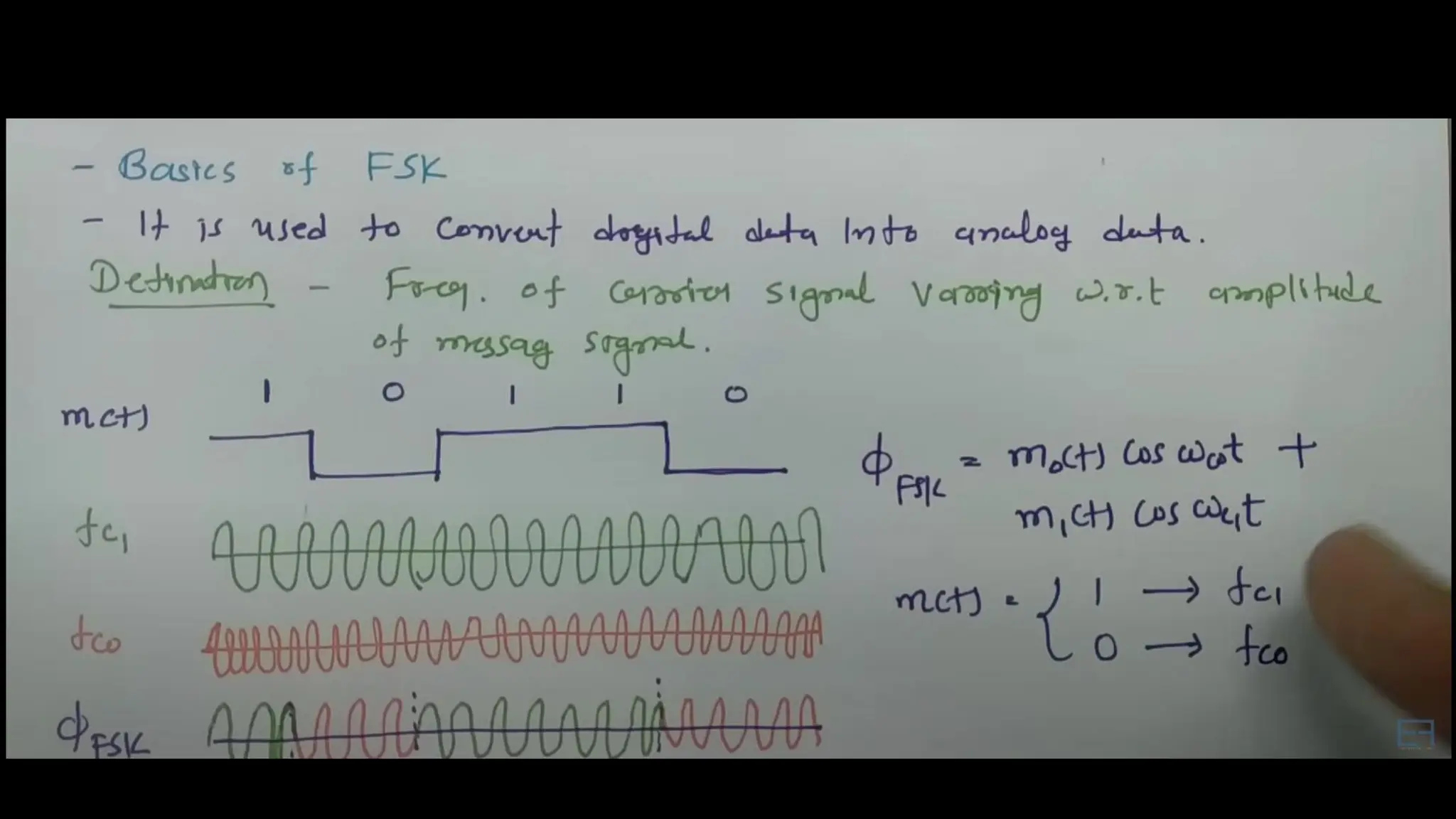
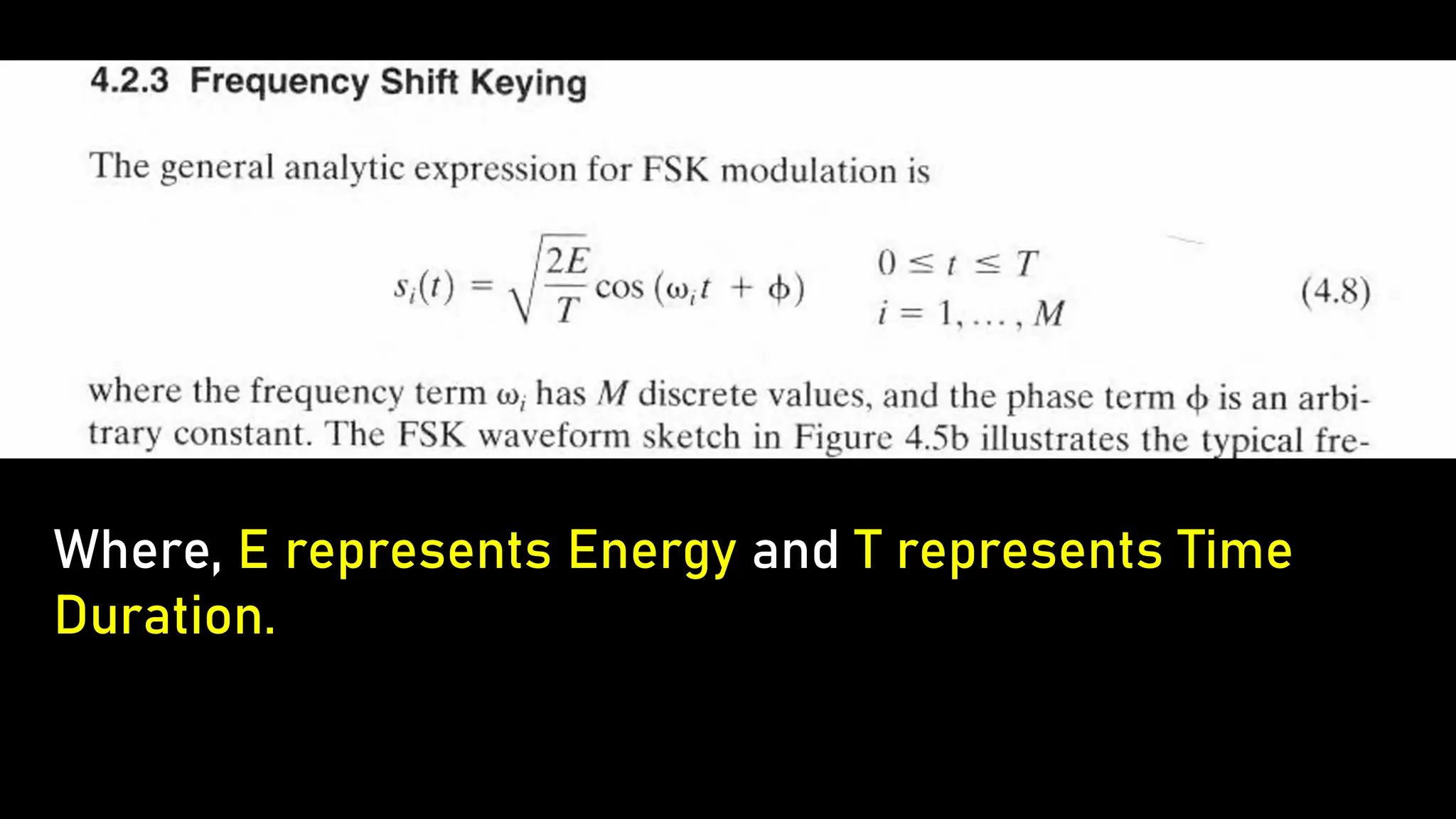
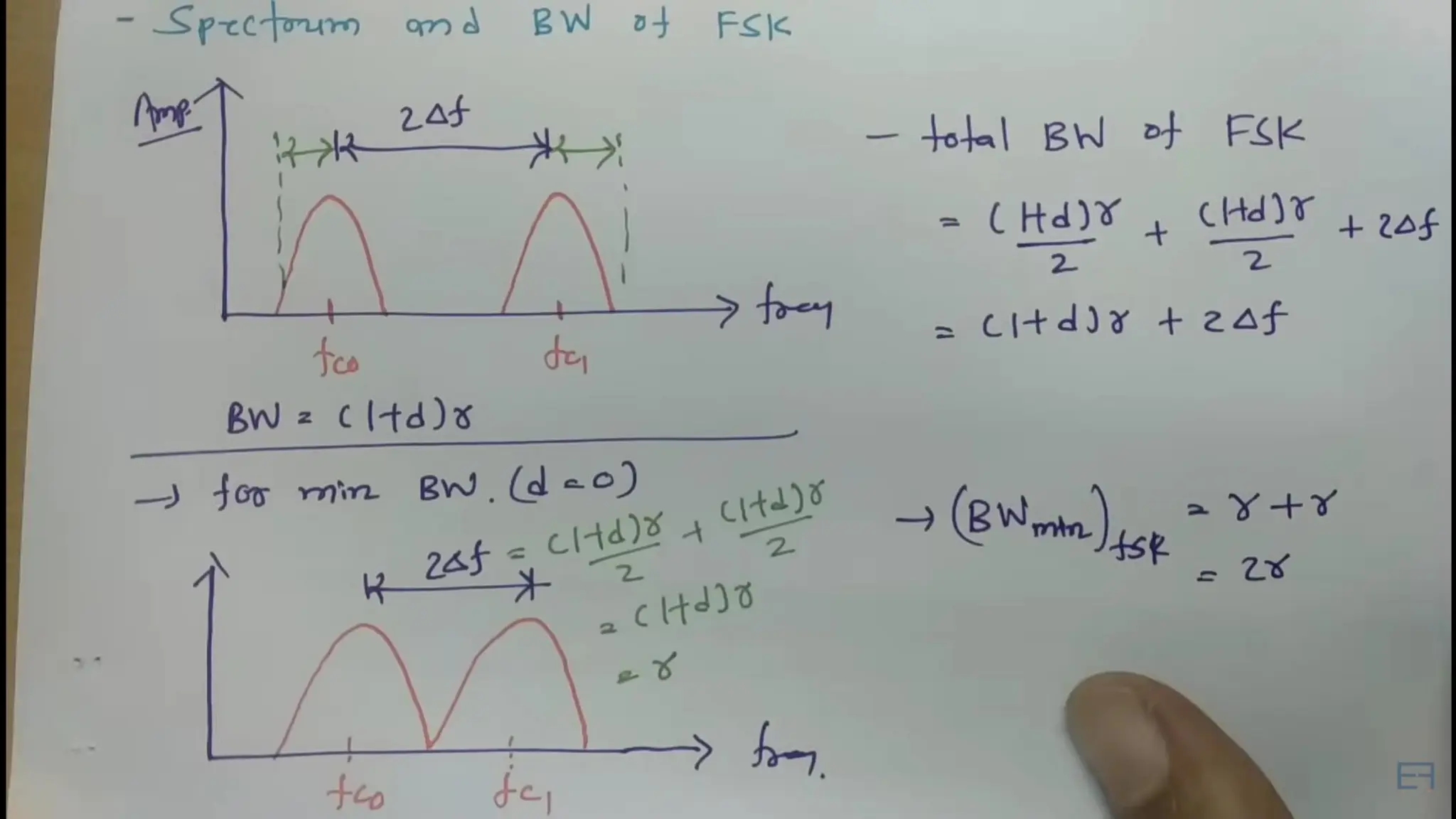
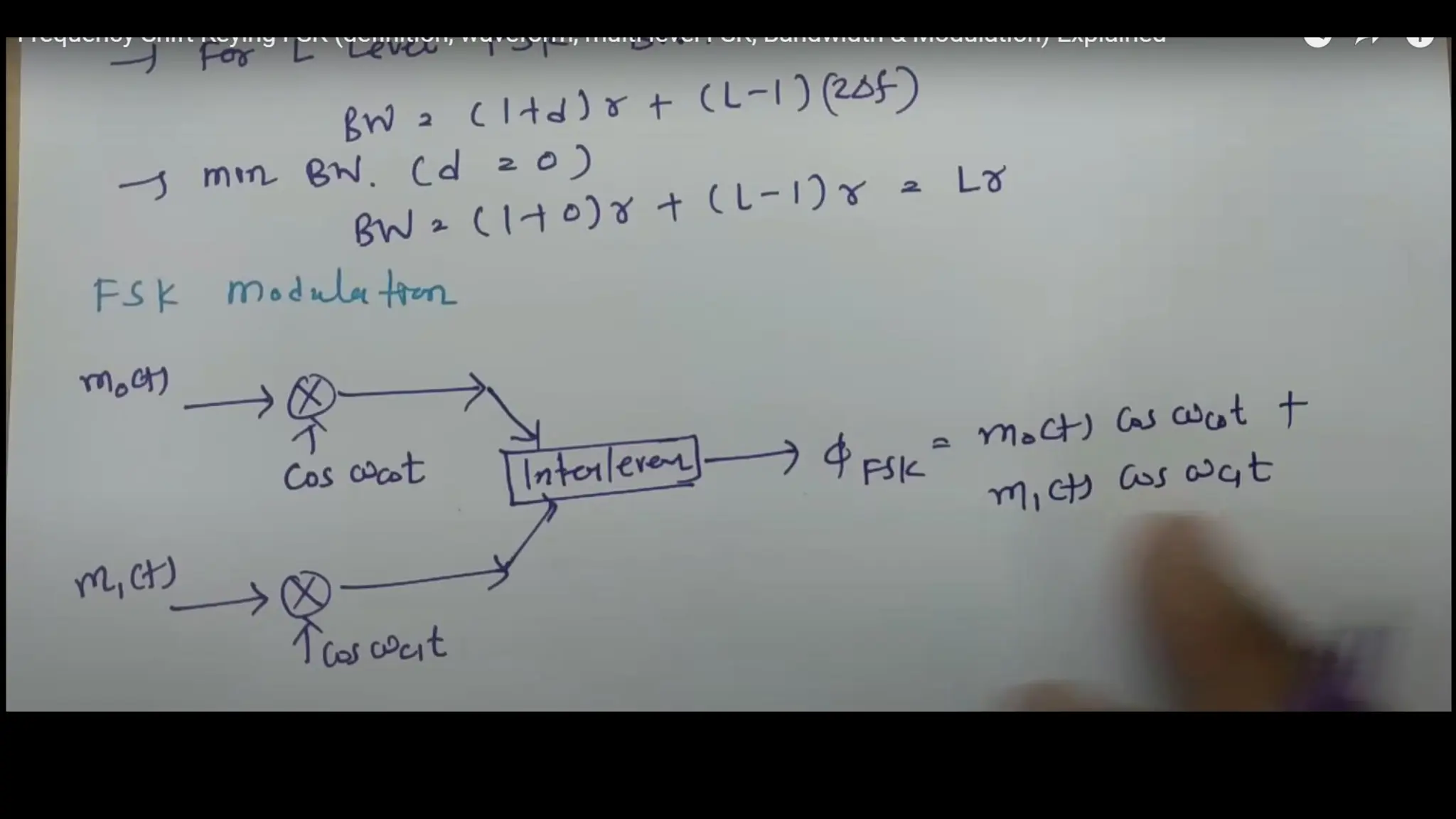
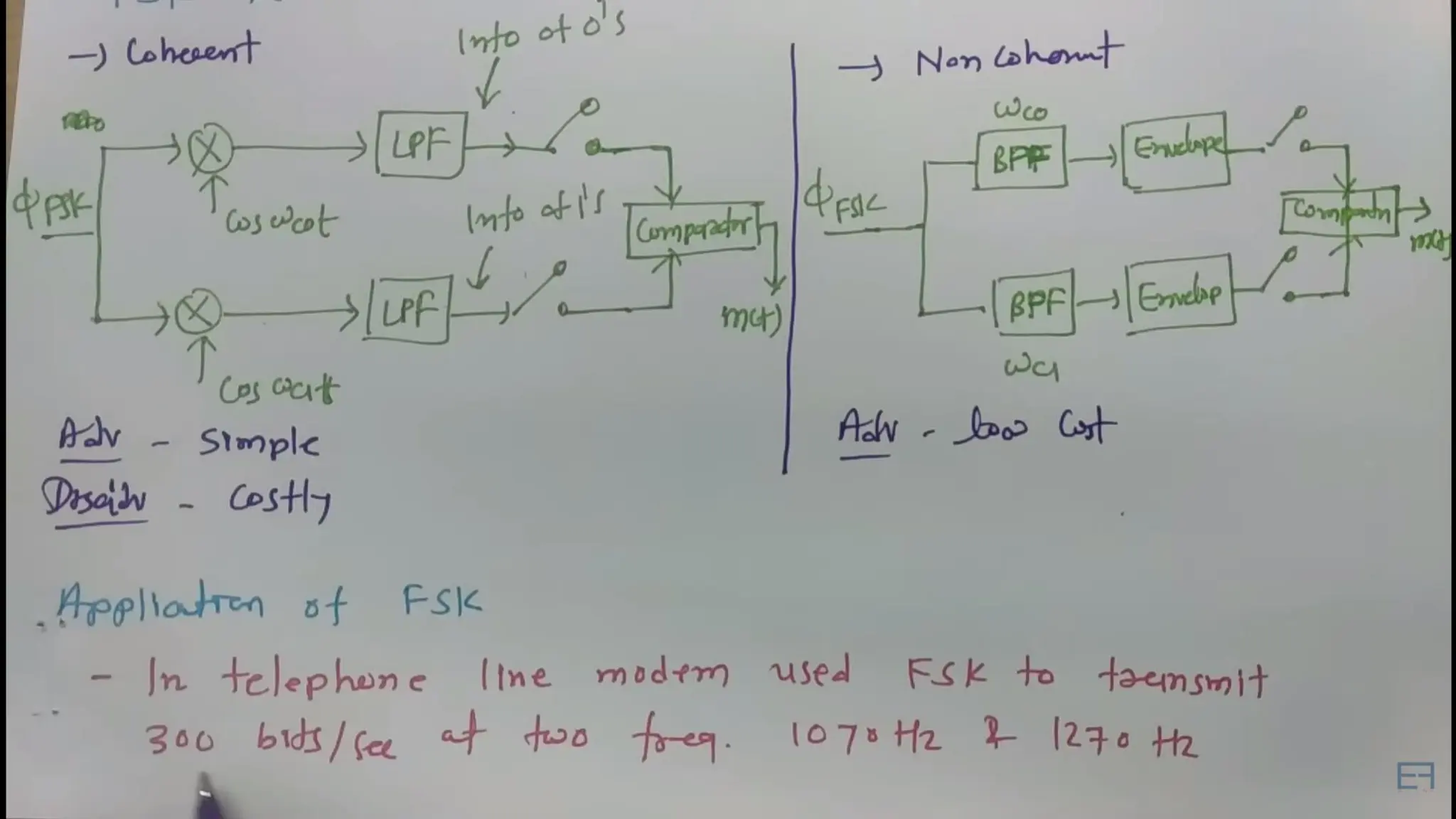
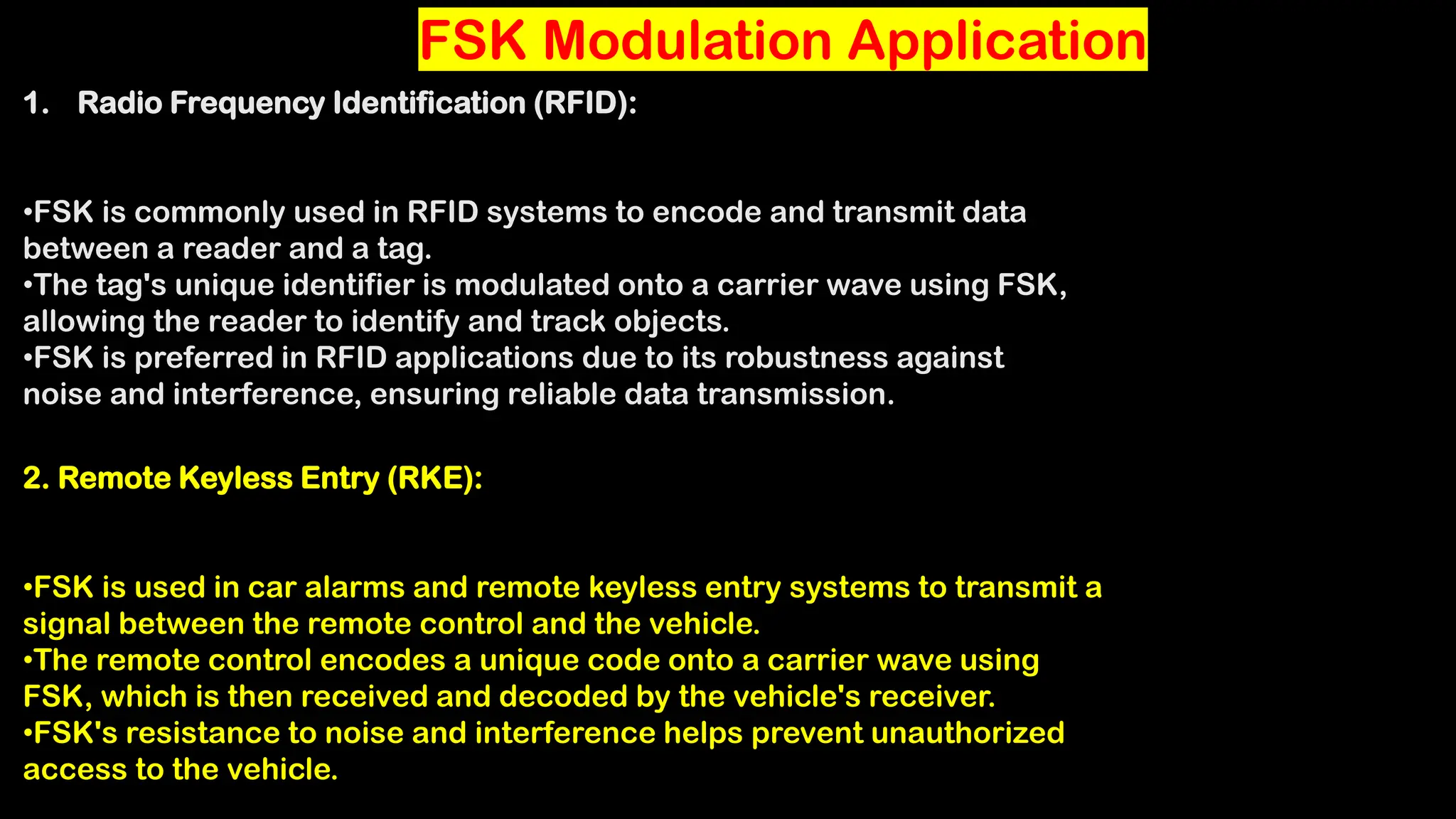
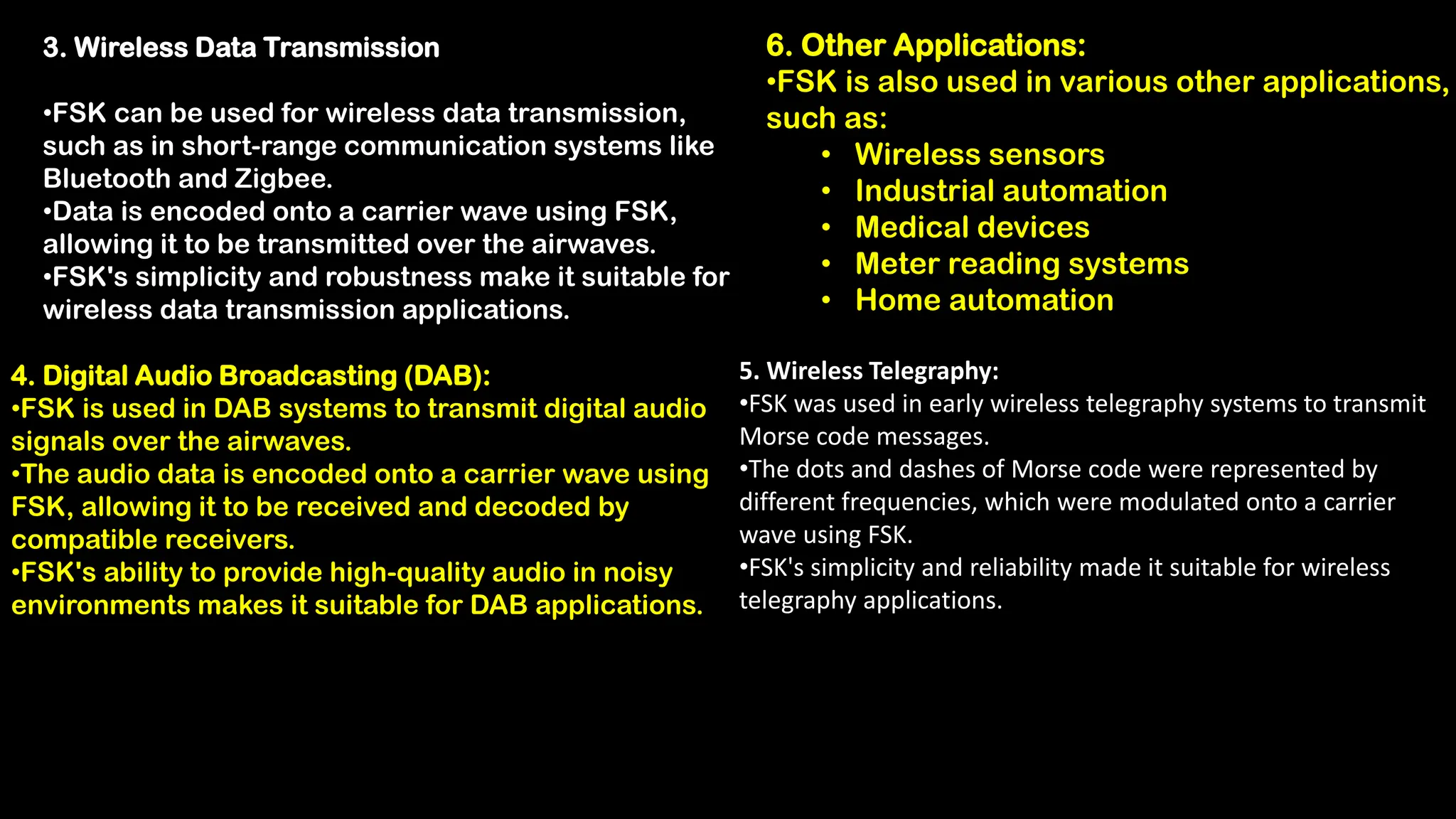
Frequency Shift Keying (FSK) is a digital modulation technique that encodes information by shifting the frequency of a carrier wave, with specific frequencies representing bits of data. FSK is utilized in various applications, including RFID systems, remote keyless entry, wireless data transmission, digital audio broadcasting, and early wireless telegraphy, due to its robustness against noise and interference. Its simplicity and reliability also allow it to be applied in industrial automation, wireless sensors, medical devices, meter reading, and home automation.