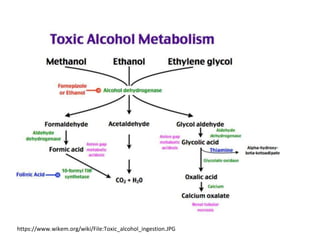
Formic acid poisoning can result from the accidental ingestion of formic acid or methanol oxidation. Formic acid is a colorless liquid with a pungent odor that is naturally produced by ants. Ingestion of formic acid can be deadly, with fatality occurring between 35-100% depending on the volume consumed. Formic acid poisoning works through several cellular mechanisms, preventing cellular respiration and producing metabolic acidosis. Symptoms range from initial vomiting and abdominal pain to later complications like shock, renal failure, and death. Treatment focuses on airway protection, fluid resuscitation, acidosis management, enhanced removal through folinic acid, furosemide, and possible hemodialysis. Severe metabolic acidosis