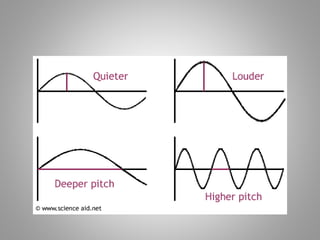
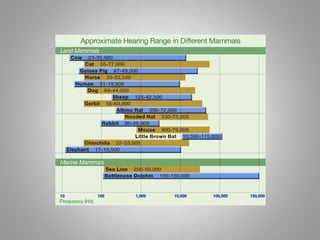
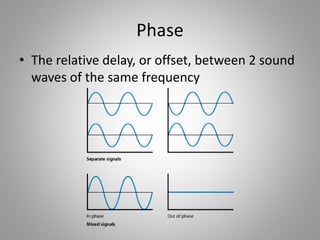
The document discusses frequency and phase in sound and audio engineering. It defines frequency as the pitch of a sound, measured in Hertz (Hz). The range of human hearing is between 20 Hz to 20 kHz, with lows between 20-250 Hz, mids between 250 Hz to 6 kHz, and highs between 5 kHz to 20 kHz. Frequency response refers to the range in which a signal can be produced uniformly and without distortion by a system. Phase is defined as the relative delay between two sound waves of the same frequency, and being in or out of phase can increase or decrease the amplitude and loudness of a wave.