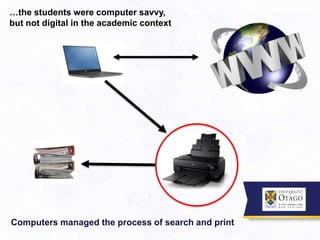
1. The document discusses formal teaching and learning approaches from both the institutional and student perspective. It notes that while people can learn outside institutions, universities provide validated qualifications and accelerated learning.
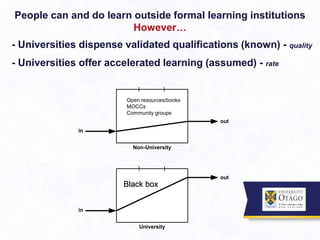
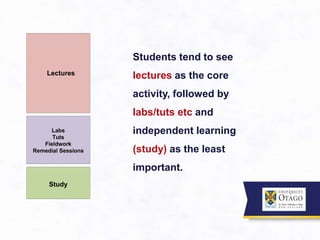
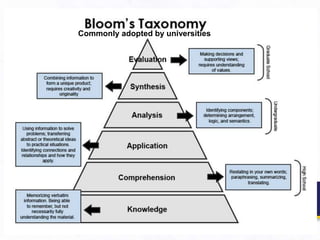
2. From the student perspective, activities like lectures are seen as the core learning activity, while independent study is seen as less important. However, higher education is about acquiring skills like analysis and application, not just knowledge consumption.
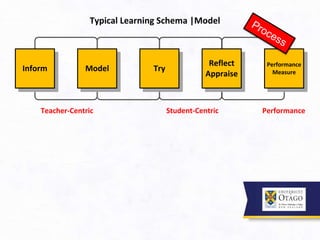
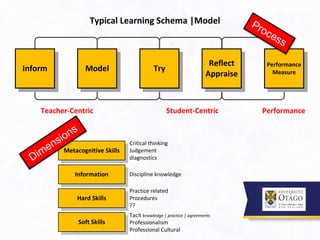
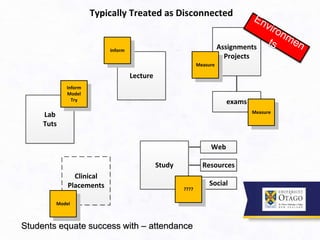
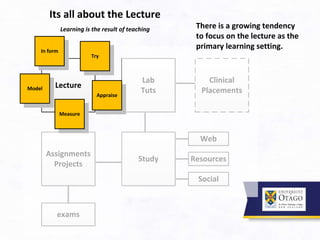
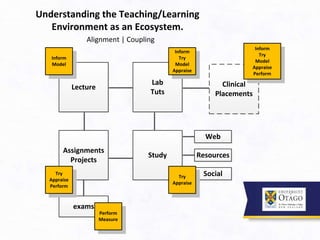
3. It argues that the teaching/learning environment should be seen as an interconnected ecosystem, rather than independent and disconnected activities. There is a need to move beyond seeing lectures as the primary learning setting.



![Institutional Approach to Teaching – two parts
1] Teaching Time / Contact time
2] Independent learning Time / Non-contact time
Lectures
Labs
Tuts
Fieldwork
Remedial Sessions
Study
20% of time BUT represents 80% of
the research on Teaching & Learning
+ high investment in institutional resources
80% of time BUT represents less than
20% of the research on Teaching & Learning
+ very low investment in institutional resources
CONTACT-TIME
TEACHING ACTIVITIES
NON-CONTACT-TIME
INDEPENDENT LEARNING](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/formalteachinglearning-schemasmodelsandpractices-160613171346/85/Formal-teaching-learning-schemas-models-and-practices-5-320.jpg)
![CURRICULUM
TEACHER
Content
Information
contextdeliverylearning
TEACHING
LINE
[optimal state]
PROFESSIONAL
DEVELOPMENT
STUDENT
LEARNING
INSTRUCTIONAL
DESIGN
ObjectivesStructure
ASSESSMENT
ALIGNMENT WITH
OBJECTIVES
A
B STUDENT
TEACHINGMETHOD
Lectures
Labs
Tuts
Fieldwork
Remedial Sessions
Study
From: Butson, R. (2011). Does higher education need deschooling? Industry & Higher Education, 25(3), 153-160. doi: 10.5367/ihe.2011.0042](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/formalteachinglearning-schemasmodelsandpractices-160613171346/85/Formal-teaching-learning-schemas-models-and-practices-6-320.jpg)

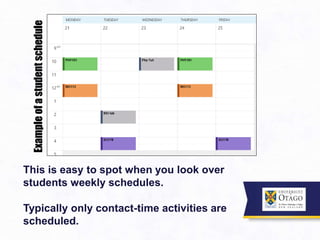











![Computer literacy was low concerning academic use:
Browser (av. 70%).
…..of this Facebook and YouTube [av.62%]
Word [av. 4.7%]
Adobe Reader [av. 4.3%].
Worth Noting…
Planning apps – outlook | google calendar
Word-processing – poor knowledge of functionality
Referencing apps – x endnote, zotera etc
Note-taking - Onenote / Evernote
Markups on website/PDF – unaware of this function](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/formalteachinglearning-schemasmodelsandpractices-160613171346/85/Formal-teaching-learning-schemas-models-and-practices-28-320.jpg)