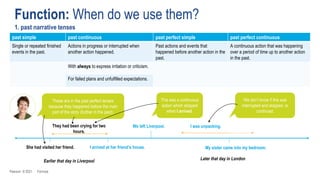
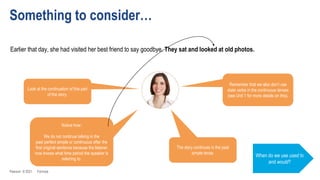
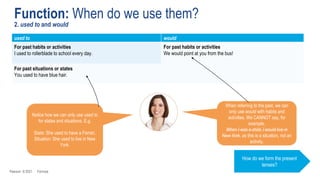
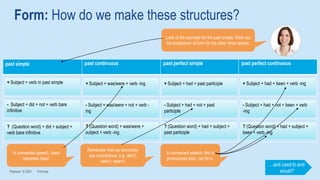
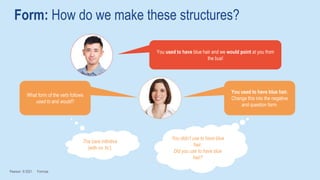
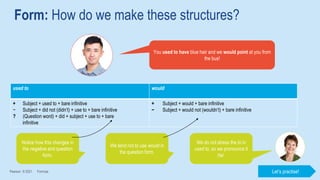
The document discusses different past tenses in English including the past simple, past continuous, past perfect simple, and past perfect continuous. It explains that these "past narrative tenses" are used to talk about finished past events and interrupted or continuous past actions. The document also discusses the uses of "used to" and "would" for describing past habits or repeated actions versus past situations or states. Examples are provided and the students practice identifying and correcting errors related to these past tense forms.