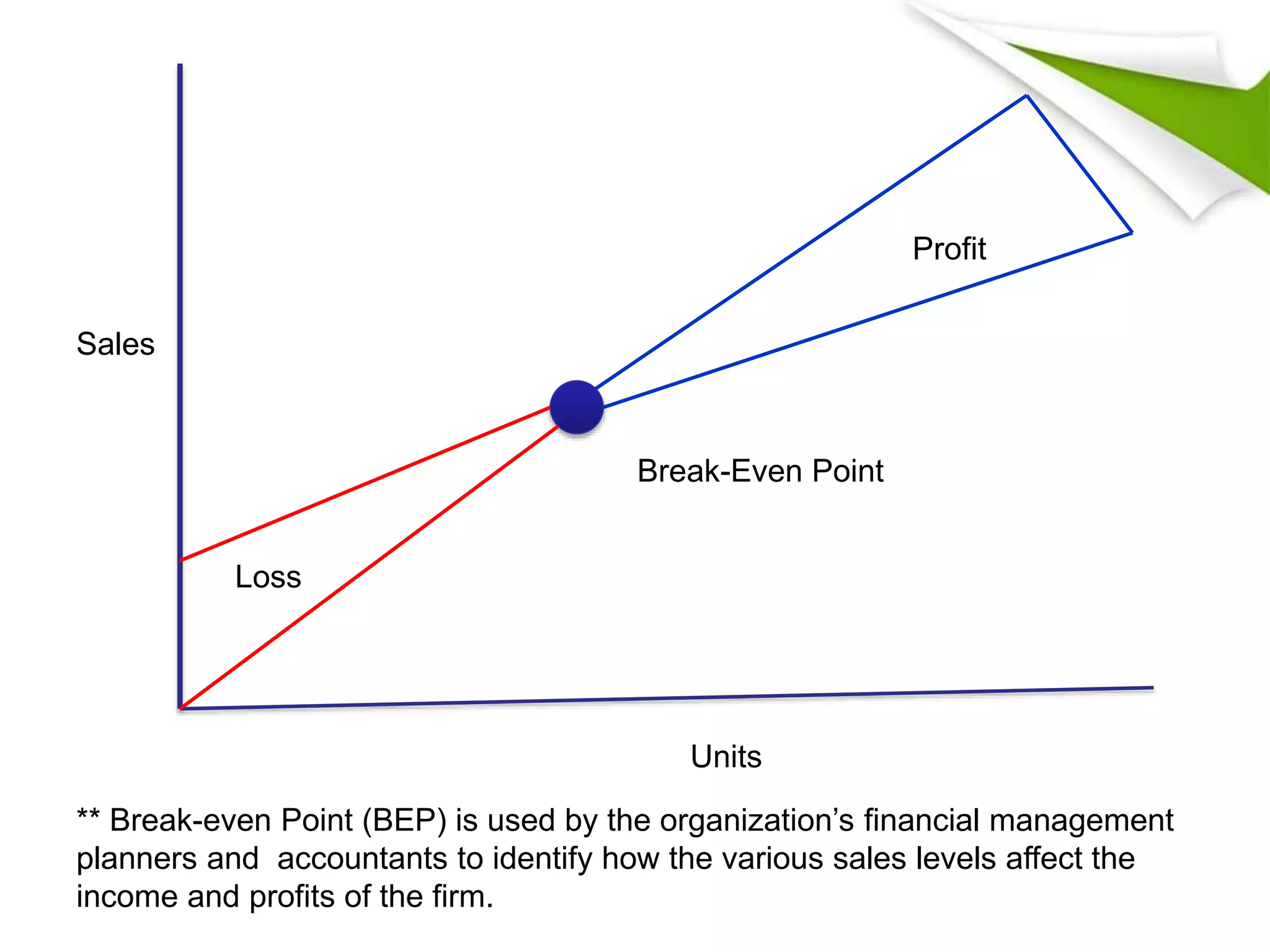
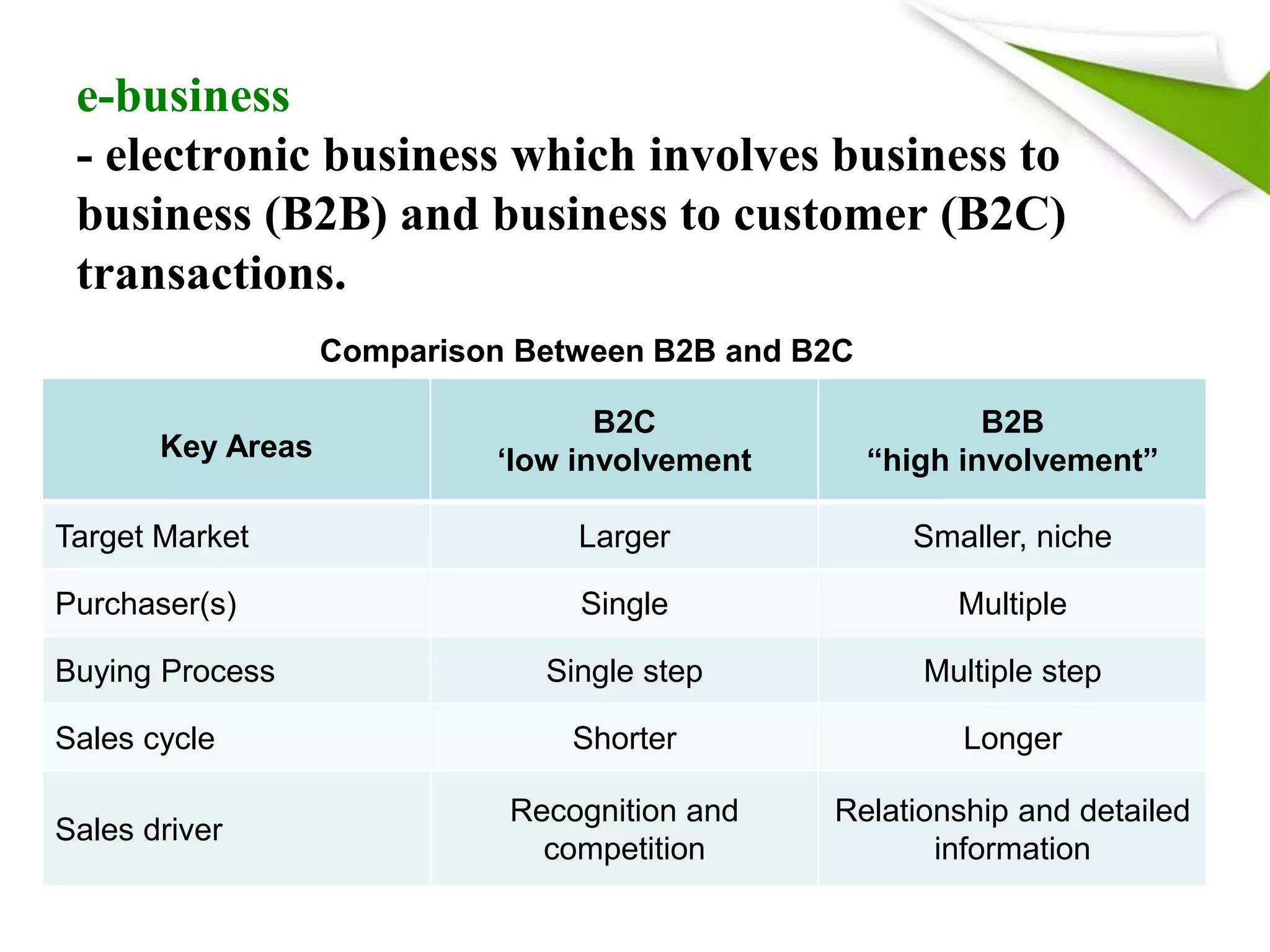
The document discusses 5 key functional areas of management: human resource management, marketing management, operations management, financial management, and ICT management. It provides an overview of each area including their main functions and importance to an organization. Human resource management involves attracting and maintaining employees. Marketing management includes promoting and distributing products to satisfy customers and goals. Operations management is concerned with transforming resources into goods and services. Financial management oversees funds to meet organizational needs. And ICT management develops technology systems for decision making.