1. The document provides an overview of different past tenses in English, including the past simple, past continuous, past perfect simple, past perfect continuous, used to, and would.
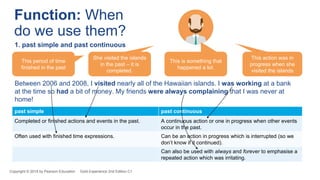
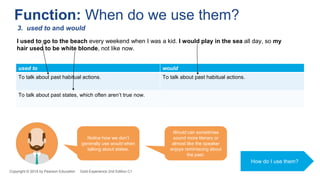
2. It examines the differences between these tenses and when each is used, with examples. Key differences explained are between the past simple and past continuous for completed vs ongoing actions, and the past perfect tenses for comparing times in the past.
3. Guidelines are given for forming the different past tenses in affirmative, negative and interrogative sentences, including use of auxiliary verbs and contractions.